
(a)
Interpretation:
The following
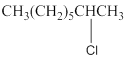
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms.
The compounds in which hydrogen atoms of an
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to one other carbon atom is known as primary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms is known as secondary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms is known as tertiary (
(b)
Interpretation:
The following alkyl halide should be classified as
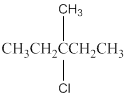
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
The compounds in which hydrogen atoms of an alkane is replaced by halogen is known as alkyl halide.
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to one other carbon atom is known as primary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms is known as secondary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms is known as tertiary (
(c)
Interpretation:
The following alkyl halide should be classified as
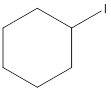
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
The compounds in which hydrogen atoms of an alkane is replaced by halogen is known as alkyl halide.
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to one other carbon atom is known as primary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms is known as secondary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms is known as tertiary (
(d)
Interpretation:
The following alkyl halide should be classified as
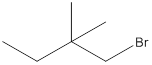
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
The compounds in which hydrogen atoms of an alkane is replaced by halogen is known as alkyl halide.
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to one other carbon atom is known as primary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms is known as secondary (
When the halogen is present on the carbon atom and that carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms is known as tertiary (
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- 7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forwardIndicate the compound formula: dimethyl iodide (propyl) sulfonium.arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning

