
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 75PQ
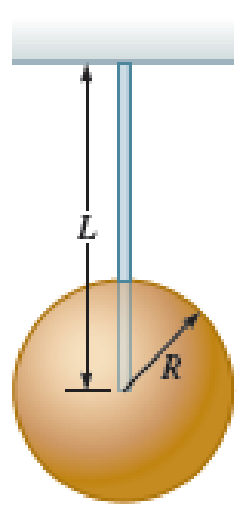
A spherical bob of mass m and radius R is suspended from a fixed point by a rigid rod of negligible mass whose length from the point of support to the center of the bob is L (Fig. P16.75). Find the period of small oscillation.
N The frequency of a physical pendulum comprising a nonuniform rod of mass 1.25 kg pivoted at one end is observed to be 0.667 Hz. The center of mass of the rod is 40.0 cm below the pivot point. What is the rotational inertia of the pendulum around its pivot point?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
One strain of bacteria was found to have a membrane potential of -120 mVmV at a pHpH of 7.5. A bacterium can be modeled as a 1.5-μmμm-diameter sphere.
How many positive ions are needed on the exterior surface to establish this membrane potential? (There are an equal number of negative ions on the interior surface.) Assume that the membrane properties are the same as those of mammalian cells.
Q: Draw the fabrication layers of a transistor with metal and semiconductor MS junction (Schottkyj unction).
physics
Chapter 16 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.1CECh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.2CECh. 16.2 - For each expression, identify the angular...Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 16.4CECh. 16.6 - Prob. 16.5CECh. 16.6 - Prob. 16.6CECh. 16 - Case Study For each velocity listed, state the...Ch. 16 - Case Study For each acceleration listed, state the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 3PQCh. 16 - Prob. 4PQ
Ch. 16 - Prob. 5PQCh. 16 - Prob. 6PQCh. 16 - The equation of motion of a simple harmonic...Ch. 16 - The expression x = 8.50 cos (2.40 t + /2)...Ch. 16 - A simple harmonic oscillator has amplitude A and...Ch. 16 - Prob. 10PQCh. 16 - A 1.50-kg mass is attached to a spring with spring...Ch. 16 - Prob. 12PQCh. 16 - Prob. 13PQCh. 16 - When the Earth passes a planet such as Mars, the...Ch. 16 - A point on the edge of a childs pinwheel is in...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16PQCh. 16 - Prob. 17PQCh. 16 - A jack-in-the-box undergoes simple harmonic motion...Ch. 16 - C, N A uniform plank of length L and mass M is...Ch. 16 - Prob. 20PQCh. 16 - A block of mass m = 5.94 kg is attached to a...Ch. 16 - A block of mass m rests on a frictionless,...Ch. 16 - It is important for astronauts in space to monitor...Ch. 16 - Prob. 24PQCh. 16 - A spring of mass ms and spring constant k is...Ch. 16 - In an undergraduate physics lab, a simple pendulum...Ch. 16 - A simple pendulum of length L hangs from the...Ch. 16 - We do not need the analogy in Equation 16.30 to...Ch. 16 - Prob. 29PQCh. 16 - Prob. 30PQCh. 16 - Prob. 31PQCh. 16 - Prob. 32PQCh. 16 - Prob. 33PQCh. 16 - Show that angular frequency of a physical pendulum...Ch. 16 - A uniform annular ring of mass m and inner and...Ch. 16 - A child works on a project in art class and uses...Ch. 16 - Prob. 37PQCh. 16 - Prob. 38PQCh. 16 - In the short story The Pit and the Pendulum by...Ch. 16 - Prob. 40PQCh. 16 - A restaurant manager has decorated his retro diner...Ch. 16 - Prob. 42PQCh. 16 - A wooden block (m = 0.600 kg) is connected to a...Ch. 16 - Prob. 44PQCh. 16 - Prob. 45PQCh. 16 - Prob. 46PQCh. 16 - Prob. 47PQCh. 16 - Prob. 48PQCh. 16 - A car of mass 2.00 103 kg is lowered by 1.50 cm...Ch. 16 - Prob. 50PQCh. 16 - Prob. 51PQCh. 16 - Prob. 52PQCh. 16 - Prob. 53PQCh. 16 - Prob. 54PQCh. 16 - Prob. 55PQCh. 16 - Prob. 56PQCh. 16 - Prob. 57PQCh. 16 - An ideal simple harmonic oscillator comprises a...Ch. 16 - Table P16.59 gives the position of a block...Ch. 16 - Use the position data for the block given in Table...Ch. 16 - Consider the position data for the block given in...Ch. 16 - Prob. 62PQCh. 16 - Prob. 63PQCh. 16 - Use the data in Table P16.59 for a block of mass m...Ch. 16 - Consider the data for a block of mass m = 0.250 kg...Ch. 16 - A mass on a spring undergoing simple harmonic...Ch. 16 - A particle initially located at the origin...Ch. 16 - Consider the system shown in Figure P16.68 as...Ch. 16 - Prob. 69PQCh. 16 - Prob. 70PQCh. 16 - Prob. 71PQCh. 16 - Prob. 72PQCh. 16 - Determine the period of oscillation of a simple...Ch. 16 - The total energy of a simple harmonic oscillator...Ch. 16 - A spherical bob of mass m and radius R is...Ch. 16 - Prob. 76PQCh. 16 - A lightweight spring with spring constant k = 225...Ch. 16 - Determine the angular frequency of oscillation of...Ch. 16 - Prob. 79PQCh. 16 - A Two springs, with spring constants k1 and k2,...Ch. 16 - Prob. 81PQCh. 16 - Prob. 82PQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. What is the spring constant of a spring that starts 10.0 cm long and extends to 11.4 cm with a 300 g mass hanging from it?arrow_forwardplease help me solve all parts of this question from physics. thanks so much in advance! :)))arrow_forwardA fluid with density 263 kg/m3 flows through a pipe of varying diameter and height. At location 1 the flow speed is 13.5 m/s and the diameter of the pipe is 7.4 cm down to location 2 the pipe diameter is 16.9 cm. Location 1 is 6.3 meters higher than location 2. What is the difference in pressure P2 - P1? Using units in Pascals and use g = 9.81 m/s2.arrow_forward
- The kitchen had a temperature 46 degrees Fahrenheit and was converted it to Kelvin. What is the correct number for this temperature (46 F) on the Kelvin scale?arrow_forwardWater is traveling at a speed of 0.65 m/s through a pipe with a cross-section radius of 0.23 meters. The water enters a section of pipe that has a smaller radius, only 0.11 meters. What is the speed of the water traveling in this narrower section of pipe?arrow_forwardA particular water pipe has a radius of 0.28 meters. If the pipe is completely filled with water, moving with average velocity 0.45 m/s, what is the flow rate of water through the pipe with units of cubic meters of water per second?arrow_forward
- Water is flowing through a horizontal pipe with two segments. In one segment, the water flows at a speed v1 = 4.52 m/s. In the second segment the speed of the water is v2 = 2.38 m/s. Based on Bernoulli's Principle, what is the difference in pressure (P2 - P1) between the two segments? Assume that the density of the water is 997 kg/m3 and give your answer as the number of Pascals (i.e. N/m2).arrow_forwardWater from the faucet is supplied to the hose at a rate of 0.00057 m3/s. At what speed (number of meters per second) does the water exit the nozzle if the cross sectional area of the narrow nozzle is 2.1 x 10-6 m2?arrow_forwardJason Fruits/Indiana University Research Communications Silver/ silver oxide Zinc zinc/oxidearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY