
Concept explainers
(a)
To graph: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Graph:
To graph the points on scatter plot, follow the steps using graphing calculator.
First press the
Go to
Now, press the
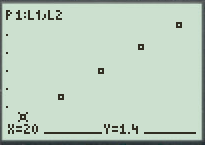
Figure (1)
(b)
To find: The equation of line that seems to best fit for the data.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19E
The equation of line that seems to best fit for the data is equal to
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Calculation:
Assume that the line is equal to
As given the value of
Substitute
Substitute
Subtract both the equations.
Substitute
Therefore, the equation of line that seems to best fit for the data is equal to
(c)
To find: The linear model for the data with the help of regression of graphing utility.
(c)
Answer to Problem 19E
The linear model for the data is equal to
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Calculation:
For the regression linear model of data follow the steps below:
First press the
Go to
Now enter the keystrokes
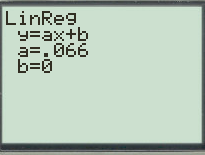
Figure(1)
Therefore, the linear model for the data is equal to
(d)
To find: The elongation of the spring when a force of
(d)
Answer to Problem 19E
The elongation of the spring when a force of
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Hooke’s law states that the force
| Force, | Elongation, |
Calculation:
As found in part(c), the model for the best fit of data is equal to
Substitute
Therefore, the elongation of the spring when a force of
Chapter 1 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach
- Don't do 14. Please solve 19arrow_forwardPlease solve 14 and 15arrow_forward1. Consider the following system of equations: x13x2 + 4x3 - 5x4 = 7 -2x13x2 + x3 - 6x4 = 7 x16x213x3 - 21x4 = 28 a) Solve the system. Write your solution in parametric and vector form. b) What is a geometric description of the solution. 7 c) Is v = 7 in the span of the set S= [28. 1 HE 3 -5 3 ·6 ? If it is, write v 6 as a linear combination of the vectors in S. Justify. d) How many solutions are there to the associated homogeneous system for the system above? Justify. e) Let A be the coefficient matrix from the system above. Find the set of all solutions to Ax = 0. f) Is there a solution to Ax=b for all b in R³? Justify.arrow_forward
- 4. Suppose that A is made up of 5 column vectors in R³, and suppose that the rank(A)=3. a. How many solutions are there to Ax=0? Justify. b. What is a geometric description for the nullspace(A)? Justify. c. Do the column vectors of A span R³? Justify. d. Is A invertible? Justify.arrow_forward3. Suppose that A is 5 x 5 and rank(A)=4. Use this information to answer the following. a. Give a geometric description of nullspace(A). Justify. b. Is A invertible? Justify. c. Give a geometric description of the span of the column vectors of A. What space are the column vectors of A in? Justify. d. What is determinant of A? Justify.arrow_forward2. Consider the matrix: A || 1 1 -3 14 2 1 01 4 1 2 2 -26 1 -3 1 5] a) What is rank(A)? b) Is A invertible? Justify. c) Find the nullspace(A). Justify. d) Is the trivial solution the only solution to Ax=0? Justify. e) What is the span of the column vectors of A? Justify.arrow_forward
- E 5. Suppose that S={v € R²: v = [2x² - 3]}. Is S a subspace of R²? Prove or disprovearrow_forward6. Suppose that V1, V2 ER", show that span{v1, v2} is a subspace of Rn.arrow_forwardRa X 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 180 Ko Sin (1) Kdl 1 sin (4) sin(3) Sin (30) اذا مرید شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 Fo lasa! G s.1000-950 20:05 1000 Capper losses: 5kw Rotor input lookw 0.05 ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 6) 1 ۳/۱ وه اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look DC 7) rotov Find the general solution of the following equations: +4y=tan2x 3 7357 Find the general solution of the following equations: - Qll y + y (³) = 0. 101arrow_forward
- B: 18060 msl Kd Ka, Sin (n) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW /0001 Rotor input 5 : loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط ١٥٠ 7) rotov DC ined sove in Deaper I need a detailed solution on paper please dy x+2y-4 = dx 2x-y-3 Find the general solution of the following equations: 02//yl-4y+13y=esinarrow_forward1) R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B msl kd 180 60 Kal Sin (1) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW Rotor input: 5 0.05 loo kw 6) 1 /0001 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Q1// Find the solution of: 'y' = x² +376 x4+316 xyo Q2 Find the solution of the initial-valued problems: ex-y y' +exarrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-18060 msl kd Kasi Sin (1) I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 120 x 50 G loo kw ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Q3// x²y// +xy/ + (x² - ½) y = x³/². اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC Q4// x²y// - (2x+x²)y/ + (2 + x)y = x³. dy 2x+2y+4 = dx 2x-y-3arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





