
Interpretation:
The reaction when hydrogen chloride reacts with 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene to form 1-chloro-3-methyl-2-butene as a major product via 1,4-addition mechanism and no product formed by 1,2-additon, is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
舧 Electrophiles are electron-deficient species, which has positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles, which accept electron pair.
舧 Nucleophiles are electron rich species, which has negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles, which donate electron pair.
舧 Free radical is an atom, molecule or ion that has an unpaired electron, which makes it highly chemically reactive.
舧 Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one of the hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon or a
舧 Elimination reaction: A reaction in which two substituent groups are detached and a double bond is formed is called elimination reaction.
舧 Addition reaction: It is the reaction in which unsaturated bonds are converted to saturated molecules by the addition of molecules.
舧 The reaction in which there is addition of hydrogen molecule is called hydrogenation reaction.
舧
舧 Hydrogenation with platinum as a catalyst is used to convert unsaturated carbohydrates to saturated hydrocarbons
舧 Oxidation of
舧 Ozonolysis helps convert the carbon–carbon double bonds to carbon–oxygen double bond (carbonyl compounds).
舧 Dimethyl sulfide is used as a reducing agent that decomposes the intermediate formed into the carbonyl group.
舧 NBS (nitro-bromo succinimide) is a special reagent used for bromination of allylic carbocations.
舧 Bromine replaces the hydrogen attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbon bearing double bond.
舧 This method of using NBS can produce allylic bromides without bromine reacting with the double bond.
舧 Dehydration of a primary alcohol in the presence of a mineral acid like concentrated sulfuric acid results in the formation of alkene via E2 elimination.
舧 The stability of carbocation:
舧 The 1,2 – addition to a diene is the addition of an electrophile to the carbon designated as 1 and a nucleophile to the carbon designated as 2. The positions of carbons as 1 and 2 are not according to the IUPAC numbering of the molecule, but as a conjugated diene molecule. 1,4-addition results in addition of hydrogen to thee carbon designated as 1 and a halogen to the carbon designated as 4.
舧 The mechanism of 1,2 addition and 1,4-addition of hydro halogenation is given below:
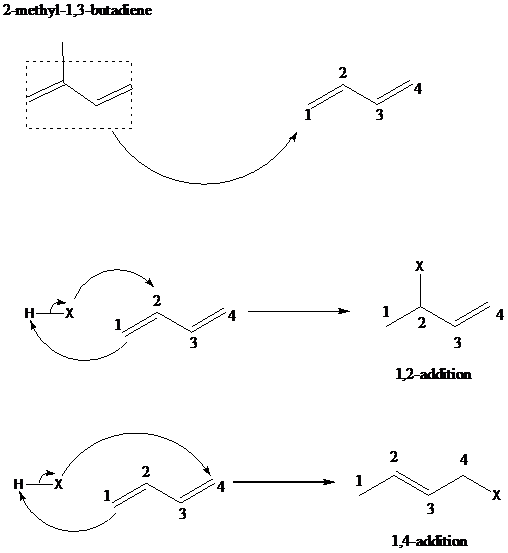
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





