
Concept explainers
a.
To determine which among the twelve basic functions does not have the property
The basic functions that do not process the property that
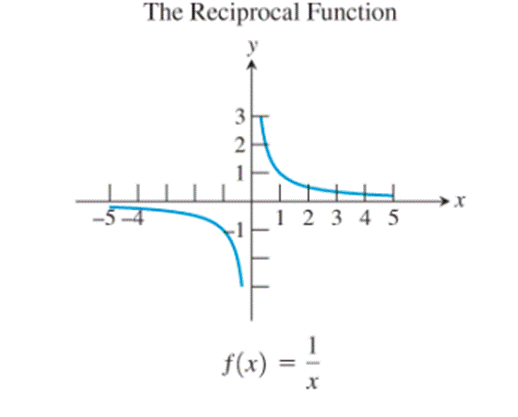
- The reciprocal function,
- The exponential function,
- The natural logarithm function,
- The cosine function
- The logistic function
Concept Used:
The twelve basic functions:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
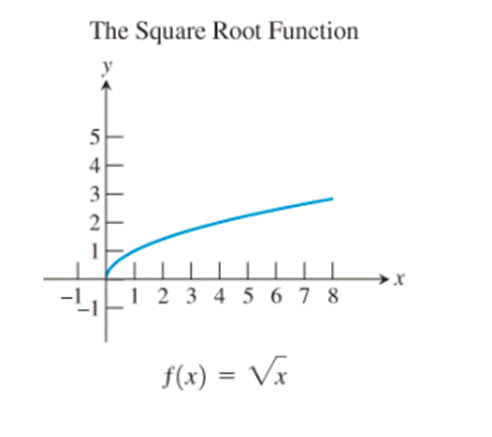
6)
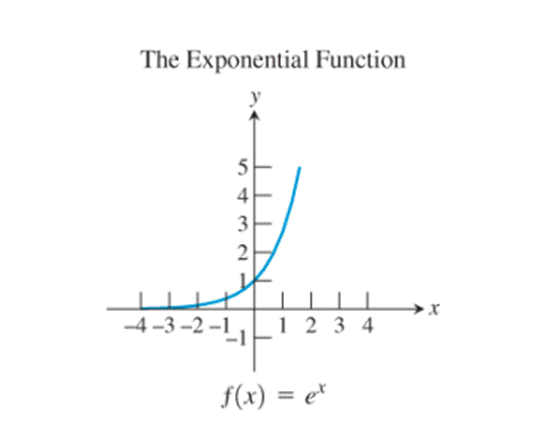
7)
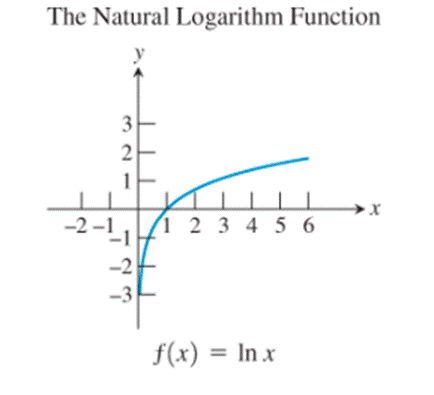
8)
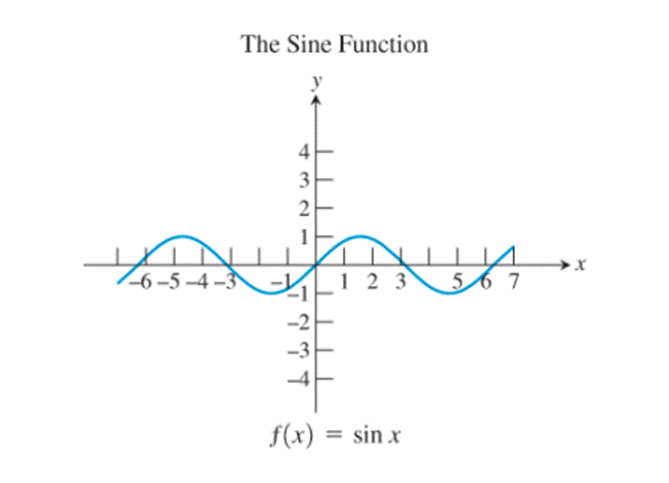
9)
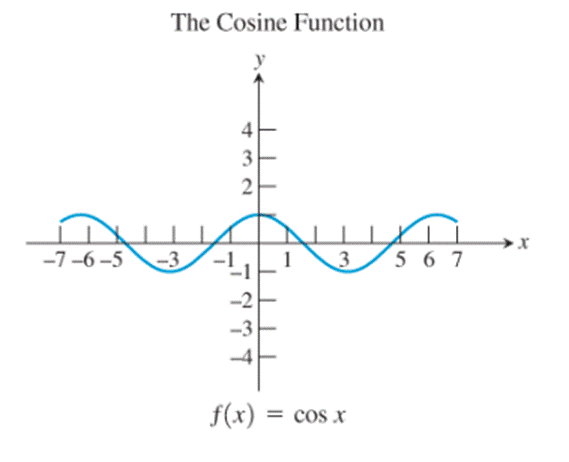
10)
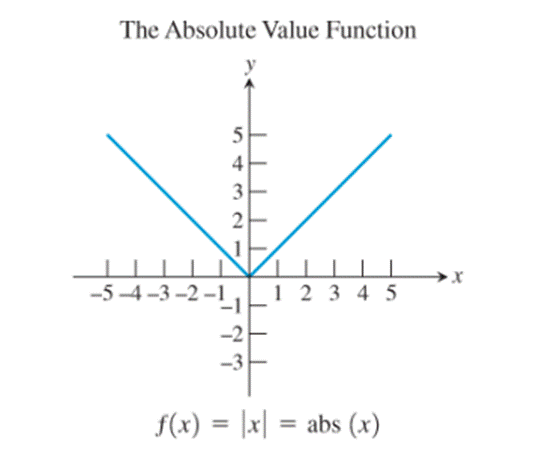
11)
12)
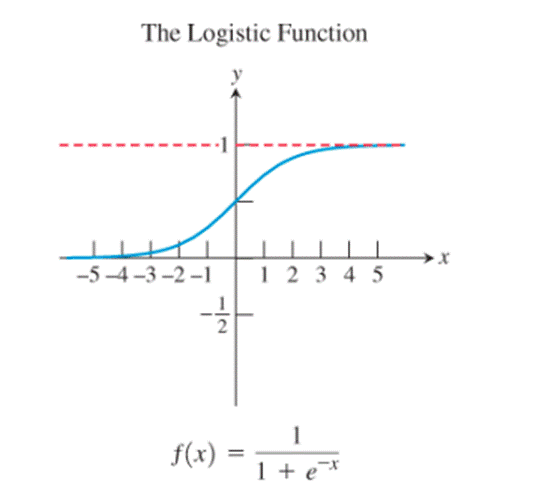
Calculation:
Any function
Now, observe the graphs of the basic functions:
The graphs of the reciprocal function, the exponential function, the natural logarithm function, the cosine function and the logistic function seem to be not passing through the origin.
Thus, the basic functions that do not process the property that
- The reciprocal function,
- The exponential function,
- The natural logarithm function,
- The cosine function
- The logistic function
Conclusion:
The basic functions that do not possess the property that
- The reciprocal function,
- The exponential function,
- The natural logarithm function,
- The cosine function
- The logistic function
b.
To determine which one among the basic functions possesses the property that
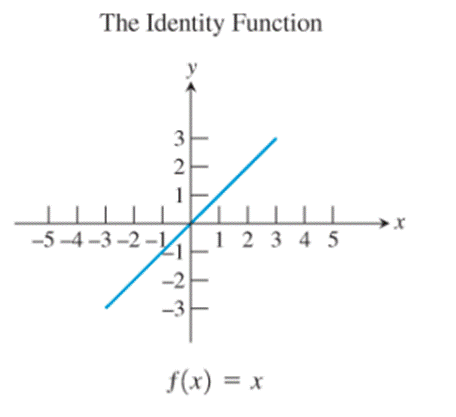
The identity function
Given:
It is given that only one basic function possesses the property that
Calculation:
Observe the identity function
Thus, the identity function possesses the property.
Since it is given that only one among the basic functions possesses this property, only the identity function possesses this property.
Conclusion:
The identity function
c.
To determine which one among the basic functions possesses the property that
The exponential function
Given:
It is given that only one basic function possesses the property that
Calculation:
Observe the exponential function
Thus, the exponential function possesses the property.
Since it is given that only one among the basic functions possesses this property, only the exponential function possesses this property.
Conclusion:
The exponential function
d.
To determine which one among the basic functions possesses the property that
The logarithmic function
Given:
It is given that only one basic function possesses the property that
Calculation:
Observe the logarithmic function
Thus, the logarithmic function possesses the property.
Since it is given that only one among the basic functions possesses this property, only the logarithmic function possesses this property.
Conclusion:
The logarithmic function
e.
To determine which four among the basic functions possess the property that
The basic functions possessing the property that
- The identity function
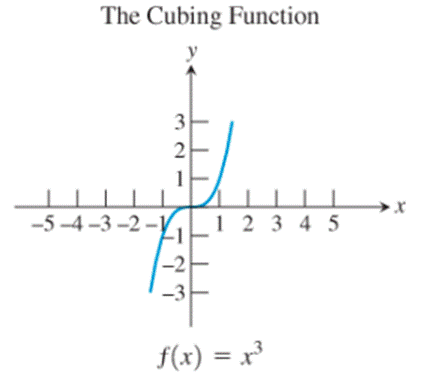
- The cubing function
- The reciprocal function
- The sine function
Given:
Given that four among the basic function possess the property that
Concept Used:
Any function showing the property that
Now, if a function is odd, its graph will be symmetrical about the origin.
Calculation:
Observe the graphs of the basic functions:
The identity function, the cubing function, the reciprocal function and the sine function are the only ones whose graphs are symmetric about the origin.
Thus, the basic functions possessing the property that
- The identity function
- The cubing function
- The reciprocal function
- The sine function
Conclusion:
The basic functions possessing the property that
- The identity function
- The cubing function
- The reciprocal function
- The sine function
Chapter 1 Solutions
Precalculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Common Core 10th Edition
- Use a graphing calculator to find where the curves intersect and to find the area between the curves. y=ex, y=-x²-4x a. The left point of intersection is (Type integers or decimals rounded to the nearest thousandth as needed. Type an ordered pair.)arrow_forwardFind the area between the curves. x= -5, x=3, y=2x² +9, y=0 The area between the curves is (Round to the nearest whole number as needed.)arrow_forwardcan you solve these questions with step by step with clear explaination pleasearrow_forward
- Find the area between the following curves. x=-1, x=3, y=x-1, and y=0 The area between the curves is (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardFind the area between the curves. x= − 2, x= 3, y=5x, y=x? - 6 6 The area between the curves is (Simplify your answer.) ...arrow_forwardplease question 9arrow_forward
- Use the definite integral to find the area between the x-axis and f(x) over the indicated interval. Check first to see if the graph crosses the x-axis in the given interval. 3. f(x) = 4x; [-5,3]arrow_forwardUse the definite integral to find the area between the x-axis and f(x) over the indicated interval. Check first to see if the graph crosses the x-axis in the given interval. f(x)=3e-4; [3,3]arrow_forwardA small company of science writers found that its rate of profit (in thousands of dollars) after t years of operation is given by P'(t) = (7t + 14) (t² + 4t+7) * (a) Find the total profit in the first four years. (b) Find the profit in the sixth year of operation. (c) What is happening to the annual profit over the long run?arrow_forward
- Calculus III May I have an expert explained how the terms were simplified into 6(3-x)^2? Thank you,arrow_forwardCalculus III May I have an expert explain how the integrand was simplified into the final for form to be integrated with respect to x? Thank you,arrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the semicolon statement in the box defined with explanation? Thank you,arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





