
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given amine has to be named and it should be indicated whether as the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary or tertiary amine.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
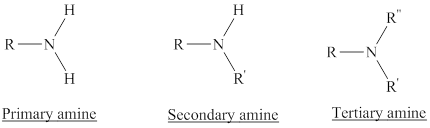
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Ammonia is very soluble in water giving an alkaline solution which can be neutralized by acids to produce ammonium salts.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given amine has to be named and it should be indicated whether as the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary or tertiary amine.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Ammonia is very soluble in water giving an alkaline solution which can be neutralized by acids to produce ammonium salts.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn and it should be indicated whether as the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary or tertiary amine.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Ammonia is very soluble in water giving an alkaline solution which can be neutralized by acids to produce ammonium salts.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the given compound has to be drawn and it should be indicated whether as the ammonium salt of a primary, secondary or tertiary amine.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.

From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Ammonia is very soluble in water giving an alkaline solution which can be neutralized by acids to produce ammonium salts.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF GENERAL, ORGANIC, A
- Specific rotation is a measure of a solution's capacity to rotate circularly polarized light. The unfolding of the a helix of a polypeptide to a random conformation is accompanied by a large decrease in specific rotation. Polyglutamate, a polypeptide made up of only 1-Glu residues, has the a helix conformation at pH 3. When researchers raise the pH to 7, there is a large decrease in the specific rotation of the solution. Similarly, polylysine (1.-Lys residues) is an a helix at pH 10, but when researchers lower the pH to 7 the specific rotation also decreases, as shown in the graph. a Helix Specific rotation Poly(Glu) a Helix Random conformation Poly(Lys) Random conformation T + ° 2 4 6 В 10 12 14 PH Complete the statements about the molecular mechanism for these changes in specific rotation. Increasing the pH of a polyglutamate solution from 6 to 7 causes the carboxyl group of each glutamate residue Comed Artwer lose a proton. The negatively charged groups in each glutamate residue…arrow_forwardFrom the reaction data below, determine whether the reaction is first order or second order and calculate the rate constant. Time (s) 0 Reactant (mM) 6.2 1 3.1 2 2.1 3 1.6 4 1.3 5 1.1 Only a plot of 1/[reactant] versus t gives a straight line, so the reaction is 0.150 mM-1 s-1 . S second order . The slope, k, isarrow_forwardFrom the reaction data below, determine whether the reaction is first order or second order and calculate the rate constant. Time (s) 0 Reactant (mM) 5.4 1 4.6 2 3.9 3 3.2 4 2.7 5 2.3 Only a plot of In[reactant] versus t gives a straight line, so the reaction is s-1. . The negative of the slope, k, isarrow_forward
- A protein has a molecular mass of 400 kDa when measured by size-exclusion chromatography. When subjected to gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), the protein gives three bands with molecular masses of 180, 160, and 60 kDa. When electrophoresis is carried out in the presence of SDS and dithiothreitol (DTT), three bands again form, this time with molecular masses of 160, 90, and 60 kDa. How many subunits does the protein have, and what is the molecular mass of each? four subunits: 180, 160, 90, and 60 kDa three subunits: 180, 160, and 60 kDa three subunits: 160, 90, and 60 kDa four subunits: 160, 90, 90, and 60 kDa Correct Answerarrow_forwardCalculate KM and Vmax from the following data: KM= i Vmax [S] (μM) vo (mM.s-¹) 0.1 0.34 0.2 0.53 0.4 0.74 0.8 0.91 1.6 1.04 μM mM s-1arrow_forwardPropose a detailed chemical mechanism for the enzyme catalyzed reaction below and briefly note similarities, if any, to enzymes that we've studied. CO2 + CO2 2 CO2 HO CH3arrow_forward
- 11. Which of the compounds below is the major product of the following reaction sequence? NOTE: PCC is pyridinium chlorochromate 1. BH 3 PCC 2. H2O2, NaOH NH HN ΗΝ, A B C CH3NH2, NaBH3CN D E NHarrow_forward10. Which of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? Ph Ph Ph A B OH 1. EtMgBr H2CrO4 Zn(Hg), aq. HCI PhCHO ? 2. H₂O, H+ Ph. C D Ph "ར HO OH Earrow_forward7. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? Ph A OH 99 Ph OH D Br HOCH2CH2OH H2SO4 1. Mg, Et₂O 2. PhCH2CHO HCI, H₂O Br OH Ph Ph OH B C Br OH Ph Earrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





