
Concept explainers
To sketch the graph of the given functions on same co-ordinate system
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given functions are:
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of f (x ) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| -1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| -2 | 2 |
By taking different values of x , the graph can be plotted.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of g (x) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 |
| -1 | 2 |
| 2 |
4 |
| -2 |
4 |
By taking different values of x , the graph can be plotted.
Calculation for graph:
Consider
| Values of x | Values of h (x ) |
| 0 | -5 |
| 1 | -7 |
| -1 | -3 |
| 2 | -5 |
| -2 | -1 |
By taking different values of x , the graph can be plotted
Graphs on the same co-ordinate system:
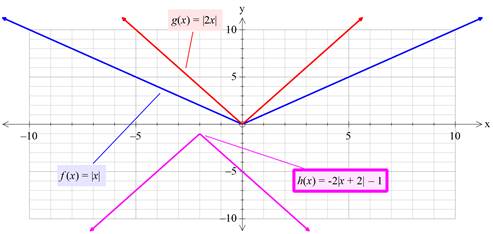
Verification:
Using graphing utility to draw the graph of given functions,
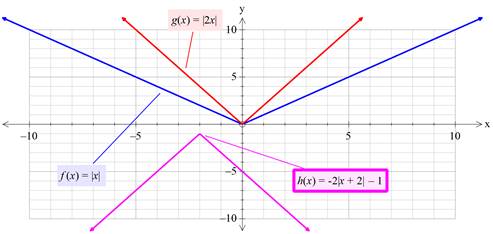
Interpretation:
From above graph, it is clear that, the drawn sketch and above graph are identical to each other.
Here,
Chapter 1 Solutions
Precalculus with Limits: A Graphing Approach
- 25-30. Normal and tangential components For the vector field F and curve C, complete the following: a. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is tangent to C. b. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is normal to C. c. Sketch C and a few representative vectors of F on C. 25. F = (2½³, 0); c = {(x, y); y − x² = 1} 26. F = x (23 - 212) ; C = {(x, y); y = x² = 1}) , 2 27. F(x, y); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 4} 28. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 1} 29. F = (x, y); C = 30. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x = 1} {(x, y): x² + y² = 1}arrow_forward٣/١ B msl kd 180 Ka, Sin (1) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW Rotor input 5 0.05 : loo kw 6) 1 /0001 ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please وه اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط ١٥٠ DC 7) rotor a ' (y+xlny + xe*)dx + (xsiny + xlnx + dy = 0. Q1// Find the solution of: ( 357arrow_forward۳/۱ R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 B. 180 msl Kas Sin (I) 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30): 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds 120×50 looo G 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Find the general solution of the following equations: QI//y(4)-16y= 0. Find the general solution of the following equations: Q2ll yll-4y/ +13y=esinx.arrow_forward
- R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-180 60 msl kd Kas Sin () 2 I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا مريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3 Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating ined sove in peaper 5) Synchronous speed s 120×50 6 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط Look 7) rotov DC I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Solve the following equations: 0 Q1// Find the solution of: ( y • with y(0) = 1. dx x²+y²arrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/3 1 B-180-60 msl Ka Sin (1) Isin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 6) 1 0.05 G 50105 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 064 2- A hot ball (D=15 cm ) is cooled by forced air T.-30°C, the rate of heat transfer from the ball is 460.86 W. Take for the air -0.025 Wim °C and Nu=144.89, find the ball surface temperature a) 300 °C 16 b) 327 °C c) 376 °C d) None か = 750 01arrow_forwardDon't do 14. Please solve 19arrow_forward
- Please solve 14 and 15arrow_forward1. Consider the following system of equations: x13x2 + 4x3 - 5x4 = 7 -2x13x2 + x3 - 6x4 = 7 x16x213x3 - 21x4 = 28 a) Solve the system. Write your solution in parametric and vector form. b) What is a geometric description of the solution. 7 c) Is v = 7 in the span of the set S= [28. 1 HE 3 -5 3 ·6 ? If it is, write v 6 as a linear combination of the vectors in S. Justify. d) How many solutions are there to the associated homogeneous system for the system above? Justify. e) Let A be the coefficient matrix from the system above. Find the set of all solutions to Ax = 0. f) Is there a solution to Ax=b for all b in R³? Justify.arrow_forward4. Suppose that A is made up of 5 column vectors in R³, and suppose that the rank(A)=3. a. How many solutions are there to Ax=0? Justify. b. What is a geometric description for the nullspace(A)? Justify. c. Do the column vectors of A span R³? Justify. d. Is A invertible? Justify.arrow_forward
- 3. Suppose that A is 5 x 5 and rank(A)=4. Use this information to answer the following. a. Give a geometric description of nullspace(A). Justify. b. Is A invertible? Justify. c. Give a geometric description of the span of the column vectors of A. What space are the column vectors of A in? Justify. d. What is determinant of A? Justify.arrow_forward2. Consider the matrix: A || 1 1 -3 14 2 1 01 4 1 2 2 -26 1 -3 1 5] a) What is rank(A)? b) Is A invertible? Justify. c) Find the nullspace(A). Justify. d) Is the trivial solution the only solution to Ax=0? Justify. e) What is the span of the column vectors of A? Justify.arrow_forwardE 5. Suppose that S={v € R²: v = [2x² - 3]}. Is S a subspace of R²? Prove or disprovearrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





