
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and product for the given reactions, when they are catalyzed by the base, are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl carbon is electrophilic in nature due to the electronegativity difference. The nucleophile adds the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group. The reaction follows a different mechanism for an acid and a base catalyst. When the reaction is catalyzed by the acid, the first step of the reaction is always protonation of the carbonyl oxygen, which increases the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon. For a base-catalyzed reaction, the first step is the deprotonation of the nucleophilic species to form the anion, which helps to enhance the nucleophilic character.
Answer to Problem 18.46P
- The mechanism for the first reaction, when it catalyzed by the base:
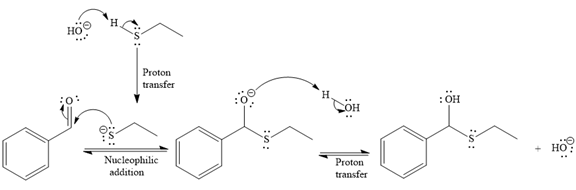
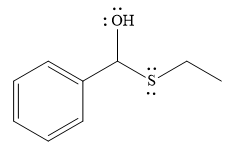
- The product for the first reaction, when it catalyzed by the base:
- The mechanism for the second reaction, when it catalyzed by the base:
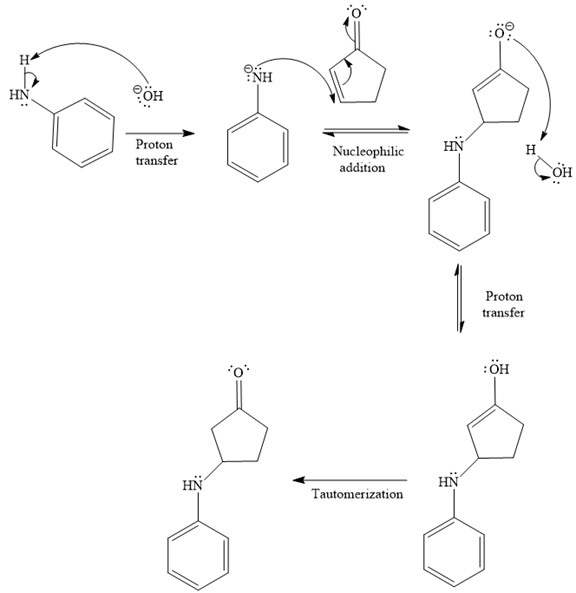
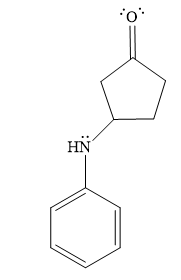
- The product for the second reaction, when it catalyzed by the base:
Explanation of Solution
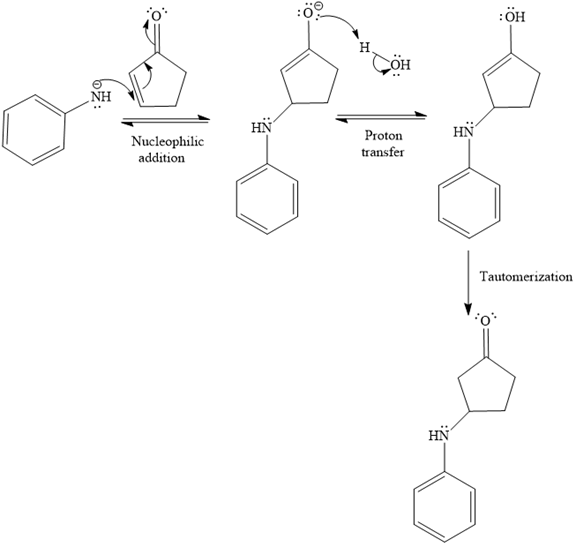
The first given reaction is
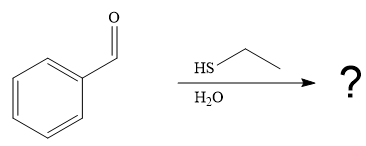
Under the basic condition, the base (
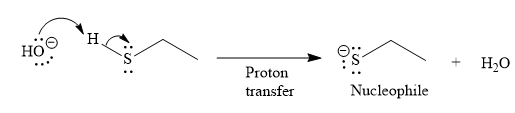
The nucleophile adds the electrophilic carbon of the given substrate, leading to form an alkoxide ion. Alkoxide ion then abstracts proton from the solvent, water, to form the uncharged product.
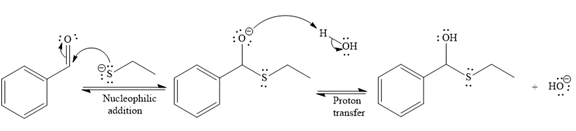
Thus, the product of the first reaction, when it catalyzed by the base, is

The second given reaction is
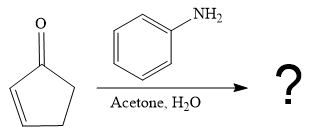
Under the basic condition, the base (
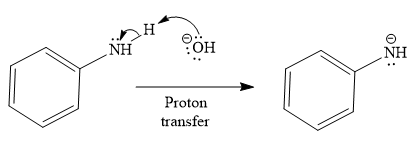
In the second step, the attack of the nucleophile (
Thus, the product of the given reaction is

The mechanism and product for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of the reaction condition.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and product for the given reactions, when they are catalyzed by the acid, are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl carbon is electrophilic in nature due to the electronegativity difference. The nucleophile adds the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group. The reaction follows a different mechanism for an acid and a base catalyst. When the reaction is catalyzed by the acid, the first step of the reaction is always protonation of the carbonyl carbon, which increases the electrophilicity of the carbonyl oxygen. For a base-catalyzed reaction, the first step is the deprotonation of the nucleophilic species to enhance the nucleophilic character.
Answer to Problem 18.46P
- The mechanism for the first given reaction, when it catalyzed by the acid:
- The product for the first reaction, when it catalyzed by the acid:

- The mechanism for the second reaction, when it catalyzed by the acid:
- The product for the second reaction, when it catalyzed by the acid:

Explanation of Solution
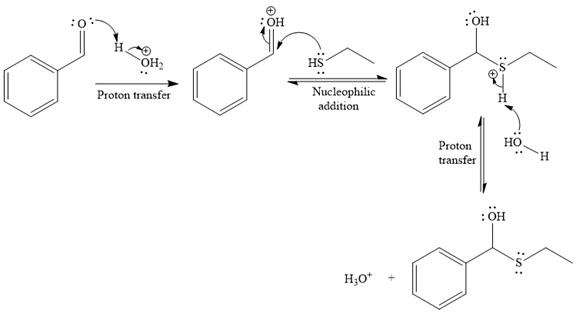
The first given reaction is

Under the acidic condition, the carbonyl oxygen of the given reactant (an
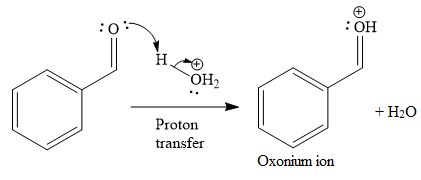
Then the nucleophile attack of (
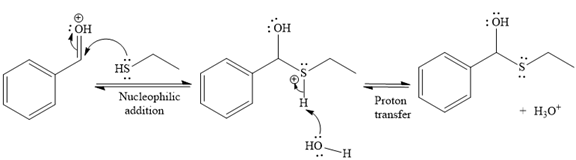
Thus, the product of the given reaction is

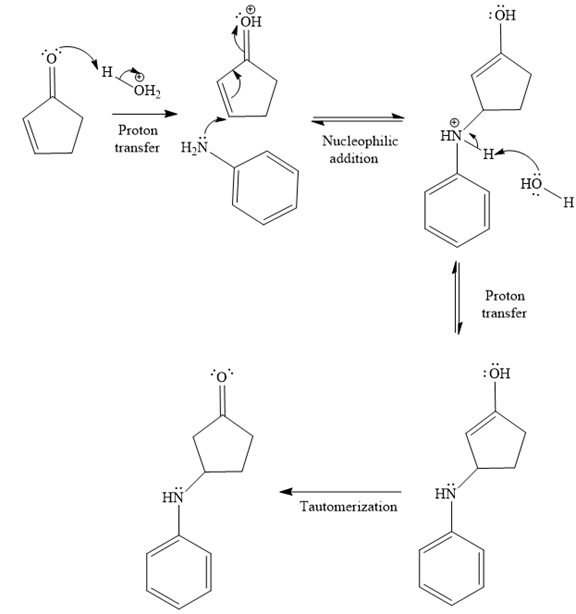
The second given reaction is

Under the acidic condition, the carbonyl oxygen of the given reactant (
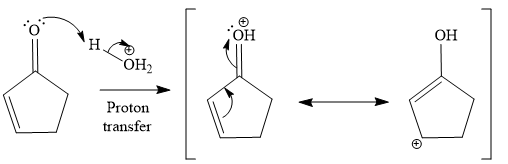
In the second step, the attack of the nucleophile (
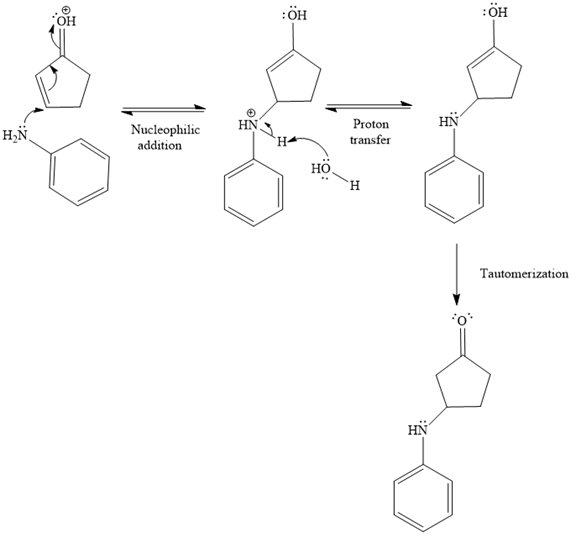
Thus, the product of the given reaction is

The mechanism and product for the given reaction are drawn on the basis of the reaction condition.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Using arrows to designate the flow of electrons, complete the reaction below and provide a detailed mechanism for the formation of the product OH conc Hydrochloric acid 40°C Temp All chemical structures should be hand drawn on a piece of paper Paragraph BI UAE +varrow_forwarddraw out the following structures plesearrow_forwardDraw everything on a piece of paper outlining the synthesis from acetaldehyde to 2 cyclopentene carboxaldehyde using carbon based reagants with 3 carbons or fewers. Here is the attached image.arrow_forward
- Manoharan Mariappan, FR.D., 34) Complete the following reaction starting from hex-1-yne proceeding via different substitution reactions forming 2-heptanone. (25 pts). A Sia₂BH H₂O₂ NaOH Br D Mechanism for reaction D - ether-cleavage: 10 B Ph-MgCI, THF H₁₂O+ D HBr (XS) C TsCl, Py CH3-CH2-CH2-ONaarrow_forwardIn the table below, the correct structure for (2R)-3-methylpentan-2-ol (IUPAC name) can be represented by the letter OH OH HE > ' ÕH C B OH D A/ E OHarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forward
- Why is analysing salt content (using Mohr titration) in both regular & salt reduced tomato sauce important?arrow_forwardIn the image below, correctly name the glassware # _P ( Blank 1) and T ( Blank 2). 景 A W Blank # 1 Blank #2 1000 +19 E E D 0 0-0 G H A A K Π 12 R M N S 0-0-arrow_forwardFeedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: CN Δ + A ? NC Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. esc Check 80 MH F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 50 @ # C % 95 € Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C A DII F6 F7 F8 7 * 8 Λ & 6 F9 F10 9 0 4arrow_forward
- Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: ཤིགས་བྱ རྩ་ཅད་ཀྱིས་༢༩ + Some important notes: A ^ ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. E Check 0 لا Save For La ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of All F9 Aarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + Δ A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privaarrow_forwardesc 2 Incorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? A O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Check F1 ! @ X C Save For Later Submit Assignment 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 80 et A ད 1 4 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 # $ 45 % A 6 87 & * 8 9 ) 0 + ||arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





