
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin riboflavin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(a)
Answer to Problem 15.116EP
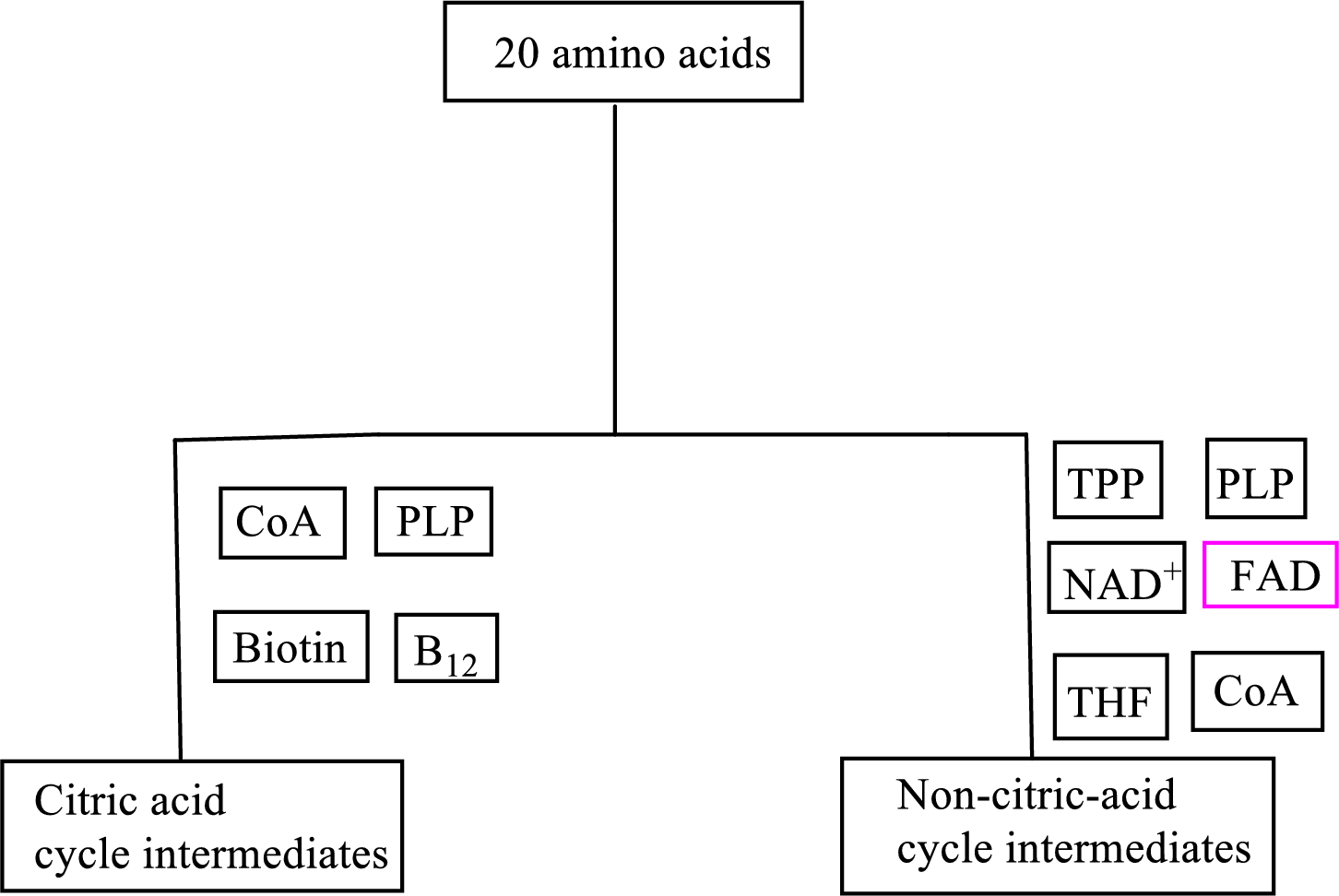
B vitamin riboflavin is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme flavin adenine dinucleotide
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
(b)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin thiamin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(b)
Answer to Problem 15.116EP
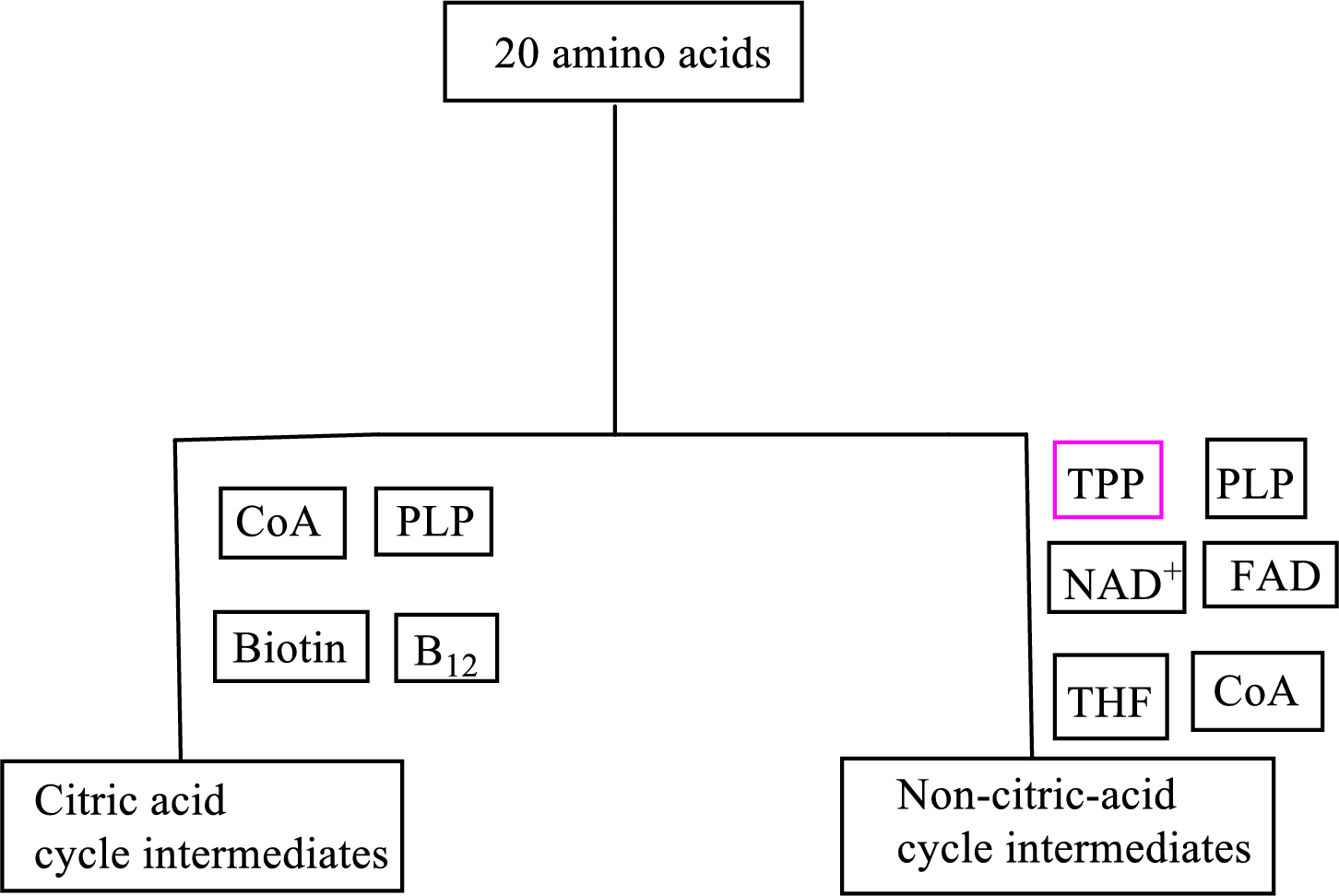
B vitamin thiamin is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme thiamin pyrophosphate
Thiamin pyrophosphate
(c)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin pantothenic is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(c)
Answer to Problem 15.116EP
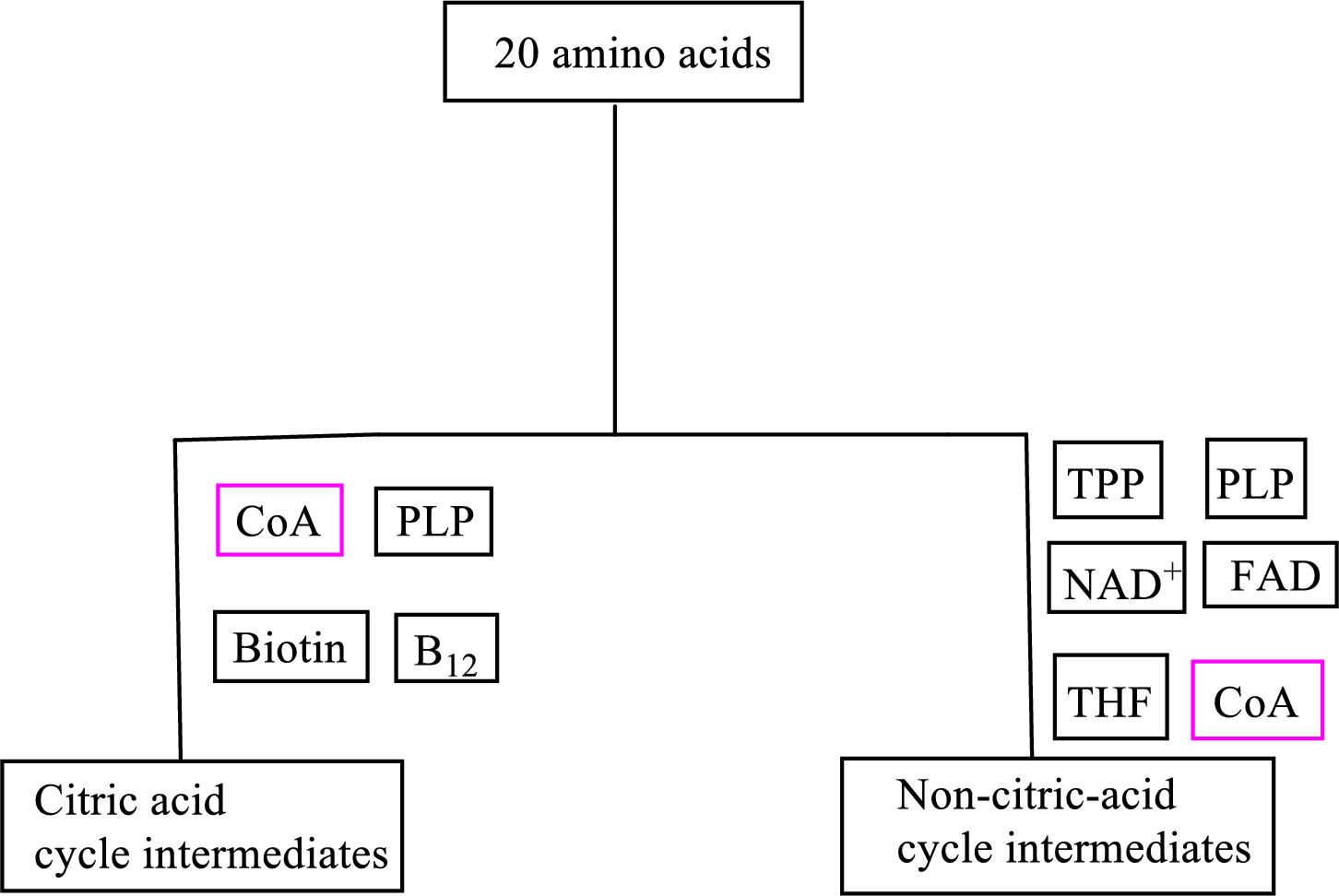
B vitamin pantothenic acid is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC and CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A
(d)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(d)
Answer to Problem 15.116EP
Explanation of Solution
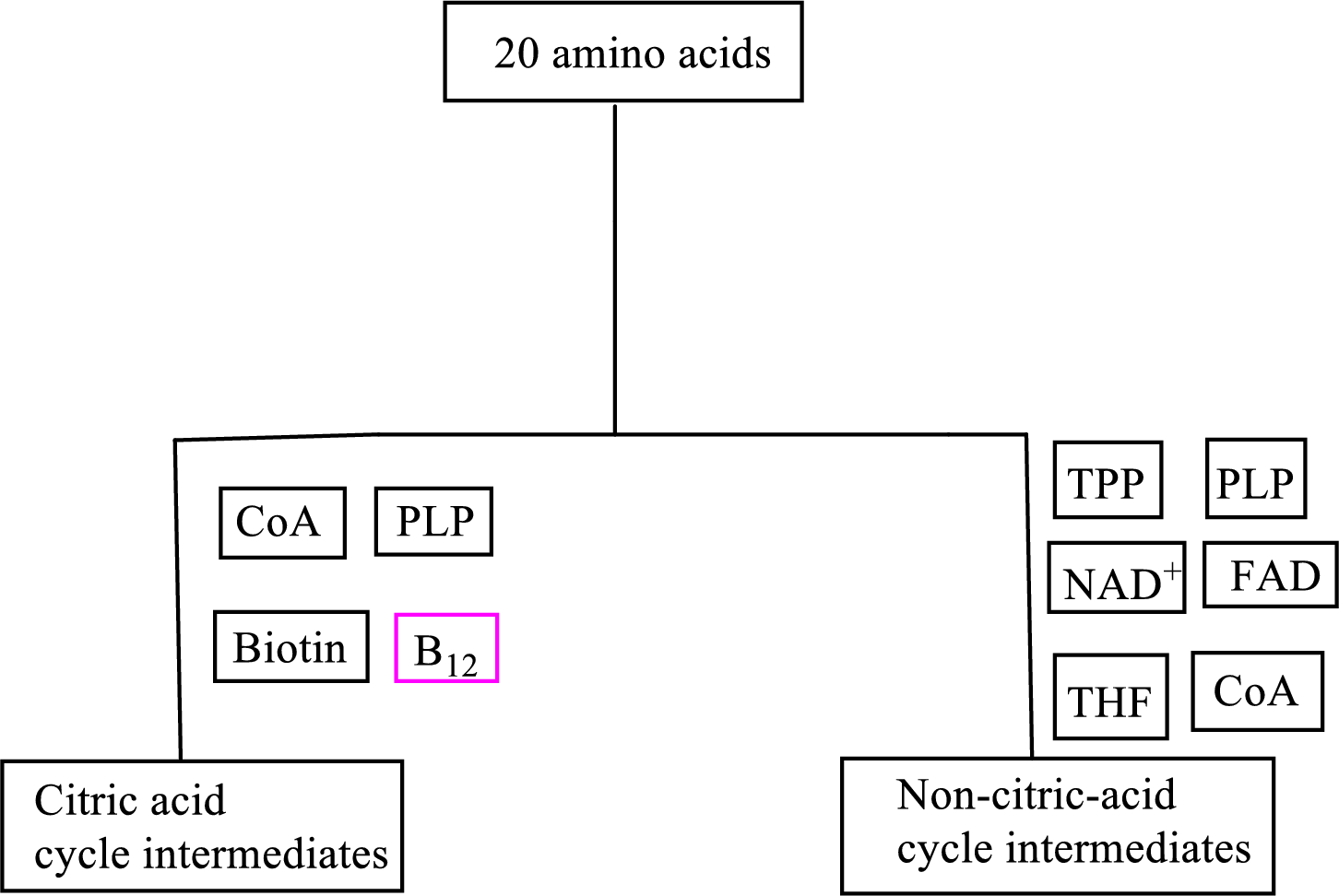
Coenzyme methylcobalamin contains the B vitamin
Coenzyme methylcobalamin is involved in the carbon skeleton degradation pathway to CAC intermediates.
An overview of the B vitamin participations in the degradation pathways for the carbon skeletons of the 20 standard amino acids is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward2,2-Dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Indicate the products obtained.arrow_forward
- Add conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformationADS fint anditions 百 Abl res condinese NC ง Add on condtions 1.0 B H,N.arrow_forward3. Provide all the steps and reagents for this synthesis. OHarrow_forwardSteps and explanationarrow_forward
- Steps and explanations please.arrow_forwardSteps on how to solve. Thank you!arrow_forward3. Name this ether correctly. H₁C H3C CH3 CH3 4. Show the best way to make the ether in #3 by a Williamson Ether Synthesis. Start from an alcohol or phenol. 5. Draw the structure of an example of a sulfide.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




