
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for ethyl butyrate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
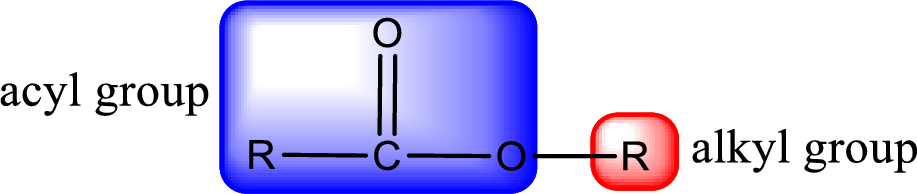
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for butyl ethanoate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
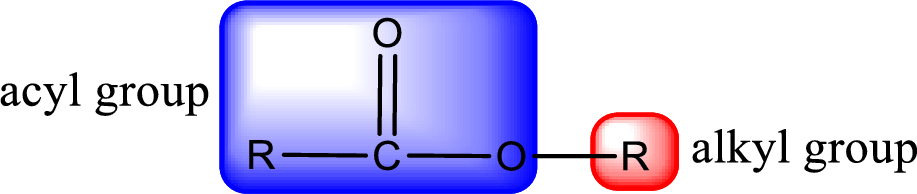
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from carboxylic acid.
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for 2-methylpropyl formate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
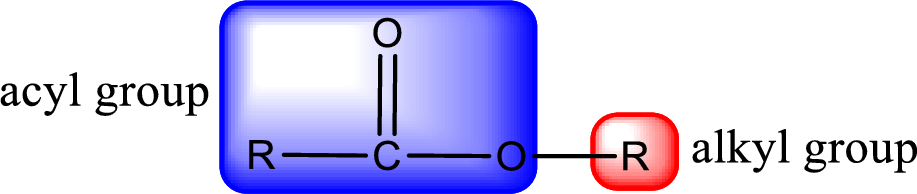
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from carboxylic acid.
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for ethyl
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
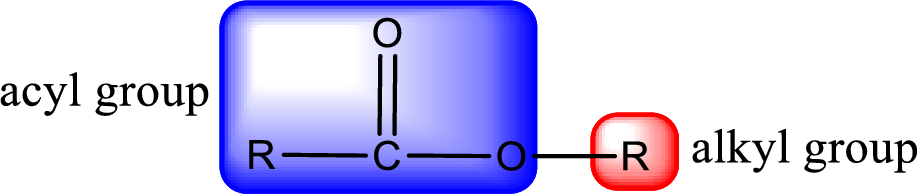
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from carboxylic acid.
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- If the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.Data: Energy of each photon: 0.7835x10-18 J.arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forward
- When propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forwardDoes Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forward
- Explain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forwardIndicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





