
Atmospheric air enters an air-conditioning system at 30°C and 70 percent relative humidity with a volume flow rate of 4 m3/min and is cooled to 20°C and 20 percent relative humidity at a pressure of 1 atm. The system uses refrigerant-134a as the cooling fluid that enters the cooling section at 350 kPa with a quality of 20 percent and leaves as a saturated vapor. Show the process on the psychrometric chart. What is the heat transfer from the air to the cooling coils, in kW? If any water is condensed from the air, how much water will be condensed from the atmospheric air per min? Determine the mass flow rate of the refrigerant, in kg/min.
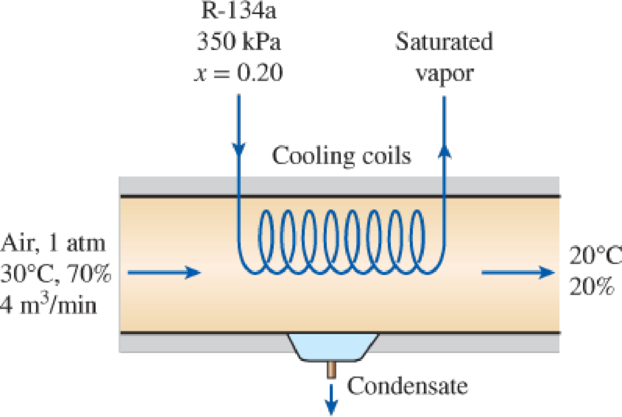
FIGURE P14–132
Show the process on the psychrometric chart; find the heat transfer from the air to the cooling coils, how much water will be condensed from the atmospheric air per min and the mass flow rate of the refrigerant.
Answer to Problem 132RP
The process on the psychrometric chart is shown below in Figure (1), the heat transfer from the air to the cooling coils is
Explanation of Solution
As the process is a steady flow and thus the mass flow rate of dry air remains constant during the entire process.
Here, the mass flow rate of air at inlet is
Express the mass flow rate of dry air.
Here, volume flow rate at inlet is
Express the mass flow rate of vapor at inlet.
Here, specific humidity at state 1 is
Express the mass flow rate of vapor at exit.
Here, specific humidity at state 2 is
Express the rate of condensation of water.
Express the enthalpy of condensate water.
Here, enthalpy of saturation liquid at temperature of
Express the rate required heat transfer rate from the atmospheric air to the evaporator fluid from an energy balance on the control volume.
Here, enthalpy at state 1 and 2 is
Express enthalpy of refrigerant at inlet.
Here, quality of refrigerant at inlet is
Express enthalpy of refrigerant at exit.
Here, quality of refrigerant at exit is
Express the mass flow rate of the refrigerant.
Here, enthalpy of refrigerant at inlet and exit is
Conclusion:
Show the psychrometric diagram as in Figure (1).
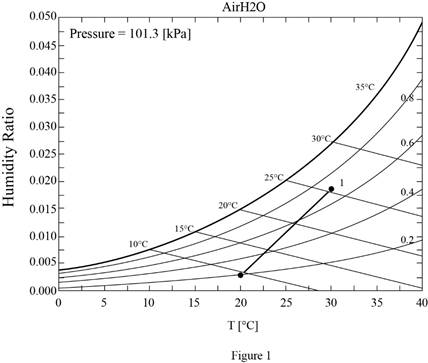
Hence, the psychrometric diagram is shown in Figure (1).
Refer Figure A-31, “psychometric chart at
Refer Figure A-31, “psychometric chart at
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the amount of water condensed from the atmospheric air per min is
Refer Table A-4, “saturated water-temperature table”, and write the enthalpy of condensate water at temperature of
Here, enthalpy of saturation liquid is
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the heat transfer from the air to the cooling coils is
Refer Table A-12, saturated refrigerant-134a-presure table”, and write enthalpy of saturation liquid at pressure of
Write the formula of interpolation method of two variables.
Here, the variables denote by x and y pressure and enthalpy of saturation liquid respectively.
Show the enthalpy of saturation liquid corresponding to pressure as in Table (1).
|
Pressure |
Enthalpy of saturation liquid |
| 320 | 55.14 |
| 350 | |
| 360 | 59.70 |
Substitute
Thus, the enthalpy of saturation liquid at pressure of
Refer Table A-12, saturated refrigerant-134a-presure table”, and write enthalpy of saturation vapor at pressure of
Show the enthalpy of saturation vapor corresponding to pressure as in Table (2).
|
Pressure |
Enthalpy of saturation liquid |
| 320 | 251.93 |
| 350 | |
| 360 | 253.86 |
Use excels and tabulates the values form Table (2) in Equation (X) to get,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the mass flow rate of the refrigerant is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach ( 9th International Edition ) ISBN:9781260092684
- Question 1. A tube rotates in the horizontal ry plane with a constant angular velocity w about the z-axis. A particle of mass m is released from a radial distance R when the tube is in the position shown. This problem is based on problem 3.2 in the text. R m 2R Figure 1 x a) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the tube is frictionless. b) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the coefficient of friction between the sides of the tube and the particle is = k = p. c) For the case where the tube is frictionless, what is the radial speed at which the particle leaves the tube? d) For the case where there is friction, derive a differential equation that would allow you to solve for the radius of the particle as a function of time. I'm only looking for the differential equation. DO NOT solve it. 1 e) If there is no friction, what is the angle of the tube when the particle exits? • Hint: You may need to solve a differential equation for the last part. The "potentially useful…arrow_forwardQuestion 2. A smooth uniform sphere of mass m and radius r is squeezed between two massless levers, each of length 1, which are inclined at an angle with the vertical. A mechanism at pivot point O ensures that the angles & remain the same at all times so that the sphere moves straight upward. This problem is based on Problem 3-1 in the text. P P r Figure 2 a) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is no friction. b) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is a coefficient of friction between the sphere and the right lever of μ. c) If a force P is applied between the ends of the levers (shown in the diagram), and there is no friction, what is the acceleration of the sphere when = 30°arrow_forwardIf you had a matrix A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] and a matrix B = [1 2 3], how would you cross multiply them i.e. what is the cross product of AxB. what would be the cross product of a dyadic with a vector?arrow_forward
- Problem 3: The inertia matrix can be written in dyadic form which is particularly useful when inertia information is required in various vector bases. On the next page is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. (a) Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q, i.e., 7%, for unit vectors ₁₁, 2, 3.arrow_forwardCan you solve for v? Also, what is A x uarrow_forwardThe external loads on the element shown below at the free end are F = 1.75 kN, P = 9.0 kN, and T = 72 Nm. The tube's outer diameter is 50 mm and the inner diameter is 45 mm. Given: A(the cross-sectional area) is 3.73 cm², Moment inertial I is 10.55 cm4, and J polar moment inertial is 21.1 cm4. Determine the following. (1) The critical element(s) of the bar. (2) Show the state of stress on a stress element for each critical element. -120 mm- Farrow_forward
- A crate weighs 530 lb and is hung by three ropes attached to a steel ring at A such that the top surface is parallel to the xy plane. Point A is located at a height of h = 42 in above the top of the crate directly over the geometric center of the top surface. Use the dimensions given in the table below to determine the tension in each of the three ropes. 2013 Michael Swanbom ↑ Z C BY NC SA b x B у D Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 30 in b 43 in с 4.5 in The tension in rope AB is lb The tension in rope AC is lb The tension in rope AD is lbarrow_forwardThe airplane weighs 144100 lbs and flies at constant speed and trajectory given by 0 on the figure. The plane experiences a drag force of 73620 lbs. a.) If = 11.3°, determine the thrust and lift forces required to maintain this speed and trajectory. b.) Next consider the case where is unknown, but it is known that the lift force is equal to 7.8 times the quantity (Fthrust Fdrag). Compute the resulting trajectory angle - and the lift force in this case. Use the same values for the weight and drag forces as you used for part a. Уллу Fdrag 10. Ө Fthrust cc 10 2013 Michael Swanbom BY NC SA Flift Fweight The lift force acts in the y' direction. The weight acts in the negative y direction. The thrust and drag forces act in the positive and negative x' directions respectively. Part (a) The thrust force is equal to lbs. The lift force is equal to Part (b) The trajectory angle is equal to deg. The lift force is equal to lbs. lbs.arrow_forwardThe hoist consists of a single rope and an arrangement of frictionless pulleys as shown. If the angle 0 = 59°, determine the force that must be applied to the rope, Frope, to lift a load of 4.4 kN. The three-pulley and hook assembly at the center of the system has a mass of 22.5 kg with a center of mass that lies on the line of action of the force applied to the hook. e ΘΕ B CC 10 BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Fhook Note the figure may not be to scale. Frope = KN HO Fropearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





