
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260663778
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.1, Problem 12.5P
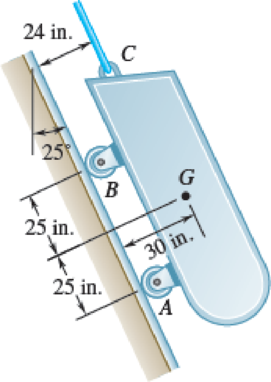
A loading car is at rest on a track forming an angle of 25° with the vertical when a force is applied to the cable attached at C. The gross weight of the car and its load is 5500 lb, and it acts at point G. Knowing the tension in the cable connected at C is 5000 lb, determine (a) the acceleration of the car, (b) the distance the car moves in 20 s, (c) the time it takes for the car to return to its original position if the cable breaks after 20 s.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful!
Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!
=
The frame shown is fitted with three 50 cm diameter
frictionless pulleys. A force of F = 630 N is applied to the
rope at an angle ◊ 43°. Member ABCD is attached to the
wall by a fixed support at A. Find the forces indicated below.
Note: The rope is tangent to the pully (D) and not secured at
the 3 o'clock position.
a
b
•C
*су
G
E
e
d
BY NC SA
2013 Michael Swanbom
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following
table. Note the figure may not be to scale.
Variable Value
a
81 cm
b
50 cm
с
59 cm
d
155 cm
For all answers, take x as positive to the right and
positive upward.
At point A, the fixed support exerts a force of:
A
=
+
ĴN
and a reaction couple of:
→>
ΜΑ
Member CG is in Select an answer
magnitude
У
as
k N-m.
and carries a force of
N.
The lower jaw AB [Purple 1] and the upper jaw-handle AD
[Yellow 2] exert vertical clamping forces on the object at R.
The hand squeezes the upper jaw-handle AD [2] and the
lower handle BC [Orane 4] with forces F. (Member CD [Red 3]
acts as if it is pinned at D, but, in a real vise-grips, its
position is actually adjustable.) The clamping force, R,
depends on the geometry and on the squeezing force F
applied to the handles. Determine the proportionality
between the clamping force, R, and the squeezing force F for
the dimensions given.
d3
d4
R
1
B
d1
2
d2
D...
d5
F
4
F
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following
table. Note the figure may not be to scale.
Variable
Value
d1
65 mm
d2
156 mm
d3
50 mm
45
d4
d5
113 mm
30 mm
R =
F
Chapter 12 Solutions
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
Ch. 12.1 - A 1000-lb boulder B is resting on a 200-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Marble A is placed in a hollow tube, and the tube...Ch. 12.1 - The two systems shown start from rest. On the...Ch. 12.1 - Blocks A and B are released from rest in the...Ch. 12.1 - People sit on a Ferris wheel at points A, B, C,...Ch. 12.1 - Crate A is gently placed with zero initial...Ch. 12.1 - Two blocks weighing WA and WB are at rest on a...Ch. 12.1 - Objects A, B, and C have masses mA, mB, and mC,...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4FBPCh. 12.1 - Blocks A and B have masses mA and mB,...
Ch. 12.1 - A pilot of mass m flies a jet in a half-vertical...Ch. 12.1 - Wires AC and BC are attached to a sphere that...Ch. 12.1 - A collar of mass m is attached to a spring and...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9FBPCh. 12.1 - At the instant shown, the length of the boom AB is...Ch. 12.1 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B has a mass m and slides along the slot in...Ch. 12.1 - The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 3.75...Ch. 12.1 - The value of g at any latitude may be obtained...Ch. 12.1 - A Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite is in...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4PCh. 12.1 - A loading car is at rest on a track forming an...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-oz model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that may...Ch. 12.1 - A tugboat pulls a small barge through a harbor....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9PCh. 12.1 - A 4-kg package is released from rest at point A...Ch. 12.1 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 12.1 - A light train made up of two cars is traveling at...Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.16PCh. 12.1 - A 5000-lb truck is being used to lift a 1000-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - The flat-bed trailer carries two 1500-kg beams...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12.1 - To unload a bound stack of plywood from a truck,...Ch. 12.1 - To transport a series of bundles of shingles A to...Ch. 12.1 - An airplane has a mass of 25 Mg and its engines...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that a...Ch. 12.1 - A constant force P is applied to a piston and rod...Ch. 12.1 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to a support...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 10 kg, and blocks B and C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.30PCh. 12.1 - A 10-lb block B rests as shown on a 20-lb bracket...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - The 30-lb block B is supported by the 55-lb block...Ch. 12.1 - Block B of mass 10 kg rests as shown on the upper...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that the swings of an amusement park ride...Ch. 12.1 - During a hammer throwers practice swings, the...Ch. 12.1 - Human centrifuges are often used to simulate...Ch. 12.1 - A single wire ACB passes through a ring at C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.41PCh. 12.1 - The 0.5-kg flyballs of a centrifugal governor...Ch. 12.1 - As part of an outdoor display, a 5-kg model C of...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12.1 - During a high-speed chase, a 2400-lb sports car...Ch. 12.1 - An airline pilot climbs to a new flight level...Ch. 12.1 - The roller-coaster track shown is contained in a...Ch. 12.1 - A spherical-cap governor is fixed to a vertical...Ch. 12.1 - A series of small packages, each with a mass of...Ch. 12.1 - A 55-kg pilot flies a jet trainer in a half...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.51PCh. 12.1 - A curve in a speed track has a radius of 1000 ft...Ch. 12.1 - Tilting trains, such as the Acela Express that...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.1 - A 3-kg block is at rest relative to a parabolic...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12.1 - A turntable A is built into a stage for use in a...Ch. 12.1 - The carnival ride from Prob. 12.51 is modified so...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.59PCh. 12.1 - A small 8-oz collar D can slide on portion AB of a...Ch. 12.1 - A small block B fits inside a slot cut in arm OA...Ch. 12.1 - The parallel-link mechanism ABCD is used to...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.63PCh. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - An advanced spatial disorientation trainer is...Ch. 12.1 - The 3-kg collar B slides on the frictionless arm...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-kg block B slides without friction inside a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B weighs 4 oz and is free to slide in a...Ch. 12.1 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to let...Ch. 12.1 - A 700-kg horse A lifts a 50-kg hay bale B as...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the mass of the earth knowing that the...Ch. 12.2 - Show that the radius r of the moons orbit can be...Ch. 12.2 - Communication satellites are placed in a...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.2 - The orbit of the planet Venus is nearly circular...Ch. 12.2 - A satellite is placed into a circular orbit about...Ch. 12.2 - The periodic time (see Prob. 12.83) of an earth...Ch. 12.2 - A 500-kg spacecraft first is placed into a...Ch. 12.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit of 2200-km...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.87PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.88PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.89PCh. 12.2 - A 1-kg collar can slide on a horizontal rod that...Ch. 12.2 - Two 2.6-lb collars A and B can slide without...Ch. 12.2 - A small ball swings in a horizontal circle at the...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass mC is being...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass m is being transported...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.94PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.95PCh. 12.3 - A particle with a mass m describes the path...Ch. 12.3 - A particle of mass m describes the parabola y =...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.99PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.100PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.101PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.103PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.104PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.105PCh. 12.3 - Halleys comet travels in an elongated elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.109PCh. 12.3 - A space probe is to be placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 12.3 - The Clementine spacecraft described an elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - A space probe is describing a circular orbit of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.115PCh. 12.3 - A space shuttle is describing a circular orbit at...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.117PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.119PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.120PCh. 12.3 - Show that the angular momentum per unit mass h of...Ch. 12 - In the braking test of a sports car, its velocity...Ch. 12 - A bucket is attached to a rope of length L = 1.2 m...Ch. 12 - A 500-lb crate B is suspended from a cable...Ch. 12 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to pull...Ch. 12 - A robot arm moves in the vertical plane so that...Ch. 12 - Telemetry technology is used to quantify kinematic...Ch. 12 - The radius of the orbit of a moon of a given...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.131RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.132RPCh. 12 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The following C++ program will not compile because the lines have been mixed up. cout Success\n; cout Success...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
The job of the _____ is to fetch instructions, carry out the operations commanded by the instructions, and prod...
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A triangular distributed load of max intensity w =460 N/m acts on beam AB. The beam is supported by a pin at A and member CD, which is connected by pins at C and D respectively. Determine the reaction forces at A and C. Enter your answers in Cartesian components. Assume the masses of both beam AB and member CD are negligible. cc 040 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl W A C D -a- B Ул -b- x Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value α 5.4 m b 8.64 m C 3.24 m The reaction at A is A = i+ ĴN. λ = i+ Ĵ N. The reaction at C is C =arrow_forward56 Clamps like the one shown are commonly used in woodworking applications. This clamp has the dimensions given in the table below the figure, and its jaws are mm thick (in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the picture). a.) The screws of the clamp are adjusted so that there is a uniform pressure of P = 150 kPa being applied to the workpieces by the jaws. Determine the force carried in each screw. Hint: the uniform pressure can be modeled in 2-D as a uniform distributed load with intensity w = Pt (units of N/m) acting over the length of contact between the jaw and the workpiece. b.) Determine the minimum vertical force (parallel to the jaws) required to pull either one of the workpieces out of the clamp jaws. Use a coefficient of static friction between all contacting surfaces of μs = 0.56 and the same clamping pressure given for part (a). 2013 Michael Swanbom A B C a Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale.…arrow_forwardDetermine the force in each member of the space truss given F=5 kN. Use positive to indicate tension and negative to indicate compression. F E Z -2 m. B 3 m C 5 m 3 m A -4 m. AB = KN FAC = FAD = KN KN KN FBC = KN FBD FBE = = KN Farrow_forward
- A short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method. (Answer: (a) 45.7C, (b)45.3C, (c)87.2 kJ)arrow_forwardA short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method.arrow_forwardA 6 cm high rectangular ice block (k=2.22 W/mK, and alpha=0.124*10^-7 m^2/s) initially at -18 degrees C is placed on a table on its square base 4 cm by 4cm in size in a room at 18 degrees C. The heat transfer coefficent on the exposed surfaces of the ice block is 12 W/m^2K. Disregarding any heat transfer from the base to the table, determine how long it will be before the ice block starts melting. Where on the ice block will the first liquid droplets appear? Solve this problem using the analytical one-term approximation method.arrow_forward
- Consider a piece of steel undergoing a decarburization process at 925 degrees C. the mass diffusivity of carbon in steel at 925 degrees C is 1*10^-7 cm^2/s. Determine the depth below the surface of the steel at which the concentration of carbon is reduced to 40 percent from its initial value as a result of the decarburization process for (a) an hour and (b) 10 hours. Assume the concnetration of carbon at the surface is zero throughout the decarburization process.arrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forwardMultiple Choice Circle the best answer to each statement. 1. Which geometry attribute deviation(s) can be limited with a profile of a surface tolerance? A. Location B. Orientation C. Form D. All of the above 2. A true profile may be defined with: A. Basic radii B. Basic angles C. Formulas D. All of the above 3. Which modifier may be applied to the profile tolerance value? A B C. D. All of the above 4. The default tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Non-uniform B. Unilateral C. Bilateral equal distribution D. Bilateral-unequal distribution 5. An advantage of using a profile tolerance in place of a coordinate tolerance is: A. A bonus tolerance is permitted. B. A datum feature sequence may be specified C. A profile tolerance always controls size D. All of the above 6. The shape of the tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Two parallel planes B. The same as the true profile of the toleranced surface C. Equal bilateral D. Cylindrical when the diameter symbol is speci- fied…arrow_forward
- One thousand kg/h of a (50-50 wt%) acetone-in-water solution is to be extracted at 25C in a continuous, countercurrent system with pure 1,1,2-trichloroethane to obtain a raffinate containing 10 wt% acetone. Using the following equilibrium data, determine with an equilateral-triangle diagram: a- the minimum flow rate of solvent; b- the number of stages required for a solvent rate equal to 1.5 times minimum, and composition of each streamleaving each stage. c- Repeat the calculation of (a) and (b) if the solvent used has purity 93wt% (4wr% acetone, 3wt% water impurities) acetone water 1,1,2-trichloroethane Raffinate. Weight Extract. Weight 0.6 0.13 0.27 Fraction Acetone Fraction Acetone 0.5 0.04 0.46 0.44 0.56 0.4 0.03 0.57 0.29 0.40 0.3 0.02 0.68 0.12 0.18 0.2 0.015 0.785 0.0 0.0 0.1 0.01 0.89 0.55 0.35 0.1 0.5 0.43 0.07 0.4 0.57 0.03 0.3 0.68 0.02 0.2 0.79 0.01 0.1 0.895 0.005arrow_forward2500 kg/hr of (20-80) nicotine water solution is to be extracted with benzene containing 0.5% nicotine in the 1st and 2ed stages while the 3rd stage is free of nicotine. Cross- current operation is used with different amounts of solvent for each stages 2000kg/hr in the 1st stage, 2300 kg/hr in the 2nd stage, 2600 kg/hr in the 3rd, determine: - a- The final raffinate concentration and % extraction. b- b- The minimum amount of solvent required for counter-current operation if the minimum concentration will be reduced to 5% in the outlet raffinate. Equilibrium data Wt % Nicotine in water Wt % Nicotine in benzene 0 4 16 25 0 4 21 30arrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1=6mm, for w2 h2 5mm, and for w3 is h3 -5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). 140 101.15 REDMI NOTE 8 PRO AI QUAD CAMERA Farrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY