
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The experimental conditions required to bring about the given conversion reaction has to be described.
Concept Introduction:
Treatment of an
Example:
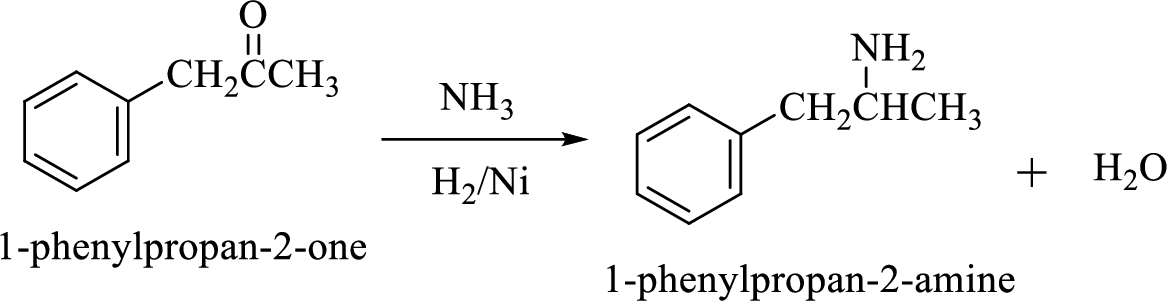
(b)
Interpretation:
Check whether the given compound Rimantadine is chiral or not and the number of stereoisomers possible for the compound has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Enantiomers: These are stereoisomers that are not superimposable mirror images of each other and the configurations at all stereo genic centers are exactly opposite.
Chiral center: A chiral center is defined as the tetrahedral carbon atom in an organic molecule that is connected to four non-identical groups/substituents. It is sometimes known as a stereo genic center.
Chirality: The geometric property of molecules where the structure of the molecule and its mirror image are not superimposable is known as chirality. Chiral molecules are optically active and they can rotate the plane polarized light.
The number of stereoisomers possible for a compound can be determined using the below mentioned equation.
Treatment of an aldehyde or ketone with ammonia or an amine in the presence of a reducing agent (like
Example:
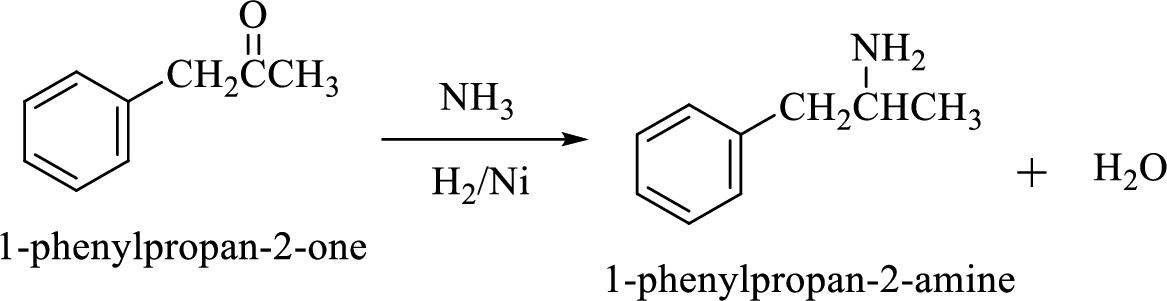
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

