
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Describes what happen in the reaction of an
Concept Introduction:
Hydrolysis Reaction: This type of reaction involving the braking of a carbon-carbon triple, double bonds in a molecules using water.
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of
Acetal formation: The acid catalysts is added to the reaction of an alcohol with an aldehyde or
A hemiacetal or a hemiketal: addition of alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone which produce hemi acetal.
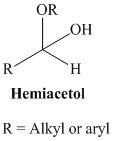
(b)
Interpretation:
The line structure should be draw and identified given the reactant of aldehyde and alcohol to form a hemiacetal, the transformation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Acetal formation: The small amount of acid catalysts is added to the reaction of an alcohol with an aldehyde or ketone, the hemi-space initially formed is converted into an acetal or a ketal substitution reaction.
A hemiacetal or a hemiketal: addition of alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone which produce hemi acetal.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
- Which type of enzyme catalyses the following reaction? oxidoreductase, transferase, hydrolase, lyase, isomerase, or ligase.arrow_forward+NH+ CO₂ +P H₂N + ATP H₂N NH₂ +ADParrow_forwardWhich type of enzyme catalyses the following reaction? oxidoreductase, transferase, hydrolase, lyase, isomerase, or ligase.arrow_forward
- Which features of the curves in Figure 30-2 indicates that the enzyme is not consumed in the overall reaction? ES is lower in energy that E + S and EP is lower in energy than E + P. What does this tell you about the stability of ES versus E + S and EP versus E + P.arrow_forwardLooking at the figure 30-5 what intermolecular forces are present between the substrate and the enzyme and the substrate and cofactors.arrow_forwardprovide short answers to the followings Urgent!arrow_forward
- Pyruvate is accepted into the TCA cycle by a “feeder” reaction using the pyruvatedehydrogenase complex, resulting in acetyl-CoA and CO2. Provide a full mechanismfor this reaction utilizing the TPP cofactor. Include the roles of all cofactors.arrow_forwardB- Vitamins are converted readily into important metabolic cofactors. Deficiency inany one of them has serious side effects. a. The disease beriberi results from a vitamin B 1 (Thiamine) deficiency and ischaracterized by cardiac and neurological symptoms. One key diagnostic forthis disease is an increased level of pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate in thebloodstream. How does this vitamin deficiency lead to increased serumlevels of these factors? b. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 5 deficiency? c. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 2 /B 3 deficiency?arrow_forwardDraw the Krebs Cycle and show the entry points for the amino acids Alanine,Glutamic Acid, Asparagine, and Valine into the Krebs Cycle - (Draw the Mechanism). How many rounds of Krebs will be required to waste all Carbons of Glutamic Acidas CO2?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





