
(a)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is
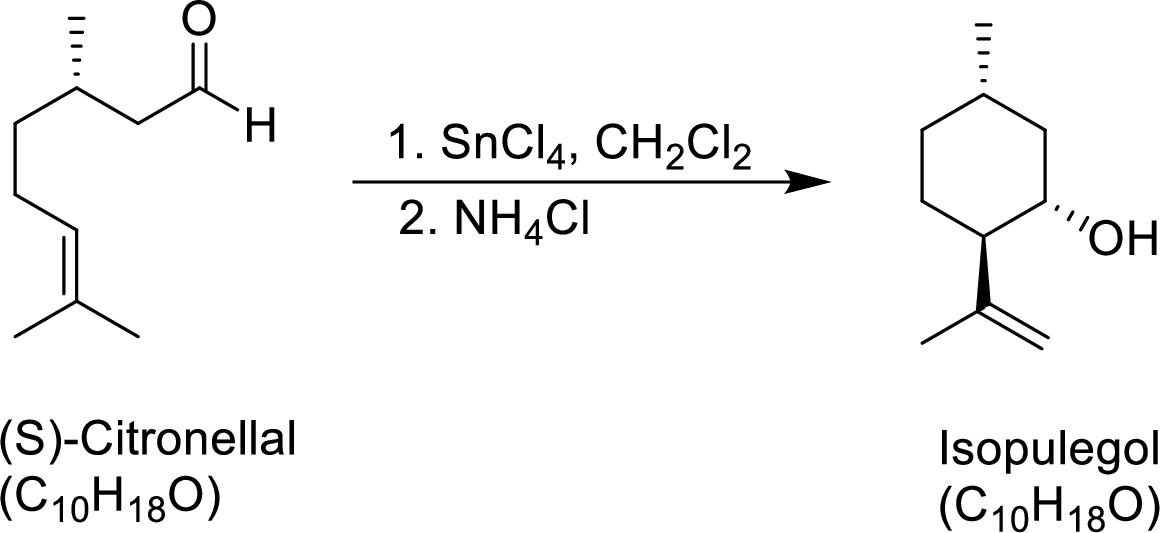
Both compounds has to be showed as terpenes.
Concept Introduction:
Terpene:
The compounds which contains two or more isoprene units in their structure are said to be terpenes.
Isoprene (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene) unit is a molecule with five carbon atoms with double bonds.
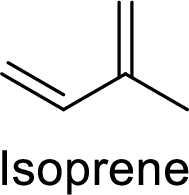
(b)
Interpretation:
A mechanism for the conversion of (S)-Citronellal to Isopulegol has to be proposed.
(c)
Interpretation:
In Isopulegol, the number of stereocenters present has to be given and the number of stereoisomers possible for a molecule with this number of stereocenters has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
A carbon which is bonded to four different groups is said to be chiral carbon. A chiral carbon in a molecule is said to be chiral center. All chiral centers are stereocenters.
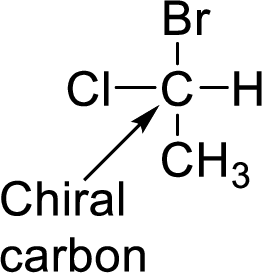
(d)
Interpretation:
Isopulegol is formed as a single stereoisomer. The fact that only single stereoisomer is formed has to be accounted.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- -C = C - C - + Br₂ + I" -> -C-C-c -C = C -C- + Br² + I₂ -C=C Br I + Brū + Iz -7- C - C-C- I Br Mechanism; - C = c - c - + Br - Br > - C-c-c- Br -C-C-C- + 1 - - -Ċ-Ċ'-c' - Br Br Iarrow_forwardWrite the mechanism of the esterification reaction (please show the mechanism included line pairs and arrows)arrow_forwardHow do I break down the reaction shown on the chalkboard and explain it correctly using the bromonium ion mechanism, instead of the (disproven) carbocation-based mechanismarrow_forward
- ¿Qué the product is obtained from tetraethoxypropano and hidrazina?. Indicate the reason why the corresponding dial is used.arrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 is reacted with hydrazine, two isomeric products are formed. Indicate their structures and the major product.arrow_forwardIs it possible to obtain addition derivatives to nitrogen in position 2 of pyrazoles by reaction with electrophilic agents? Reason for this.arrow_forward
- Starting from 1,3-dicarbonyl derivatives to obtain isooxazoles and isothiazoles. Indicate whether synthetic methods exist.arrow_forwardIn the synthesis of benzotriazole, adding NaNO2 heats the solution. State the reason.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by treating benzotriazole with dimethyl sulfate or methyl iodide in a basic medium.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

