
Concept explainers
A spring-loaded piston–cylinder device contains a mixture of gases whose pressure fractions are 25 percent Ne, 50 percent O2, and 25 percent N2. The piston diameter and spring are selected for this device such that the volume is 0.1 m3 when the pressure is 200 kPa and 1.0 m3 when the pressure is 1000 kPa. Initially, the gas is added to this device until the pressure is 200 kPa and the temperature is 10°C. The device is now heated until the pressure is 500 kPa. Calculate the total work and heat transfer for this process.
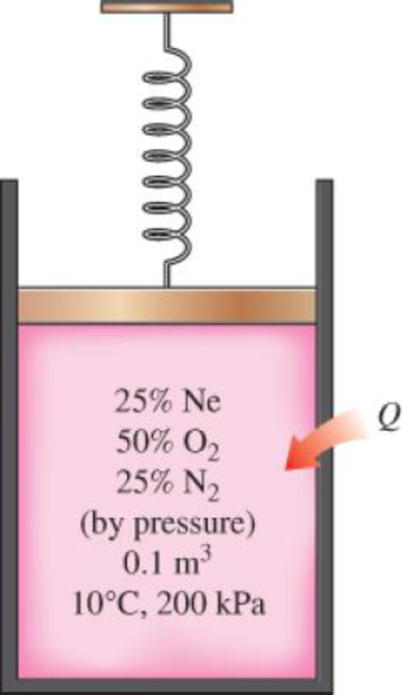
The total work done and heat transfer for the process.
Answer to Problem 94RP
The total work done for the process is
The heat transfer for the process is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the partial pressure of
Here, mixture pressure is
Write the expression to calculate the partial pressure of
Here, mixture pressure is
Write the expression to calculate the partial pressure of
Here, mixture pressure is
Write the expression to calculate the mass of
Write the expression to calculate the mass of
Write the expression to calculate the mass of
Write the expression to calculate the total mass of each component
Write the expression to calculate the mass fraction of
Write the expression to calculate the mass fraction of
Write the expression to calculate the mass fraction of
Write the expression to calculate the mole number of
Here, molar mass of
Write the expression to calculate the mole number of
Here, molar mass of
Write the expression to calculate the mole number of
Here, molar mass of
Write the expression to calculate the total number of moles
Write the expression to calculate the apparent molecular weight of the mixture
Write the expression to calculate the constant volume specific heat of the mixture
Here, mole fraction of
Write the expression to calculate the apparent gas constant of the mixture
Here, universal gas constant is
Write the expression for the mass contained in the system
Write the expression to calculate the final temperature
Write the expression to calculate the work done during the process.
Conclusion:
From Table A-1, “Molar mass, gas constant, and critical point properties”, obtain the values of molar masses for
From Table A-2a, “Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases”, obtain the following properties for
For
For
For
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The pressure changes linearly with volume as shown is Figure (1).
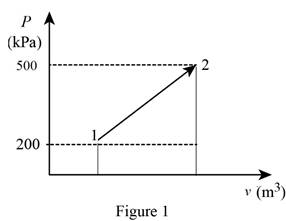
Using the data form Prob. 13–94 obtain the value of final volume by linear interpolation.
Write the straight line equation for two points.
Here, coordinates of the point 1 is
Substitute
The final volume
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the total work done for the process is
Write a energy balance on the system.
Here, input energy transfer and output energy transfer is
The rate of change in energy of a system
For given system the energy balance Equation (XXII) is expressed as follows:
The rate of change in energy of a system
Substitute
Thus, the heat transfer for the process is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS (LL)-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
- The Mach number NM for flow of a perfect gas in a pipe depends upon the specific-heat ratio k (dimensionless), the pressure p, the density ρ, and the velocity V. Obtain by dimensional reasoning the form of the Mach number expression. (Buckingham pi)Answer: NM = f(V/sqrt(p/ρ), k)arrow_forwardoyfr 3. The figure shows a frame under the influence of an external loading made up of five forces and two moments. Use the scalar method to calculate moments. a. Write the resultant force of the external loading in Cartesian vector form. b. Determine the & direction of the resultant moment of the external loading about A. 15 cm 18 cm 2.2 N-m B 50 N 45° 10 cm 48 N.m 250 N 60 N 20 21 50 N 25 cm 100 N A 118, 27cm 5, 4:1arrow_forwardAssume the Link AO is the input and revolves 360°, determine a. the coordinates of limit positions of point B, b. the angles (AOC) corresponding to the limit positionsarrow_forward
- oyfr 3. The figure shows a frame under the influence of an external loading made up of five forces and two moments. Use the scalar method to calculate moments. a. Write the resultant force of the external loading in Cartesian vector form. b. Determine the & direction of the resultant moment of the external loading about A. 15 cm 18 cm 2.2 N-m B 50 N 45° 10 cm 48 N.m 250 N 60 N 20 21 50 N 25 cm 100 N A 118, 27cm 5, 4:1arrow_forwardThe 2-mass system shown below depicts a disk which rotates about its center and has rotational moment of inertia Jo and radius r. The angular displacement of the disk is given by 0. The spring with constant k₂ is attached to the disk at a distance from the center. The mass m has linear displacement & and is subject to an external force u. When the system is at equilibrium, the spring forces due to k₁ and k₂ are zero. Neglect gravity and aerodynamic drag in this problem. You may assume the small angle approximation which implies (i) that the springs and dampers remain in their horizontal / vertical configurations and (ii) that the linear displacement d of a point on the edge of the disk can be approximated by d≈re. Ө K2 www m 4 Cz 777777 Jo Make the following assumptions when analyzing the forces and torques: тв 2 0>0, 0>0, x> > 0, >0 Derive the differential equations of motion for this dynamic system. Start by sketching LARGE and carefully drawn free-body-diagrams for the disk and the…arrow_forwardA linear system is one that satisfies the principle of superposition. In other words, if an input u₁ yields the output y₁, and an input u2 yields the output y2, the system is said to be linear if a com- bination of the inputs u = u₁ + u2 yield the sum of the outputs y = y1 + y2. Using this fact, determine the output y(t) of the following linear system: given the input: P(s) = = Y(s) U(s) = s+1 s+10 u(t) = e−2+ sin(t) =earrow_forward
- The manometer fluid in the figure given below is mercury where D = 3 in and h = 1 in. Estimate the volume flow in the tube (ft3/s) if the flowing fluid is gasoline at 20°C and 1 atm. The density of mercury and gasoline are 26.34 slug/ft3 and 1.32 slug/ft3 respectively. The gravitational force is 32.2 ft/s2.arrow_forwardUsing the Bernoulli equation to find the general solution. If an initial condition is given, find the particular solution. y' + xy = xy¯¹, y(0) = 3arrow_forwardTest for exactness. If exact, solve. If not, use an integrating factor as given or obtained by inspection or by the theorems in the text. a. 2xydx+x²dy = 0 b. (x2+y2)dx-2xydy = 0 c. 6xydx+5(y + x2)dy = 0arrow_forward
- Newton's law of cooling. A thermometer, reading 5°C, is brought into a room whose temperature is 22°C. One minute later the thermometer reading is 12°C. How long does it take until the reading is practically 22°C, say, 21.9°C?arrow_forwardSolve a. y' + 2xy = ex-x² b. y' + y sin x = ecosx, y(0) = −1 y(0) = −2.5arrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 3.pdf 2/6 90% + + 5. The boat is traveling along the circular path with a speed of v = (0.0625t²) m/s, where t is in seconds. Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when t = 10 s. 40 m v = 0.0625² 6. If the motorcycle has a deceleration of at = (0.001s) m/s² and its speed at position A is 25 m/s, determine the magnitude of its acceleration when it passes point B. .A 90° 300 m n B 2arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





