
Concept explainers
Calculate the impedance
Answer to Problem 25P
The impedance
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 13.94 in the textbook for the circuit with coupled coils.
The coupling co-efficient is 0.5.
Calculation:
Consider the expression for the mutual inductance.
Substitute 0.5 for k, 1 H for
From Figure 13.94, the value of
Consider the expression for the inductive reactance.
Substitute 1 H for L and
Substitute 2 H for L and
Consider the expression for the capacitive reactance.
Substitute 0.5 F for C and
Modify the Figure 13.94 by transforming the time-domain circuit with coupled-coils to frequency domain of the circuit with coupled-coil. The frequency domain equivalent circuit is shown in Figure 1.
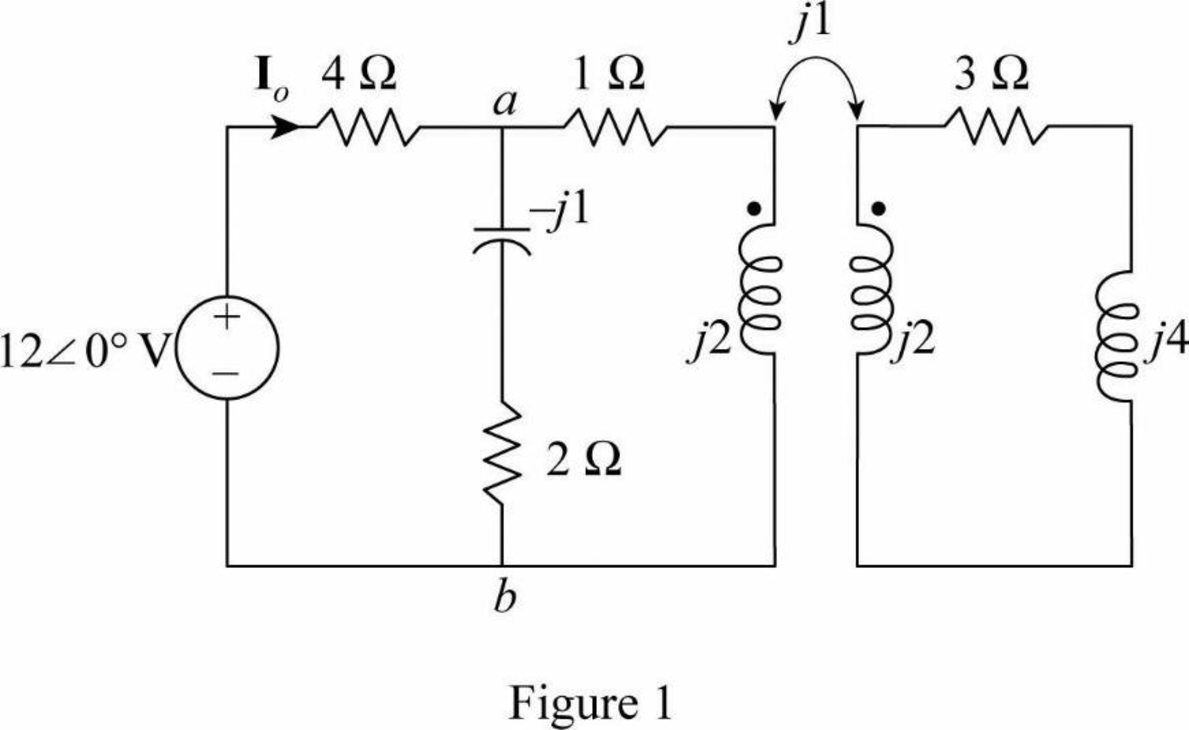
Write the expression for the impedance
Consider the expression for the reflected impedance
Substitute 2 for
Substitute
Simplify the Equation as follows.
Write the expression for the current
Substitute
The value of current
Convert the current from polar form to time domain form.
MATLAB code:
The MATLAB code using equations (3), (4) and (5) is,
M=0.5;
R2=3;
w=2;
L2=1;
ZL=4*j;
ZR=(w^2 * M^2)/(R2 + j*w*L2 + ZL);
Zab= (2-1*j)*(1+2*j+ZR)/(2-j+1+2*j+ZR)
Io=12/(Zab+4)
Then the MATLAB output is,
Zab = 1.4354 + 0.4639i
Io = 2.1918 - 0.1871i
Form the MATLAB output, impedance
Form the MATLAB output, current
The output is satisfied with analytical solution.
Conclusion:
Thus, the impedance
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
- 3) Find the valve of V using the Thevenin Equivalent Circuit and then determine if the 8 ohm resistor allows maximum power transfer. If not, then what value should the 8 ohm resist or be changed to for maximum power transfer? ZA 360 Am 6t + 22V V 3402 22 62 Mw marrow_forwardFind the valve of the voltage Vx using the THEVENIN 2) equivalent circuit and redo the problem with the NORTON equivalent circuit. Show both the flavinen and Norton Circuits DAY ww 1 23 www + 4444 5 63arrow_forwardFigure shows the block diagram of a feedback control system with a disturbance signal N(s). Obtain the output Y(s) due to both R(s) and N(s).arrow_forward
- A 3-phase, 6-pole induction motor is con- nected to a 60 Hz supply. The voltage in- duced in the rotor bars is 4 V when the ro- tor is locked. If the motor turns in the same direction as the flux, calculate the approxi- mate voltage induced and its frequency: a. At 300 r/min b. At 1000 r/min c. At 1500 r/minarrow_forwardMake a drawing of the magnetic field cre- ated by a 3-phase, 12-pole induction motor. How can we change the direction of rota- tion of a 3-phase induction motor?arrow_forwardDescribe the principle of operation of a lin- ear induction motor.arrow_forward
- Name the principal components of an in- duction motor. Explain how a revolving field is set up in a 3-phase induction motor.arrow_forwardAnswer all the questions (a) How much power is the wind farm generating? (b) How much power is the solar farm generating? (c) Find the power delivered to the AC motor. (d) If the AC motor requires at least 45 kW of power, is the system able to provide that power? If not, how many additional series PV modules should be added to each string (we want to keep the same number of modules in each string)? If so, how many modules can be removed from each string while still meeting the requirements?arrow_forwardAn open-circuit voltage of 240 V appears across the slip-rings of a wound-rotor in- duction motor when the rotor is locked. The stator has 6 poles and is excited by a 60 Hz source. If the rotor is driven by a variable-speed dc motor, calculate the open-circuit voltage and frequency across the slip-rings if the dc motor turns a. At 600 r/min, in the same direction as the rotating field b. At 900 r/min, in the same direction as the rotating field c. At 3600 r/min, opposite to the rotating fieldarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





