
(a)
Interpretation: The products for radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are to be drawn. The compounds which form single constitutional isomer for both reactions are to be predicted. The true structure of a reactant for both reactions to form a single product is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Chlorination and bromination are radical substitution reaction. In the reaction of chlorination,
Answer to Problem 15.41P
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are,
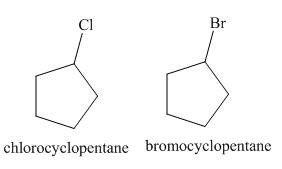
A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reactions.
Explanation of Solution
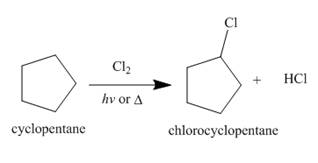
Figure 1
Alkanes undergo bromination through free radical mechanism when they are treated with
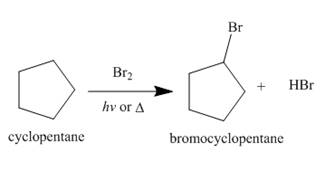
Figure 2
A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reaction because all hydrogen atoms of given compound are present in a same chemical environment. Therefore, to form a single product, the chemical environment of hydrogen atoms should be same.
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively. A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reactions.
(b)
Interpretation: The products for radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are to be drawn. The compounds which form single constitutional isomer for both reactions are to be predicted. The true structure of a reactant for both reactions to form a single product is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Chlorination and bromination are radical substitution reaction. In the reaction of chlorination,
Answer to Problem 15.41P
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are,
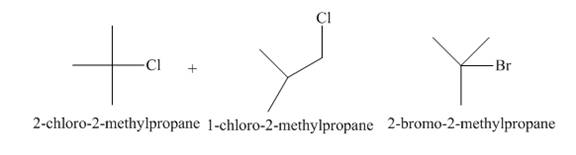
A single constitutional isomer is not formed for both reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes undergo chlorination when they are treated with
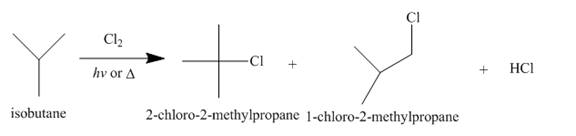
Figure 3
Alkanes undergo bromination by free radical mechanism when they are treated with
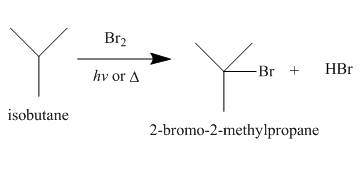
Figure 4
A single constitutional isomer is formed for bromination reaction but not for chlorination because bromine is more selective than chlorine.
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively. A single constitutional isomer is not formed for both reactions.
(c)
Interpretation: The products for radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are to be drawn. The compounds which form single constitutional isomer for both reactions are to be predicted. The true structure of a reactant for both reactions to form a single product is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Chlorination and bromination are radical substitution reaction. In the reaction of chlorination,
Answer to Problem 15.41P
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are,
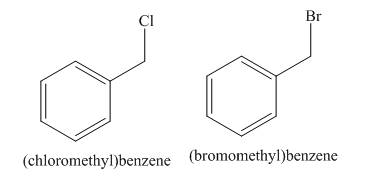
A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes undergo chlorination when they are treated with
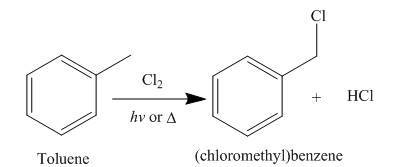
Figure 5
Alkanes undergo bromination when they are treated with
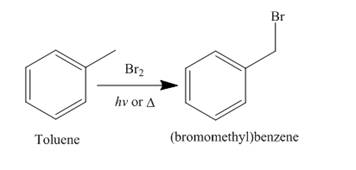
Figure 6
A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reaction because all hydrogen atoms of given compound are present in same chemical environment. Therefore, to form a single product, the chemical environment of hydrogen atoms should be same.
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reactions.
(d)
Interpretation: The products for radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are to be drawn. The compounds which form single constitutional isomer for both reactions are to be predicted. The true structure of a reactant for both reactions to form a single product is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Chlorination and bromination are radical substitution reaction. In the reaction of chlorination,
Answer to Problem 15.41P
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are,
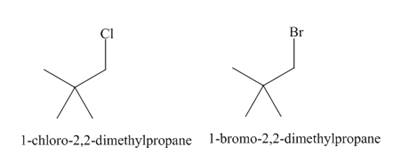
A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes undergo chlorination when they are treated with
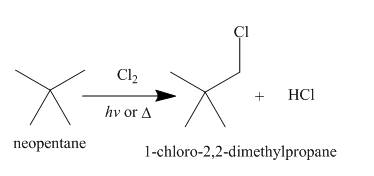
Figure 7
Alkanes undergo bromination when they are treated with
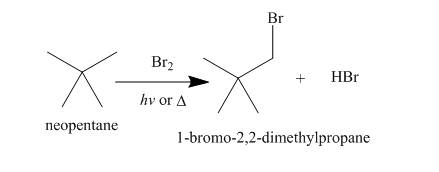
Figure 8
A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reaction because all hydrogen atoms of given compound are present in same chemical environment. Therefore, to form a single product, the chemical environment of hydrogen atoms should be same.
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively. A single constitutional isomer is formed for both reactions.
(e)
Interpretation: The products for radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are to be drawn. The compounds which form single constitutional isomer for both reactions are to be predicted. The true structure of a reactant for both reactions to form a single product is to be identified.
Concept introduction: Chlorination and bromination are radical substitution reaction. In the reaction of chlorination,
Answer to Problem 15.41P
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are,
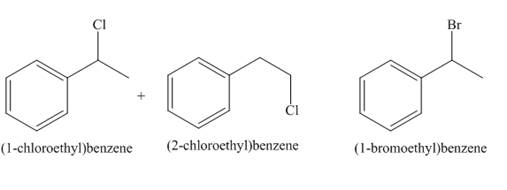
A single constitutional isomer is not formed for both reactions.
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes undergo chlorination when they are treated with
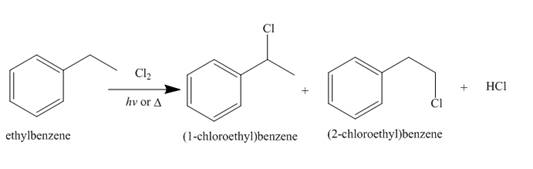
Figure 9
Alkanes undergo bromination by free radical mechanism when they are treated with
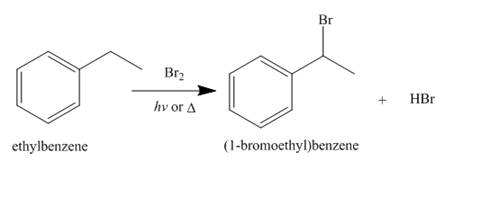
Figure 10
A single constitutional isomer is formed for bromination reaction but not for chlorination because bromine is more selective than chlorine.
The products of radical chlorination and bromination of given compound are shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10, respectively. A single constitutional isomer is not formed for both reactions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Including activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forward
- Can I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forward
- Can I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forwardState the detailed mechanism of the reaction of benzene with isopropanol in sulfuric acid.arrow_forwardDo not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction. For the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) · 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 -> NO2 + NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 →> N2O5 (k-1) → NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Give the expression for the acceptable rate. (A). d[N₂O] dt = -1 2k,k₂[N205] k₁+k₂ d[N₂O5] (B). dt =-k₁[N₂O₂] + k₁[NO2][NO3] - k₂[NO2]³ (C). d[N₂O] dt =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[N205] - K3 [NO] [N205] (D). d[N2O5] =-k₁[NO] - K3[NO] [N₂05] dtarrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 20.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





