
(a)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
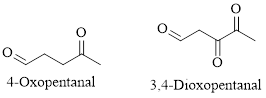
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:
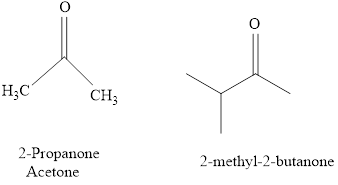
Naming of compounds with two
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
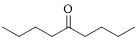
Let’s given numbering to this compound as follows,
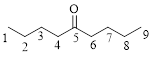
The parent chain contains 9 carbon atoms; in the fifth carbon atom a ketone functional group is attached.
Thus, according to IUPAC this compound can be named as 5-Nonanone.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
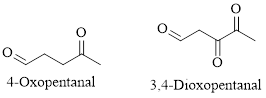
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Naming of compounds with two functional groups,
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
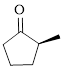
Let’s write give the numbering to this compound.
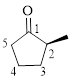
This parent ring has five carbon atoms; a methyl group was attached to the second carbon atom. Therefore, according to the IUPAC rules, the compound can be named as
Here, this compound has a chiral center (it is highlighted as *); its configuration can be specified as follows,
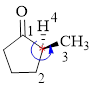
The numbering follows an anti-clock wise direction and so molecule is in as S configuration.
Thus, the compound name can be written as
(c)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
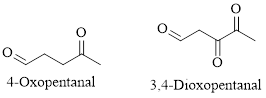
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
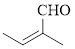
Let’s give the numbering to the given compound.
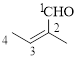
The parent hydrocarbon chain has two functional groups and they are
(d)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
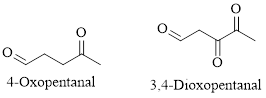
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
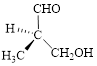
Let’s write give the numbering to this compound.
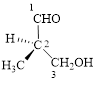
This parent chain has three carbon atoms; a methyl group was attached to the second carbon atom and hydroxyl group was attached to the third carbon atom. Therefore, according to the IUPAC rules, the compound can be named as 3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-propanal.
Here, this compound has a chiral center (it is highlighted as *); its configuration can be specified as follows,
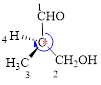
The numbering of substituents on the chiral center follows clock wise direction and so molecule is in R configuration.
Thus, the compound name can be written as (R)-3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-propanal.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
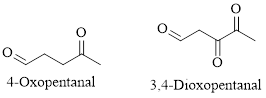
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
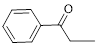
Let’s give the numbering to the given compound.
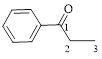
A phenyl ring is attached to the first carbon atom in the three membered parent carbon chains. According to IUPAC the aldehyde group has higher priority. Thus the compound can be named as 1-phenyl-1-propanone.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
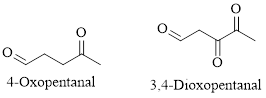
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:
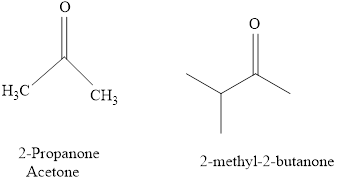
Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
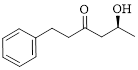
Let’s write give the numbering to this compound.
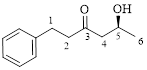
This parent ring has six carbon atoms; a hydroxyl (–OH) and a phenyl ring were attached to the first and fifth carbon atoms in the parent chain respectively. Therefore, according to the IUPAC rules, the compound can be named as 5-Hydroxy-1-phenyl-3-hexanone.
Here, this compound has a chiral center (it is highlighted as *); its configuration can be specified as follows,
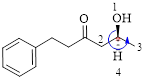
The numbering follows an anti-clock wise direction and so molecule is in as S configuration.
Thus, the compound name can be written as (S)-5-Hydroxy-1-phenyl-3-hexanone.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
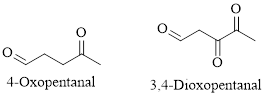
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
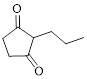
Let’s give the numbering to the given compound.
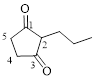
The parent hydrocarbon ring has five carbon atoms. A propyl group was attached to the second carbon atom in the ring and two ketone groups were present in first and third carbon atom respectively. Thus the compound can be named as
(h)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
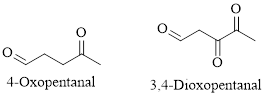
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
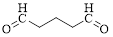
Let’s give the numbering to the given compound.
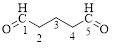
The parent hydrocarbon chain has five carbon atoms with two aldehydes on both ends. Thus according to IUPAC the compound can be named as pentanedial.
(i)
Interpretation:
The given compound’s IUPAC name has to be determined and the relevant stereochemistry should be specified.
Concept introduction:
The functional group in the aldehydes and Ketones are carbonyl group.
Naming Aldehydes:
Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon atom.
The IUPAC naming of aldehydes is obtained by replacing the final "e" on the name of the parent hydrocarbon with "al".
For example:
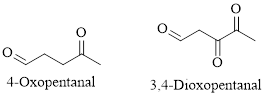
Naming Ketones:
The IUPAC name of a ketones are obtained by replacing the "e" on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with "one".
Only few ketones have common name.
For example:

Naming of compounds with two functional groups;
If a compound has two functional groups, the one with lower priority is indicated by a prefix and another with the higher priority by a suffix.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows.
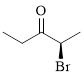
Let’s give the numbering to the given compound.
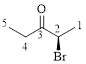
The parent hydrocarbon chain has two functional groups and they are bromine and ketone. According to IUPAC the bromine has higher priority. Thus the compound can be named as 2-bromo-3-pentanone.
Here, this compound has a chiral center (it is highlighted as *); its configuration can be specified as follows,
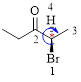
The numbering follows a clock wise direction and so molecule is in R configuration.
Thus, the compound name can be written as (R)-2-bromo-3-pentanone.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Steps on how to solve. Thank you!arrow_forward3. Name this ether correctly. H₁C H3C CH3 CH3 4. Show the best way to make the ether in #3 by a Williamson Ether Synthesis. Start from an alcohol or phenol. 5. Draw the structure of an example of a sulfide.arrow_forward1. Which one(s) of these can be oxidized with CrO3 ? (could be more than one) a) triphenylmethanol b) 2-pentanol c) Ethyl alcohol d) CH3 2. Write in all the product(s) of this reaction. Label them as "major" or "minor". 2-methyl-2-hexanol H2SO4, heatarrow_forward
- 3) Determine if the pairs are constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or mesocompounds. (4 points)arrow_forwardIn the decomposition reaction in solution B → C, only species C absorbs UV radiation, but neither B nor the solvent absorbs. If we call At the absorbance measured at any time, A0 the absorbance at the beginning of the reaction, and A∞ the absorbance at the end of the reaction, which of the expressions is valid? We assume that Beer's law is fulfilled.arrow_forward> You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: 1. ☑ CI 2. H3O+ O Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check ? DO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardConsider a solution of 0.00304 moles of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.442) dissolved in 25 mL water and titrated with 0.0991 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the equivalence pointarrow_forwardWhat is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forward
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
