
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.1, Problem 12.39P
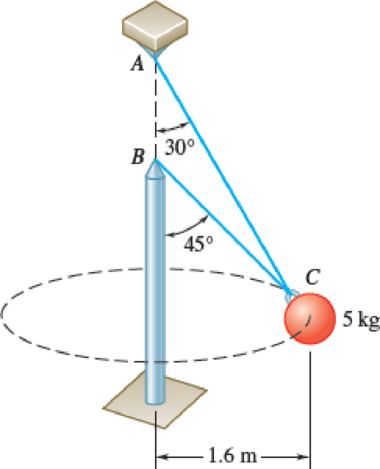
A single wire ACB passes through a ring at C attached to a sphere which revolves at a constant speed v in the horizontal circle shown. Knowing that the tension is the same in both portions of the wire, determine the speed v.
Fig. P12.39 and P12.40
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Mueh
Battery operated train
Coll
160,000kg 0.0005 0.15 5m² 1.2kg/m³
CD
Af Pair
19
пре neng
0.98 0.9
0.88
Tesla Prated
Tesla Trated "wheel ng
Joxle
270 kW
440NM
0,45m 20
8.5kg m2
the middle
Consider a drive cycle of a 500km trip with 3 stops in
Other than the acceleration and deceleration
associated with the three stops, the tran maintains
constat cruise speed velocity of 324 km/hr. The
tran will fast charge at each stop for 15 min at a
rate Peharge = 350 kW
ΟΙ
15MIN
Stop
w charging
(350kW)
(ผม
τ
(AN
GMIJ
t
6M
1) HOW MUCH DISTANCE dace is covered DURING THE
ACCELERATION TO 324 km/hr?
2)
DETERMINE HOW LONG (IN seconds) the tran will
BE TRAVELING AT FULL SPEED
2
?
3) CALCULATE THE NET ENERGY GAW PER STOP
ete
Please stop screenshoting ai solution,it always in accurate solve normal
Research and select any different values for the Ratio of connecting rod length to crank radius from various engine models, then analyze how these changes affect instantaneous velocity and acceleration, presenting your findings visually using graphs.
Chapter 12 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 12.1 - A 1000-lb boulder B is resting on a 200-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Marble A is placed in a hollow tube, and the tube...Ch. 12.1 - The two systems shown start from rest. On the...Ch. 12.1 - Blocks A and B are released from rest in the...Ch. 12.1 - People sit on a Ferris wheel at points A, B, C,...Ch. 12.1 - Crate A is gently placed with zero initial...Ch. 12.1 - Two blocks weighing WA and WB are at rest on a...Ch. 12.1 - Objects A, B, and C have masses mA, mB, and mC,...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4FBPCh. 12.1 - Blocks A and B have masses mA and mB,...
Ch. 12.1 - A pilot of mass m flies a jet in a half-vertical...Ch. 12.1 - Wires AC and BC are attached to a sphere that...Ch. 12.1 - A collar of mass m is attached to a spring and...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9FBPCh. 12.1 - At the instant shown, the length of the boom AB is...Ch. 12.1 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B has a mass m and slides along the slot in...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.1PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.2PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.3PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.5PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.6PCh. 12.1 - A tugboat pulls a small barge through a harbor....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.8PCh. 12.1 - 12.9 If an automobile’s braking distance from 90...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.10PCh. 12.1 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 12.1 - A light train made up of two cars is traveling at...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.13PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.14PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.16PCh. 12.1 - A 5000-lb truck is being used to lift a 1000-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - The flat-bed trailer carries two 1500-kg beams...Ch. 12.1 - 12.21 A baggage conveyor is used to unload luggage...Ch. 12.1 - To unload a bound stack of plywood from a truck,...Ch. 12.1 - To transport a series of bundles of shingles A to...Ch. 12.1 - An airplane has a mass of 25 Mg and its engines...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.25PCh. 12.1 - A constant force P is applied to a piston and rod...Ch. 12.1 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to a support...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 10 kg, and blocks B and C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.30PCh. 12.1 - A 10-lb block B rests as shown on a 20-lb bracket...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.34PCh. 12.1 - Block B of mass 10 kg rests as shown on the upper...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.36PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.37PCh. 12.1 - Human centrifuges are often used to simulate...Ch. 12.1 - A single wire ACB passes through a ring at C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.41PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.42PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.43PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12.1 - During a high-speed chase, a 2400-lb sports car...Ch. 12.1 - An airline pilot climbs to a new flight level...Ch. 12.1 - The roller-coaster track shown is contained in a...Ch. 12.1 - A spherical-cap governor is fixed to a vertical...Ch. 12.1 - A series of small packages, each with a mass of...Ch. 12.1 - 12.50 A 54-kg pilot flies a jet trainer in a...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.51PCh. 12.1 - A curve in a speed track has a radius of 1000 ft...Ch. 12.1 - Tilting trains, such as the Acela Express that...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.1 - A 3-kg block is at rest relative to a parabolic...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12.1 - A turntable A is built into a stage for use in a...Ch. 12.1 - The carnival ride from Prob. 12.51 is modified so...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.59PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.60PCh. 12.1 - A small block B fits inside a slot cut in arm OA...Ch. 12.1 - The parallel-link mechanism ABCD is used to...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.63PCh. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - An advanced spatial disorientation trainer is...Ch. 12.1 - The 3-kg collar B slides on the frictionless arm...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-kg block B slides without friction inside a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B weighs 4 oz and is free to slide in a...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.71PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.72PCh. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the mass of the earth knowing that the...Ch. 12.2 - Show that the radius r of the moons orbit can be...Ch. 12.2 - Communication satellites are placed in a...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.2 - The orbit of the planet Venus is nearly circular...Ch. 12.2 - A satellite is placed into a circular orbit about...Ch. 12.2 - The periodic time (see Prob. 12.83) of an earth...Ch. 12.2 - A 500-kg spacecraft first is placed into a...Ch. 12.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit of 2200-km...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.87PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.88PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.89PCh. 12.2 - A 1-kg collar can slide on a horizontal rod that...Ch. 12.2 - Two 2.6-lb collars A and B can slide without...Ch. 12.2 - A small ball swings in a horizontal circle at the...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass mC is being...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass m is being transported...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.94PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.95PCh. 12.3 - A particle with a mass m describes the path...Ch. 12.3 - A particle of mass m describes the parabola y =...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.99PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.100PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.101PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.103PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.104PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.105PCh. 12.3 - Halleys comet travels in an elongated elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.109PCh. 12.3 - A space probe is to be placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 12.3 - The Clementine spacecraft described an elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - A space probe is describing a circular orbit of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.115PCh. 12.3 - A space shuttle is describing a circular orbit at...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.117PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.119PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.120PCh. 12.3 - Show that the angular momentum per unit mass h of...Ch. 12 - In the braking test of a sports car, its velocity...Ch. 12 - A bucket is attached to a rope of length L = 1.2 m...Ch. 12 - A 500-lb crate B is suspended from a cable...Ch. 12 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to pull...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.128RPCh. 12 - Telemetry technology is used to quantify kinematic...Ch. 12 - The radius of the orbit of a moon of a given...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.131RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.132RPCh. 12 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pb 9) 4.44 bas gnibus& WX 002 grillimatul fred bail (e) For the simply supported I-beam, a load of 1000 lb in center. Find the maximum transverse shear stress. Compare your answer with the approximation obtained by dividing the shear load by the area of the web only with the web considered to extend for the full 8-in depth. - 3½ in. 12 bas in 0% to tolerabib tormi no grived in. 8 in. 38 in. 12 ½ in.arrow_forwardPb 12) 4.61 Draw the Mohr circle for the stresses experienced by the surface of an internally pressurized steel tube that is subject to the tangential and axial stresses in the outer surface of 45 ksi and 30 ksi, respectively, and a torsional stress of 18 ksi. yx 18 45 30arrow_forwardPb 8) 4.39 For the C-clamp shown, what force F can be exerted by the screw if the maximum tensile stress in the clamp is to be limited to 30 ksi? F 2 in. სის 3436 16 13 blos 0101 alos12 nodus 121A (s 3 in. in. 16 in. 16 web leonas OFF elson yollA (d 016 (& d of bolow-bloo ai 15912 020112LA sue) vilisub 22 bal.90 Swman a bris ctxibasqqA) laste is tools?arrow_forward
- Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 6mm, for w2 h2 = 5mm, and for w3 is h3 =5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). 140 S Find the centroid I want university professor solutions O REDMI NOTE 8 PRO CAI QUAD CAMERA 101.15 Farrow_forwardPb 6) 4.31 do = 25 mm 4.31 What bending moment is required to produce a maximum normal stress of 400 MPa: (a) In a straight round rod of 40-mm diameter? (b) In a straight square rod, 40 mm on a side (with bending about the X axis as shown for a rectangular section in Appendix B-2)?arrow_forwardPb 13) 4.73 Find the maximum value of stress at the hole and semicircular notch. 45000 N 50 mm 100 mm 15 mm 25 mm 45000 Narrow_forward
- Pb 11) 4.53 Consider the 1-in solid round shaft supported by self-aligning bearings at A and B. Attached to the shaft are two chain sprockets that are loaded as shown. Treat this as a static loading problem and identify the specific shat location subjected to the most severe state of stress and make a Mohr circle representation of this stress state. 1-in.-dia. shaft 500 lb 2 in. 1000 lb 3 in. 3 in.arrow_forwardPb 5) 4.19 Estimate the torque required to produce a maximum shear stress of 570 MPa in a hollow shaft having an inner diameter of 20 mm and an outer diameter of 25 mm. d; = 20 mm T d = 25 mm Tmax = 570 MPaarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 6mm, for w2 h2 = 5mm, and for w3 is h3 =5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). I want university professor solutions O REDMI NOTE 8 PRO CAI QUAD CAMERA 140 S 101.15 Farrow_forward
- Research and select different values for the R ratio from various engine models, then analyze how these changes affect instantaneous velocity and acceleration, presenting your findings visually using graphsarrow_forwardMeh Battery operated train Coll CD Af Pair 160,000kg 0.0005 0.15 5m² 1.2kg/m³ 19 7et nong 0.98 0.9 0.88 Tesla Prated Tesla Trated Ywheel ng Jaxle. 270kW 440NM 0.45m 20 2 8.5kgm² Consider a drive cycle of a 500km trip with 3 stops in the middle. Other than the acceleration and deceleration associated with the three stops, the tran maintains. constant cruise speed velocity of 324 km/hr. The tran will fast charge at each stop for 15 min at a rate Peharge = 350 kW (ผม τ (MN 15MIN Stop w charging (350kW GMIJ restored during 15 minutes of fast charging at Calculate the battery energy Pcharge = 350kW Calculate the net energy gain per stop t 64 Determice the total battery energy required Ebat to complete the 500km trip with 3 stops. etcarrow_forwardDO NOT COPY SOLUTION The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe? c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY