
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
After volume of
Concept Introduction:
The relationship between
The
The
The relationship between
The concentration of
The concentration of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The titration of
Volume of the solution is given below,
Mole of hydroxide ion is calculated as follows,
The
The
The
(b)
Interpretation:
After volume of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The titration of
Volume of the acid solution is given below,
Mole of hydronium ion is calculated as follows,
The concentration of
The
The
The
(c)
Interpretation:
After volume of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The titration of
Volume of the acid solution is given below,
Mole of hydronium ion is calculated as follows,
The concentration of
The
The
The
(d)
Interpretation:
After volume of
Concept introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The titration of
Volume of the acid solution is given below,
Mole of hydronium ion is calculated as follows,
The total moles of hydronium ion
(e)
Interpretation:
After volume of
Concept introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The titration of
Volume of the acid solution is given below,
Mole of hydronium ion is calculated as follows,
The concentration of
The
The
The
(f)
Interpretation:
After volume of
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The titration of
Volume of the acid solution is given below,
Mole of hydronium ion is calculated as follows,
The concentration of
The
The
The
(g)
Interpretation:
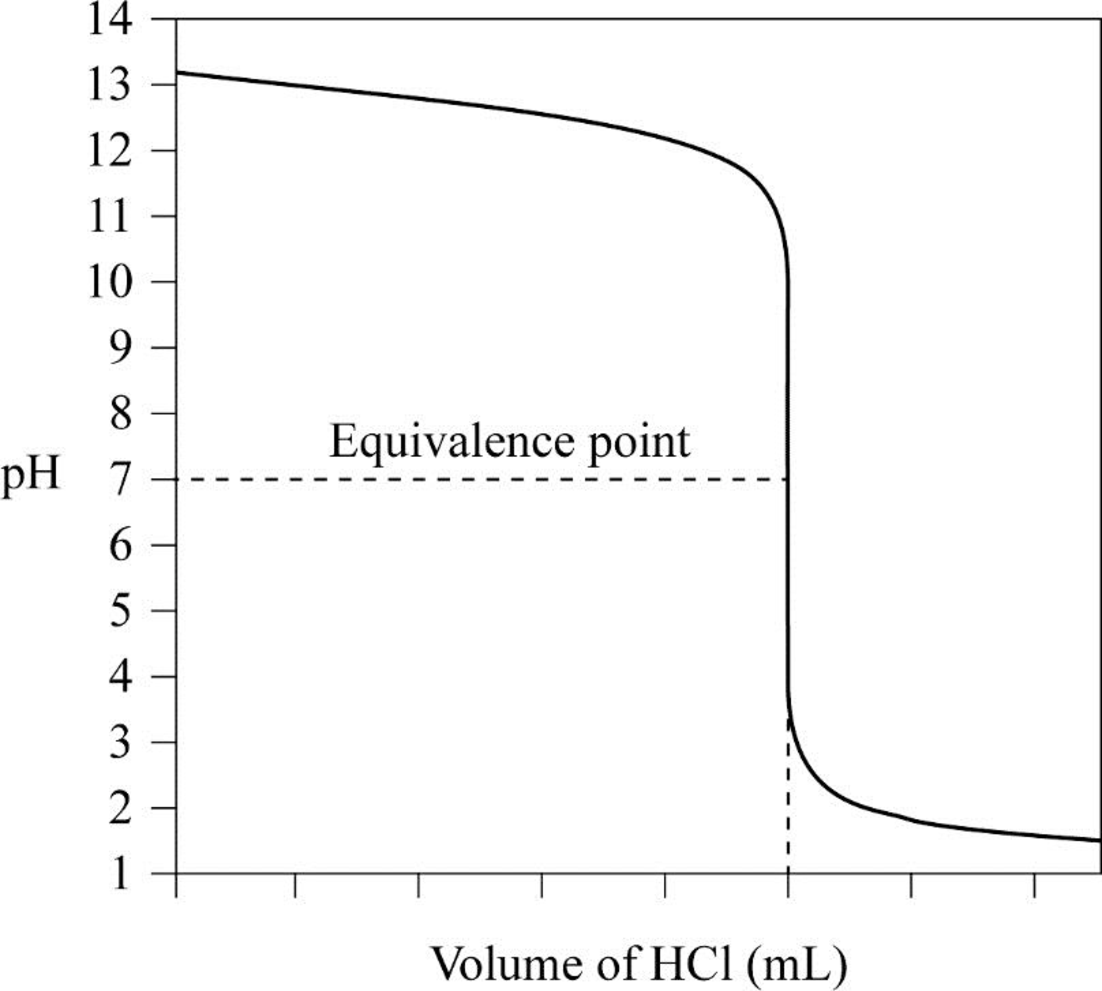
From the result titration curve has to be plotted and position of the equivalent point has to be indicated.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Table for the volume of
| S.No | Volume of | |
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 |
The equivalent point of the given solution is seven when the volume of
From the result, the titration curve is plotted and position of the equivalent point is indicated as follows.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- Under aqueous basic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2: NC H₂O он- H₂O 1 2 OH Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardAssign these COSY Spectrumarrow_forwardAssign these C-NMR and H-NMR Spectrumarrow_forward
- Predict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forward
- What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forwardDE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: + H₂O H* ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





