
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction between 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene and hydrogen bromide is to be determined. The reaction energy coordinate diagram that illustrates kinetic and thermodynamic pathways is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
舧 Electrophiles are electron-deficient species, which has positive or partially positive charge. Lewis acids are electrophiles, which accept electron pair.
舧 Nucleophiles are electron-rich species, which has negative or partially negative charge. Lewis bases are nucleophiles, which donate electron pair.
舧 Free radical is an atom, molecule, or ion that has an unpaired electron, which makes it highly chemically reactive.
舧 Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one of the hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon or a
舧 Elimination reaction: A reaction in which two substituent groups are detached and a double bond is formed is called elimination reaction.
舧 Addition reaction: It is the reaction in which unsaturated bonds are converted to saturated molecules by the addition of molecules.
舧 The reaction in which there is addition of hydrogen molecule is called hydrogenation reaction.
舧
舧 Hydrogenation with platinum as a catalyst is used to convert unsaturated carbohydrates to saturated hydrocarbons
舧 Oxidation of
舧 Ozonolysis helps convert the carbon – carbon double bonds to carbon – oxygen double bond (carbonyl compounds).
舧 Dimethyl sulfide is used as a reducing agent that decomposes the intermediate formed into the carbonyl group.
舧 NBS (nitro-bromo succinimide) is a special reagent used for bromination of allylic carbocations.
舧 Bromine replaces the hydrogen attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbon bearing double bond.
舧 This method of using NBS can produce allylic bromides without bromine reacting with the double bond.
舧 Dehydration of a primary alcohol in the presence of a mineral acid like concentrated sulfuric acid results in the formation of alkene via E2 elimination.
舧 1,2–addition of hydrohalogenation (HX) to a diene is the addition of hydrogen to the carbon designated as 1 and halogen to the carbon designated as 2. The positions of carbon as 1 and 2 are not according to the IUPAC numbering of the molecule, but as a conjugated diene. The mechanism is similar to 1,4-addition. The mechanism of 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition of hydrohalogenation is given below:
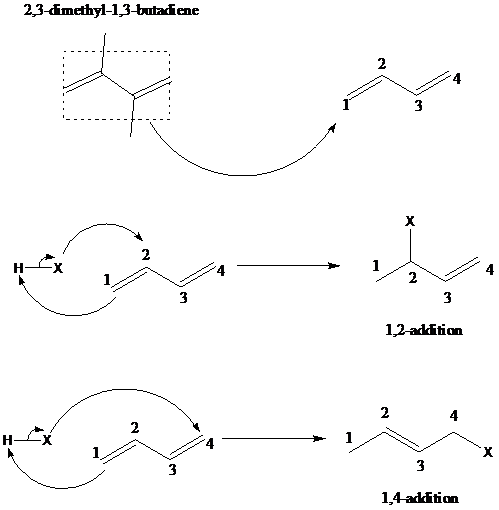
舧 When conjugated diene is attacked by an electrophile, the resultant products are formed via 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition reaction mechanism. Kinetics and
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- V Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


