
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260663778
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.1, Problem 12.10P
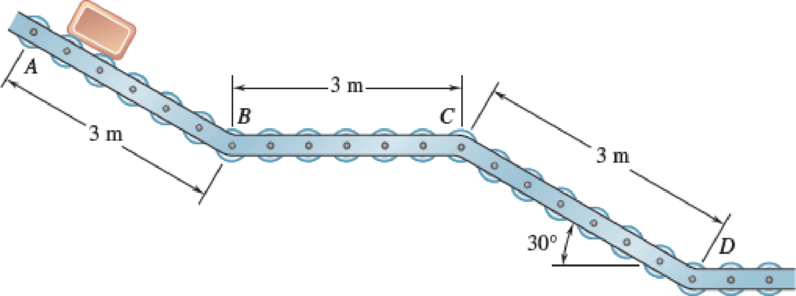
A 4-kg package is released from rest at point A and travels down the conveyor shown. Portions AB and CD are parallel to each other. Neglecting friction and any other energy loss, determine (a) the acceleration of the package at A, (b) the acceleration of the package during the horizontal portion of the track, (c) the speed of the package at point D.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
It is decided to install several single-jet Pelton wheels to produce a total power of 18 MW. The
available head is 246 m. The wheel rotational speed is 650 rpm and the speed ratio (❤) = 0.46.
The diameter of the nozzle (jet) is limited to be 0.167 m with a Cv of 0.95. The efficiency of each
turbine is 87%. Determine: (1) The number of Pelton wheels to be used, and (2) The bucket
angle.
Please show All work and fill it in thermodynamics
Quick solution required.
My request, Don't use Ai.
Mechanical engineering
Chapter 12 Solutions
VECTOR MECH. FOR EGR: STATS & DYNAM (LL
Ch. 12.1 - A 1000-lb boulder B is resting on a 200-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Marble A is placed in a hollow tube, and the tube...Ch. 12.1 - The two systems shown start from rest. On the...Ch. 12.1 - Blocks A and B are released from rest in the...Ch. 12.1 - People sit on a Ferris wheel at points A, B, C,...Ch. 12.1 - Crate A is gently placed with zero initial...Ch. 12.1 - Two blocks weighing WA and WB are at rest on a...Ch. 12.1 - Objects A, B, and C have masses mA, mB, and mC,...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4FBPCh. 12.1 - Blocks A and B have masses mA and mB,...
Ch. 12.1 - A pilot of mass m flies a jet in a half-vertical...Ch. 12.1 - Wires AC and BC are attached to a sphere that...Ch. 12.1 - A collar of mass m is attached to a spring and...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9FBPCh. 12.1 - At the instant shown, the length of the boom AB is...Ch. 12.1 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B has a mass m and slides along the slot in...Ch. 12.1 - The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 3.75...Ch. 12.1 - The value of g at any latitude may be obtained...Ch. 12.1 - A Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite is in...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4PCh. 12.1 - A loading car is at rest on a track forming an...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-oz model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that may...Ch. 12.1 - A tugboat pulls a small barge through a harbor....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9PCh. 12.1 - A 4-kg package is released from rest at point A...Ch. 12.1 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 12.1 - A light train made up of two cars is traveling at...Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.16PCh. 12.1 - A 5000-lb truck is being used to lift a 1000-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - The flat-bed trailer carries two 1500-kg beams...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12.1 - To unload a bound stack of plywood from a truck,...Ch. 12.1 - To transport a series of bundles of shingles A to...Ch. 12.1 - An airplane has a mass of 25 Mg and its engines...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that a...Ch. 12.1 - A constant force P is applied to a piston and rod...Ch. 12.1 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to a support...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 10 kg, and blocks B and C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.30PCh. 12.1 - A 10-lb block B rests as shown on a 20-lb bracket...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - The 30-lb block B is supported by the 55-lb block...Ch. 12.1 - Block B of mass 10 kg rests as shown on the upper...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that the swings of an amusement park ride...Ch. 12.1 - During a hammer throwers practice swings, the...Ch. 12.1 - Human centrifuges are often used to simulate...Ch. 12.1 - A single wire ACB passes through a ring at C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.41PCh. 12.1 - The 0.5-kg flyballs of a centrifugal governor...Ch. 12.1 - As part of an outdoor display, a 5-kg model C of...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12.1 - During a high-speed chase, a 2400-lb sports car...Ch. 12.1 - An airline pilot climbs to a new flight level...Ch. 12.1 - The roller-coaster track shown is contained in a...Ch. 12.1 - A spherical-cap governor is fixed to a vertical...Ch. 12.1 - A series of small packages, each with a mass of...Ch. 12.1 - A 55-kg pilot flies a jet trainer in a half...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.51PCh. 12.1 - A curve in a speed track has a radius of 1000 ft...Ch. 12.1 - Tilting trains, such as the Acela Express that...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.1 - A 3-kg block is at rest relative to a parabolic...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12.1 - A turntable A is built into a stage for use in a...Ch. 12.1 - The carnival ride from Prob. 12.51 is modified so...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.59PCh. 12.1 - A small 8-oz collar D can slide on portion AB of a...Ch. 12.1 - A small block B fits inside a slot cut in arm OA...Ch. 12.1 - The parallel-link mechanism ABCD is used to...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.63PCh. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - An advanced spatial disorientation trainer is...Ch. 12.1 - The 3-kg collar B slides on the frictionless arm...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-kg block B slides without friction inside a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B weighs 4 oz and is free to slide in a...Ch. 12.1 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to let...Ch. 12.1 - A 700-kg horse A lifts a 50-kg hay bale B as...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the mass of the earth knowing that the...Ch. 12.2 - Show that the radius r of the moons orbit can be...Ch. 12.2 - Communication satellites are placed in a...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.2 - The orbit of the planet Venus is nearly circular...Ch. 12.2 - A satellite is placed into a circular orbit about...Ch. 12.2 - The periodic time (see Prob. 12.83) of an earth...Ch. 12.2 - A 500-kg spacecraft first is placed into a...Ch. 12.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit of 2200-km...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.87PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.88PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.89PCh. 12.2 - A 1-kg collar can slide on a horizontal rod that...Ch. 12.2 - Two 2.6-lb collars A and B can slide without...Ch. 12.2 - A small ball swings in a horizontal circle at the...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass mC is being...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass m is being transported...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.94PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.95PCh. 12.3 - A particle with a mass m describes the path...Ch. 12.3 - A particle of mass m describes the parabola y =...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.99PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.100PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.101PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.103PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.104PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.105PCh. 12.3 - Halleys comet travels in an elongated elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.109PCh. 12.3 - A space probe is to be placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 12.3 - The Clementine spacecraft described an elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - A space probe is describing a circular orbit of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.115PCh. 12.3 - A space shuttle is describing a circular orbit at...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.117PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.119PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.120PCh. 12.3 - Show that the angular momentum per unit mass h of...Ch. 12 - In the braking test of a sports car, its velocity...Ch. 12 - A bucket is attached to a rope of length L = 1.2 m...Ch. 12 - A 500-lb crate B is suspended from a cable...Ch. 12 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to pull...Ch. 12 - A robot arm moves in the vertical plane so that...Ch. 12 - Telemetry technology is used to quantify kinematic...Ch. 12 - The radius of the orbit of a moon of a given...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.131RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.132RPCh. 12 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please give handwritten solution, don't use chatgpt. Fbd should be includedarrow_forward(I) [40 Points] Using centered finite difference approximations as done in class, solve the equation for O: d20 dx² + 0.010+ Q=0 subject to the boundary conditions shown in the stencil below. Do this for two values of Q: (a) Q = 0.3, and (b) Q= √(0.5 + 2x)e-sinx (cos(5x)+x-0.5√1.006-x| + e −43*|1+.001+x* | * sin (1.5 − x) + (cosx+0.001 + ex-1250+ sin (1-0.9x)|) * x - 4.68x4. For Case (a) (that is, Q = 0.3), use the stencil in Fig. 1. For Case (b), calculate with both the stencils in Fig. 1 and Fig 2. For all the three cases, show a table as well as a plot of O versus x. Discuss your results. Use MATLAB and hand in the MATLAB codes. 1 0=0 x=0 2 3 4 0=1 x=1 Fig 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0=0 x=0 0=1 x=1 Fig 2arrow_forwardFig 2 (II) [60 Points] Using centered finite difference approximation as done in class, solve the equation: 020 020 + მx2 მy2 +0.0150+Q=0 subject to the boundary conditions shown in the stencils below. Do this for two values of Q: (a) Q = 0.3, and (b) Q = 10.5x² + 1.26 * 1.5 x 0.002 0.008. For Case (a) (that is, Q = 0.3) use Fig 3. For Case (b), use both Fig. 3 and Fig 4. For all the three cases, show a table as well as the contour plots of versus (x, y), and the (x, y) heat flux values at all the nodes on the boundaries x = 1 and y = 1. Discuss your results. Use MATLAB and hand in the MATLAB codes. (Note that the domain is (x, y)e[0,1] x [0,1].) 0=0 0=0 4 8 12 16 10 Ꮎ0 15 25 9 14 19 24 3 11 15 0=0 8-0 0=0 3 8 13 18 23 2 6 сл 5 0=0 10 14 6 12 17 22 1 6 11 16 21 13 e=0 Fig 3 Fig 4 Textbook: Numerical Methods for Engineers, Steven C. Chapra and Raymond P. Canale, McGraw-Hill, Eighth Edition (2021).arrow_forward
- Ship construction question. Sketch and describe the forward arrangements of a ship. Include componets of the structure and a explanation of each part/ term. Ive attached a general fore end arrangement. Simplfy construction and give a brief describion of the terms.arrow_forwardProblem 1 Consider R has a functional relationship with variables in the form R = K xq xx using show that n ✓ - (OR 1.) = i=1 2 Их Ux2 Ихэ 2 (177)² = ² (1)² + b² (12)² + c² (1)² 2 UR R x2 x3arrow_forward4. Figure 3 shows a crank loaded by a force F = 1000 N and Mx = 40 Nm. a. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to force F. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. b. Draw a free-body diagram of arm 2 showing the values of all forces, moments, and torques that act due to moment Mr. Label the directions of the coordinate axes on this diagram. Draw a free body diagram of the wall plane showing all the forces, torques, and moments acting there. d. Locate a stress element on the top surface of the shaft at A and calculate all the stress components that act upon this element. e. Determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stresses at this point at A.arrow_forward
- 3. Given a heat treated 6061 aluminum, solid, elliptical column with 200 mm length, 200 N concentric load, and a safety factor of 1.2, design a suitable column if its boundary conditions are fixed-free and the ratio of major to minor axis is 2.5:1. (Use AISC recommended values and round the ellipse dimensions so that both axes are whole millimeters in the correct 2.5:1 ratio.)arrow_forward1. A simply supported shaft is shown in Figure 1 with w₁ = 25 N/cm and M = 20 N cm. Use singularity functions to determine the reactions at the supports. Assume El = 1000 kN cm². Wo M 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 cm Figure 1 - Problem 1arrow_forwardPlease AnswerSteam enters a nozzle at 400°C and 800 kPa with a velocity of 10 m/s and leaves at 375°C and 400 kPa while losing heat at a rate of 26.5 kW. For an inlet area of 800 cm2, determine the velocity and the volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit. Use steam tables. The velocity of the steam at the nozzle exit is m/s. The volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit is m3/s.arrow_forward
- 2. A support hook was formed from a rectangular bar. Find the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at sections just above and just below O-B. -210 mm 120 mm 160 mm 400 N B thickness 8 mm = Figure 2 - Problem 2arrow_forwardSteam flows steadily through a turbine at a rate of 45,000 lbm/h, entering at 1000 psia and 900°F and leaving at 5 psia as saturated vapor. If the power generated by the turbine is 4.1 MW, determine the rate of heat loss from the steam. The enthalpies are h1 = 1448.6 Btu/lbm and h2 = 1130.7 Btu/lbm. The rate of heat loss from the steam is Btu/s.arrow_forwardThe A/D converter wit the specifications listed below is planned to be used in an environment in which the A/D converter temperature may change by ± 10 °C. Estimate the contributions of conversion and quantization errors to the uncertainty in the digital representation of an analog voltage by the converter. FSO N Linearity error Temperature drift error Analog to Digital (A/D) Converter 0-10 V 12 bits ± 3 bits 1 bit/5 °Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanical Design (Machine Design) Clutches, Brakes and Flywheels Intro (S20 ME470 Class 15); Author: Professor Ted Diehl;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eMvbePrsT34;License: Standard Youtube License