
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a. ![]() d.
d. ![]() g.
g. 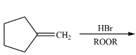
b.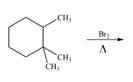 e.
e. 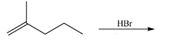 h.
h.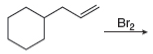
c. ![]() f.
f. 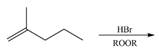 i.
i.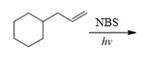
(a)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
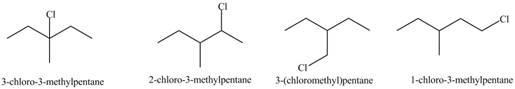
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes undergo chlorination when they are treated with
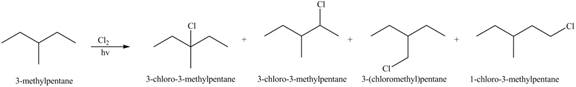
Figure 1
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
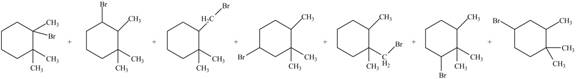
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes undergo bromination by free radical mechanism when they are treated with
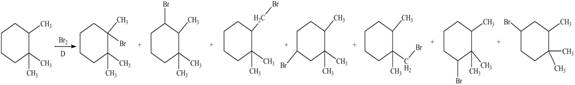
Figure 2
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes undergo bromination by free radical mechanism when they are treated with
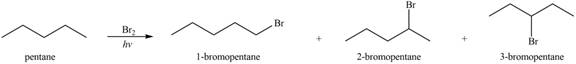
Figure 3
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
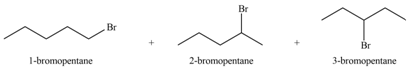
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
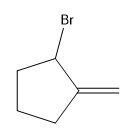
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes undergo bromination by free radical mechanism when they are treated with NBS in the presence of light. Bromination takes place at allylic carbon atom. One product is formed by the given bromination reaction as shown in Figure 3.
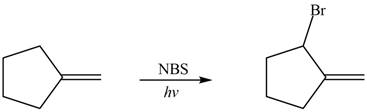
Figure 4
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
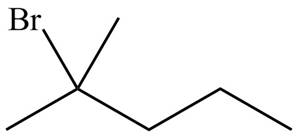
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes undergo addition reaction when they are treated with
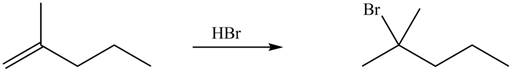
Figure 5
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
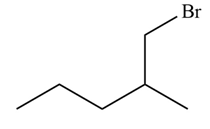
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes undergo addition reaction when they are treated with
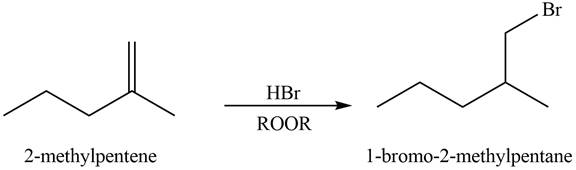
Figure 6
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
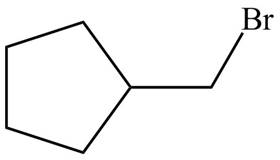
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes undergo addition reaction when they are treated with
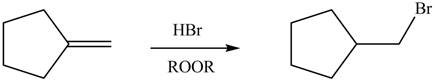
Figure 7
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
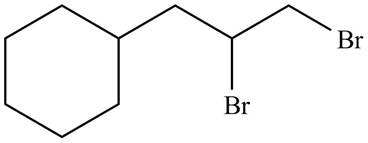
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes undergo addition reaction when they are treated with
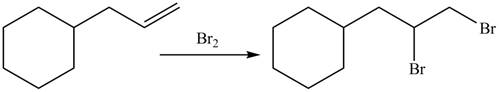
Figure 8
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation: The organic products formed by the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes and alkynes show addition reaction due to presence of one and two pi-bonds, respectively. Alkanes show substitution reaction due to absence of pi-bond.
Answer to Problem 15.48P
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown below.
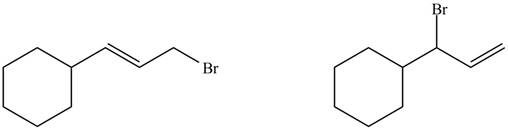
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes undergo bromination by free radical mechanism when they are treated with NBS in the presence of light. Bromination takes place at allylic carbon atom. Two different products are formed by the given bromination reaction as shown in Figure 9.
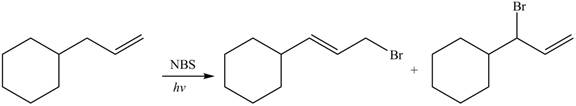
Figure 9
The organic products formed by the given reaction are shown in Figure 9.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- utron eutro cle TH tro (Na (b) Atoms are said to be electrically neutral. Explain. (c) Distinguish between the following: (i) Atomic number and mass number. (ii) Mass number and relative atomic mass. 2. An isotope Q, has 18 neutrons a mass number of 34. (a) (i) Draw the atomic structure of Q. (ii) Write its electron arrangement (b) To which period and group does Q belong? Explain your answer. (c) How does Q form its ion? Explain. 3. (a) Determine the relative atomic mass of the following elements = compositions occur in the proportions given. (i) Neon 20 21 22. Ne (90.92%), 10Ne (0.26%), and 10Ne (8.82%) (ii) Argon 36 38 40 18 Ar (0.34%), 18 Ar (0.06%) and 18 Ar (99.6%)arrow_forwardIn the normal hydrogen electrode, the balance potential difference in the interface is this, the maximum potential is 5 mV. Explain briefly.arrow_forwardThe electrode balance potential is -0.118 V and the interface potential difference is +5 mV. The overvoltage n will be 0.005 - (-0.118) = 0.123 V. Is it correct?arrow_forward
- In the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), if the electrode balance potential is -0.118 V and the interface potential difference is +5 mV. The current voltage will be 0.005 - (-0.118) = 0.123 V ¿Correcto?arrow_forwardIn the electrode Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1) at 298K is 0.79 mA cm-2. If the balance potential of the electrode is -0.118 V and the potential difference of the interface is +5 mV. Determine its potential.arrow_forwardIn one electrode: Pt, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density at 298K is 0.79 mA·cm-2. If the voltage difference of the interface is +5 mV. What will be the correct intensity at pH = 2?. Maximum transfer voltage and beta = 0.5.arrow_forward
- In a Pt electrode, H2(1 atm) | H+(a=1), the interchange current density of an electrode is 0.79 mA cm-2. ¿Qué corriente flow across the electrode of área 5 cm2 when the difference in potential of the interface is +5 mV?.arrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V, indicate which of the 2 voltage formulas of the ley of Tafel must be applied i a a) == exp (1-B). xp[(1 - ß³): Fn Fn a b) == exp B RT RTarrow_forwardIf the current voltage is n = 0.14 V. Indicate which of the 2 formulas must be applied a) = a T = i exp[(1 - p) F Fn Fn b) i==exp B RTarrow_forward
- Topic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forwardTwo cations that exchange an electron in an interface, the exchange density is worth 1.39 mA/cm2 and the current density is worth 15 mA/cm2 at 25°C. If the overvoltage is 0.14 V, calculate the reaction rate and symmetry factor. Data: R = 8,314 J mol-1 k-1: F = 96500 Carrow_forwardWith the help of the Tafel line, it is estimated that the interchange density of the VO2+/VO2+ system on the carbon paper has a value of 3 mA cm-2. Calculate a) the current density if the voltage has a value of 1.6 mV and the temperature is 25°C. b) the beta value of the anódico process if the Tafel pendulum is 0.6 V at 25°C. Data: R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1, y F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





