
Interpretation: The product formed after reaction of cyclohexane in the presence of
Concept introduction:
Molecules that have one unpaired electron are called free radicals.
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:

Explanation of Solution
Given information:
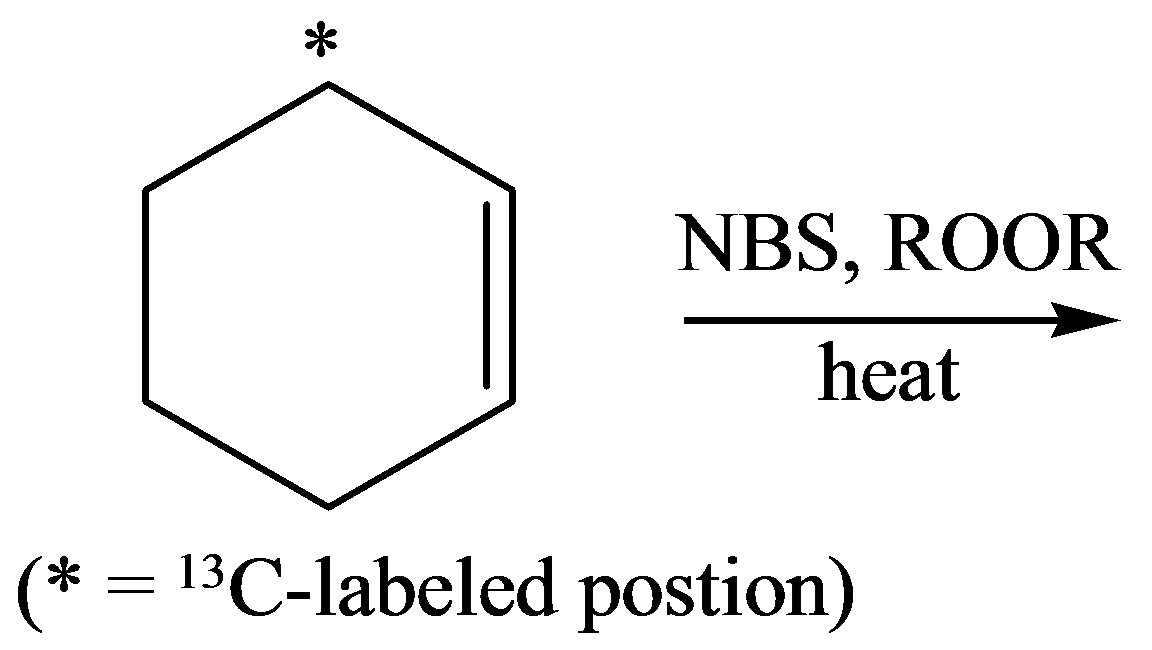
The reaction in the presence of
Allylic bromination is a free radical substitution reaction in which removal of hydrogen atom on carbon adjacent to a double bond with bromine.
Free radical substitution reaction takes place in the presence of
The structure of 3-bromocyclohexence is as follows:

The product formed after free radical substitution is 3-bromocyclohexence.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Phenol is the starting material for the synthesis of 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol, known al-ternatively as pentachlorophenol, or more simply as penta. At one time, penta was widely used as a wood preservative for decks, siding, and outdoor wood furniture. Draw the structural formula for pentachlorophenol and describe its synthesis from phenol.arrow_forward12 Mass Spectrometry (d) This unknown contains oxygen, but it does not show any significant infrared absorption peaks above 3000 cm . 59 100- BO 40 Relative Abundance M(102) - 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 5 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 mizarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H HO H HO H HO H H -OH CH2OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : Darrow_forward
- : Draw the structure of valylasparagine, a dipeptide made from valine and asparagine, as it would appear at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. P Darrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection of α-L-mannose. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS Data resource. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ཊི Х Darrow_forwardDraw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forward
- Take a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forward
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22.30 Predict all possible products formed from the following nucleophilic substitution reactions. (a) (b) 9 1. NaOH 2. HCI, H₂O CI NH₁(!) +NaNH, -33°C 1. NaOH 2. HCl, H₂Oarrow_forwardSyntheses 22.35 Show how to convert toluene to these compounds. (a) -CH,Br (b) Br- -CH3 22.36 Show how to prepare each compound from 1-phenyl-1-propanone. 1-Phenyl-1-propanone ہتی. Br. (b) Br (racemic) 22.37 Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid. 22.38 Show reagents and conditions to bring about the following conversions. (a) 9 NH2 8 CO₂H NH2 CO₂Et (d) NO2 NH2 S NH₂ NO2 CHS CHarrow_forwardive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all rant stereochemistry. [10 only] A. B. NaN3 1. LiAlH4, ether Br 2. H₂O CH3 HNO3 H₂/Pt H₂SO ethanol C. 0 0 CH3CC1 NaOH NHCCH AICI H₂O . NH₂ CH3CH2 N CH2CH3 + HCI CH₂CH 3 1. LIAIH, THE 2. H₂Oarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

