
Concept explainers
Draw the product(s) formed when each
![]()
(a)
Interpretation:
The product(s) formed by the reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
The reaction of hydrogen halide with alkene results in the formation of alkyl halide. This type of reaction is an electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide. Electrophilic addition reactions are those in which breaking of pi bond take place to form new sigma bond.
Answer to Problem 15.24P
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
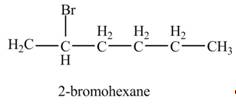
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
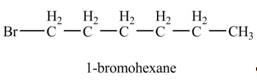
Explanation of Solution
Electrophilic addition reaction follows Markovnikov rule. According to Markovnikov rule, the positive part of halogen acid attached to that carbon atom in
The given alkene is shown below.
![]()
Figure 1
The steps followed by electrophilic addition reaction are stated below:
➢ First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
➢ The halide ion will attack on the carbocation to give the final product.
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
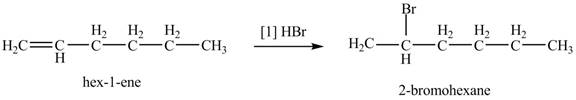
Figure 2
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
The addition of
The addition of
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
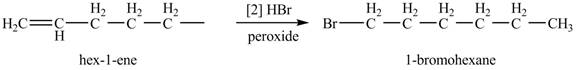
Figure 3
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
The product(s) formed by the reaction of given alkene with
(b)
Interpretation:
The product(s) formed by the reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
The reaction of hydrogen halide with alkene results in the formation of alkyl halide. This type of reaction is an electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide. Electrophilic addition reactions are those in which breaking of pi bond take place to form new sigma bond.
Answer to Problem 15.24P
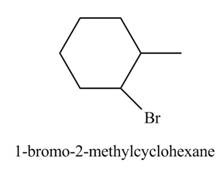
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
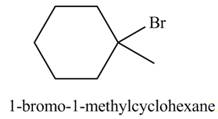
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
Explanation of Solution
Electrophilic addition reaction follows Markovnikov rule. According to Markovnikov rule, the positive part of halogen acid attached to that carbon atom in
The given alkene is shown below.
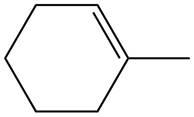
Figure 4
The steps followed by electrophilic addition reaction are stated below:
➢ First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
➢ The halide ion will attack on the carbocation to give the final product.
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
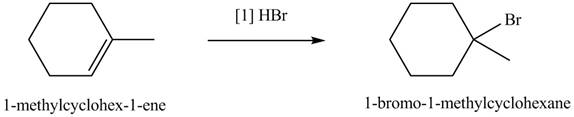
Figure 5
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
The addition of
The addition of
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
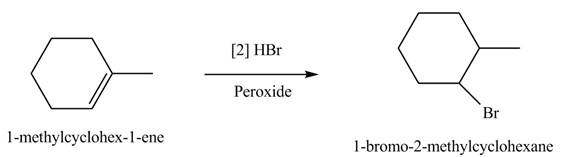
Figure 6
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
The product(s) formed by the reaction of given alkene with
(c)
Interpretation:
The product(s) formed by the reaction of given alkene with
Concept introduction:
The reaction of hydrogen halide with alkene results in the formation of alkyl halide. This type of reaction is an electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide. Electrophilic addition reactions are those in which breaking of pi bond take place to form new sigma bond.
Answer to Problem 15.24P
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
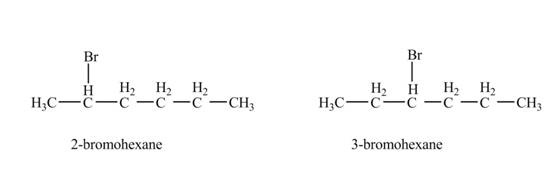
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with

Explanation of Solution
Electrophilic addition reaction follows Markovnikov rule. According to Markovnikov rule, the positive part of halogen acid attached to that carbon atom in
The given alkene is shown below.

Figure 7
The steps followed by electrophilic addition reaction are stated below:
➢ First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
➢ The halide ion will attack on the carbocation to give the final product.
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
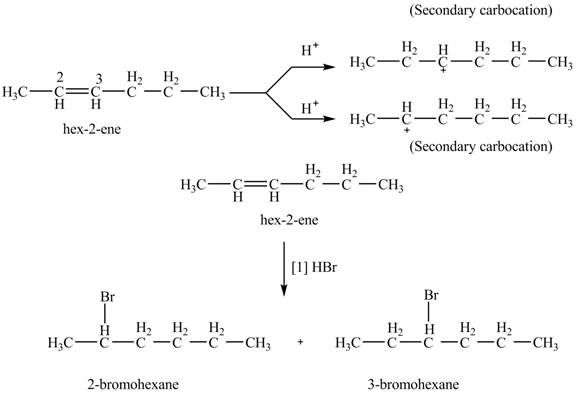
Figure 8
The reaction of given alkene with
The addition of
The addition of
The product formed by the reaction of given alkene with
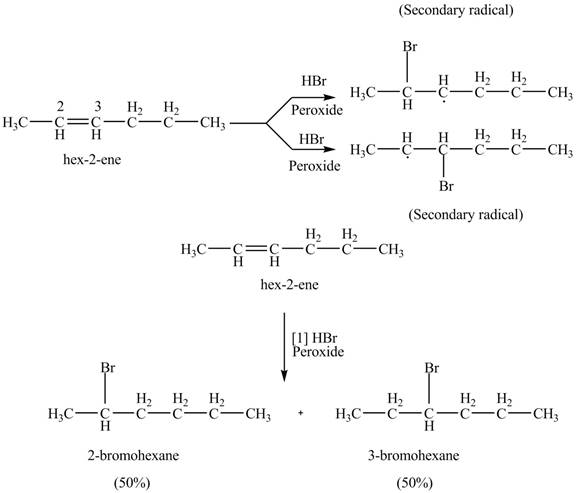
Figure 9
The reaction of given alkene with
The product(s) formed by the reaction of given alkene with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





