
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780078028229
Author: Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.4, Problem 4PP
Find the input impedance of the circuit in Fig. 13.25 and the current from the voltage source.
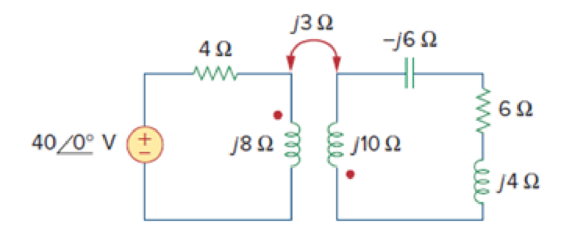
Figure 13.25
For Practice Prob. 13.4.
Answer: 8.58∠58.05° Ω, 4.662∠− 58.05° A.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve problems 5.2 in detail and thank you
5.1 Determine the three zone settings for the relay Rab in the system shown in Figure 5.26. The
system nominal voltage is 138 kV, and the positive sequence impedances for the various
elements are given in the figure. The transformer impedance is given in ohms as viewed
from the 138 kV side. Assume that the maximum load at the relay site is 120 MVA, and
select a CT ratio accordingly. The available distance relay has zone 1 and zone 2 settings
from 0.2 to 10 2, and zone 3 settings from 0.5 to 40 2, in increments of 0.1 2. The angle
of maximum torque can be adjusted to 75° or 80°. Remember that the zone 3 of the relay
must back up the line BC, as well as the transformer.
A
Rab
(3+j40)
B
(2+ j50)
(0+j9)
с
Fu
D
Figure 5.26 System for problem 5.1
Please solve question 4.7 in detail and thank you
Chapter 13 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Ch. 13.2 - Determine the voltage Vo in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 13.2 - Determine the phasor currents I1 and I2 in the...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 3PPCh. 13.4 - Find the input impedance of the circuit in Fig....Ch. 13.4 - For the linear transformer in Fig. 13.26(a), find...Ch. 13.4 - Solve the problem in Example 13.1 (see Fig. 13.9)...Ch. 13.5 - The primary current to an ideal transformer rated...Ch. 13.5 - In the ideal transformer circuit of Fig. 13.38,...Ch. 13.5 - Find Vo in the circuit of Fig. 13.40. Figure 13.40...Ch. 13.6 - Refer to Fig. 13.43. If the two-winding...
Ch. 13.6 - In the autotransformer circuit of Fig. 13.45, find...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 12PPCh. 13.8 - Prob. 13PPCh. 13.9 - Refer to Fig. 13.61. Calculate the turns ratio...Ch. 13.9 - Calculate the turns ratio of an ideal transformer...Ch. 13.9 - In Example 13.17, if the eight 100-W bulbs are...Ch. 13 - Refer to the two magnetically coupled coils of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 2RQCh. 13 - Prob. 3RQCh. 13 - Prob. 4RQCh. 13 - The ideal transformer in Fig. 13.70(a) has N2/N1 =...Ch. 13 - Prob. 6RQCh. 13 - A three-winding transformer is connected as...Ch. 13 - Prob. 8RQCh. 13 - Prob. 9RQCh. 13 - Prob. 10RQCh. 13 - For the three coupled coils in Fig. 13.72,...Ch. 13 - Using Fig. 13.73, design a problem to help other...Ch. 13 - Two coils connected in series-aiding fashion have...Ch. 13 - (a) For the coupled coils in Fig. 13.74(a), show...Ch. 13 - Two coils are mutually coupled, with L1 = 50 mH,...Ch. 13 - Given the circuit shown in Fig. 13.75, determine...Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.76, find Vo. Figure...Ch. 13 - Find v(t) for the circuit in Fig. 13.77.Ch. 13 - Prob. 9PCh. 13 - Find vo in the circuit of Fig. 13.79. Figure 13.79...Ch. 13 - Use mesh analysis to find ix in Fig. 13.80, where...Ch. 13 - Determine the equivalent Leq in the circuit of...Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.82, determine the...Ch. 13 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent circuit for the...Ch. 13 - Find the Norton equivalent for the circuit in Fig....Ch. 13 - Obtain the Norton equivalent at terminals a-b of...Ch. 13 - In the circuit of Fig. 13.86, ZL is a 15-mH...Ch. 13 - Find the Thevenin equivalent to the left of the...Ch. 13 - Determine an equivalent T-section that can be used...Ch. 13 - Determine currents I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit...Ch. 13 - Prob. 21PCh. 13 - Find current Io in the circuit of Fig. 13.91.Ch. 13 - Let is = 5 cos (100t) A. Calculate the voltage...Ch. 13 - In the circuit of Fig. 13.93, (a) find the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 25PCh. 13 - Find Io in the circuit of Fig. 13.95. Switch the...Ch. 13 - Find the average power delivered to the 50-...Ch. 13 - In the circuit of Fig. 13.97, find the value of X...Ch. 13 - Prob. 29PCh. 13 - (a) Find the input impedance of the circuit in...Ch. 13 - Using Fig. 13.100, design a problem to help other...Ch. 13 - Two linear transformers are cascaded as shown in...Ch. 13 - Determine the input impedance of the air-core...Ch. 13 - Using Fig. 13.103, design a problem to help other...Ch. 13 - Find currents I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit of...Ch. 13 - As done in Fig. 13.33, obtain the relationships...Ch. 13 - A 2402,400-V rms step-up ideal transformer...Ch. 13 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 13 - A 1,200240-V rms transformer has impedance on the...Ch. 13 - The primary of an ideal transformer with a turns...Ch. 13 - Given I2 = 2 A, determine the value of Is in Fig....Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.107, determine the...Ch. 13 - Obtain V1 and V2 in the ideal transformer circuit...Ch. 13 - In the ideal transformer circuit of Fig. 13.109,...Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.110, find the value of...Ch. 13 - (a) Find I1 and I2 in the circuit of Fig. 13.111...Ch. 13 - Prob. 47PCh. 13 - Using Fig. 13.113, design a problem to help other...Ch. 13 - Find current ix in the ideal transformer circuit...Ch. 13 - Prob. 50PCh. 13 - Use the concept of reflected impedance to find the...Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.117, determine the...Ch. 13 - Refer to the network in Fig. 13.118. (a) Find n...Ch. 13 - A transformer is used to match an amplifier with...Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.120, calculate the...Ch. 13 - Find the power absorbed by the 100- resistor in...Ch. 13 - For the ideal transformer circuit of Fig. 13.122...Ch. 13 - Determine the average power absorbed by each...Ch. 13 - In the circuit of Fig. 13.124, let vs = 165...Ch. 13 - Refer to the circuit in Fig. 13.125 on the...Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.126, find Il, I2, and...Ch. 13 - For the network in Fig. 13.127, find: (a) the...Ch. 13 - Find the mesh currents in th circuit of Fig....Ch. 13 - For the circuit in Fig. 13.129. find the turns...Ch. 13 - Calculate the average power dissipated by the 20-...Ch. 13 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 13 - An autotransformer with a 40 percent tap is...Ch. 13 - In the ideal autotransformer of Fig. 13.131,...Ch. 13 - In the circuit of Fig. 13.131, N1 = 190 turns and...Ch. 13 - In the ideal transformer circuit shown in Fig....Ch. 13 - When individuals travel, their electrical...Ch. 13 - In order to meet an emergency, three single-phase...Ch. 13 - Figure 13.135 on the next page shows a three-phase...Ch. 13 - Consider the three-phase transformer shown in Fig....Ch. 13 - A balanced three-phase transformer bank with the...Ch. 13 - Using Fig. 13.138, design a problem to help other...Ch. 13 - The three-phase system of a town distributes power...Ch. 13 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to determine the mesh...Ch. 13 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to find I1, I2, and I3 in...Ch. 13 - Prob. 80PCh. 13 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to find I1, I2, and I3 in...Ch. 13 - A stereo amplifier circuit with ail output...Ch. 13 - A transformer having 2,400 turns on the primary...Ch. 13 - A radio receiver has an input resistance of 300 ....Ch. 13 - A step-down power transformer with a turns ratio...Ch. 13 - A 240120-V rms power transformer is rated at 10...Ch. 13 - A 4-kVA, 2,400240-V rms transformer has 250 turns...Ch. 13 - A 25,000240-V rms distribution transformer has a...Ch. 13 - A 4,800-V rms transmission line feeds a...Ch. 13 - A four-winding transformer (Fig. 13.146) is often...Ch. 13 - A 440/110-V ideal transformer can be connected to...Ch. 13 - Ten bulbs in parallel are supplied by a 7,200120-V...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve in detail to understandarrow_forwardE2.6 Consider the following neural network. Input Sat. Linear Layer Linear Layer purelin(Wa+b) Sketch the following responses (plot the indicated variable versus p for (-3arrow_forwardE2.3 Given a two-input neuron with the following weight matrix and input vector: w=[32] and p = [-5 7], we would like to have an output of 0.5. Do you suppose that there is a combination of bias and transfer function that might allow this? i. Is there a transfer function from Table 2.1 that will do the job if the bias is zero? ii. Is there a bias that will do the job if the linear transfer function is used? If yes, what is it? iii. Is there a bias that will do the job if a log-sigmoid transfer function is used? Again, if yes, what is it? iv. Is there a bias that will do the job if a symmetrical hard limit transfer function is used? Again, if yes, what is it?arrow_forwardE2.2 Consider a single-input neuron with a bias. We would like the output to be -1 for inputs less than 3 and +1 for inputs greater than or equal to 3. i. What kind of a transfer function is required? ii. What bias would you suggest? Is your bias in any way related to the input weight? If yes, how? iii. Summarize your network by naming the transfer function and stating the bias and the weight. Draw a diagram of the network.arrow_forwardE2.1 A single input neuron has a weight of 1.3 and a bias of 3.0. What possible kinds of transfer functions, from Table 2.1, could this neuron have, if its output is given below. In each case, give the value of the input that would produce these outputs. i. 1.6 ii. 1.0 iii. 0.9963 iv. -1.0arrow_forwardQ2. The slew rate of an amplifier can cause signal distortion at its output if wrongly chosen. State the criterion for selecting the slew rate of an amplifier to avoid signal distortion. A step signal of 5 mV is applied to an inverting amplifier shown in Figure 2, which has a slew rate of 0.05 V/us. Estimate the time required for the output voltage of the amplifier to reach within 10% of its final value. If the input to Figure 2 is a sinusoidal signal of 0.02 sin(2πft) V, determine the maximum frequency that can be applied to the circuit without causing signal distortion due to the limitation of its slew rate (0.05 V/µs). In order to minimise the output offset voltage of Figure 2, a compensating resistor should be added to Figure 2. Draw a modified circuit diagram that includes the compensating resistor. Determine the appropriate value for the compensating resistor. V₁ 2 ΚΩ 100 ΚΩ +arrow_forwardQ3) A single-phase semiconverter, shown in Fig.(3), is used to control the speed of small separately excited d.c. motor rated at 4.5 kW, 220V, 1500 rpm. The converter is connected to a single phase 230 V, 50 Hz supply. The armature resistance is Ra = 0.50 ohm and the armature circuit inductance is La 10 mH. The motor voltage constant is Ke D = 0.1 V/rpm. With the converter operates as a rectifier, the d.c. motor runs at 1200 rpm and carries an armature current of 16 A Assume that the motor current is continuous and ripple-free == (a) Draw and drive an equation for output voltage of semiconverter (b) The firing angle a. (c) The power delivered to the motor. (d) The supply power factor. R₂ FWD Thi Th₂ D. D FWD ep Fig.(3) Da ectearrow_forwardQ3) A single-phase semiconverter, shown in Fig.(3), is used to control the speed of small separately excited d.c. motor rated at 4.5 kW, 220V, 1500 rpm. The converter is connected to a single phase 230 V, 50 Hz supply. The armature resistance is Ra = 0.50 ohm and the armature circuit inductance is La = 10 mH. The motor voltage constant is Ke Q=0.1 V/rpm. With the converter operates as a rectifier, the d.c. motor runs at 1200 rpm and carries an armature current of 16 A Assume that the motor current is continuous and ripple-free (a) Draw and drive an equation for output voltage of semiconverter (b) The firing angle a. (c) The power delivered to the motor. (d) The supply power factor. R FWD Th₁ Th₂ D. D FWD ep Fig.(3) Da ectearrow_forwardE2.4 A two-layer neural network is to have four inputs and six outputs. The range of the outputs is to be continuous between 0 and 1. What can you tell about the network architecture? Specifically: i. How many neurons are required in each layer? ii. What are the dimensions of the first-layer and second-layer weight matrices? iii. What kinds of transfer functions can be used in each layer? iv. Are biases required in either layer?arrow_forwardE2.5 Consider the following neuron. Input General Neuron ΣΠ Sketch the neuron response (plot a versus p for -2arrow_forwardQ1. All transistors shown in Figure 1 are identical. They have the following properties: ẞ = 200, VT = 0.026 V and VBE = 0.7 V. In order to set the bias current of the differential amplifier to I = 1.8 mA (see Figure 1), determine the value of the resistor, R. Determine the DC output voltage at the output terminals V01 and V02. The input signal to the differential amplifier is given as (v1 - Viz) = 12 sin(wt) mV, determine the total output voltage at terminal vo1. Explain how to eliminate the DC voltage at the output terminal, V01. Sketch a circuit diagram that can fulfil this requirement. R +20 V 20 ΚΩ Vil V02 ના 50711 20 ΚΩ I = 1.8 mA Vizarrow_forwarda. An amplifier has a gain of 500. What is the dB gain? b. A three-stage amplifier system has dB gains of 15 dB, 32 dB, and 6 dB. What is the overall gain of the system in dB?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Lesson 2 - Source Transformations, Part 2 (Engineering Circuits); Author: Math and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7gno74RhVGQ;License: Standard Youtube License