
Concept explainers
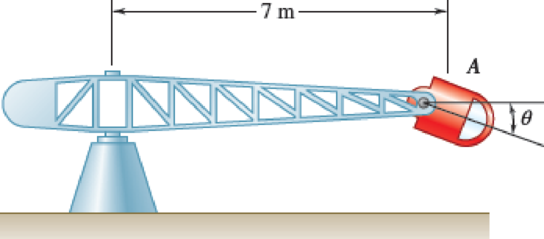
Human centrifuges are often used to simulate different acceleration levels for pilots. When aerospace physiologists say that a pilot is pulling 9 g’s, they mean that the resultant normal force on the pilot from the bottom of the seat is nine times their weight. Knowing that the centrifuge starts from rest and has a constant angular acceleration of 1.5 RPM per second until the pilot is pulling 9 g’s and then continues with a constant angular velocity, determine (a) how long it will take for the pilot to reach 9 g’s (b) the angle θ of the normal force once the pilot reaches 9 g’s.
Fig. P12.38
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Problem 3: The inertia matrix can be written in dyadic form which is particularly useful when inertia information is required in various vector bases. On the next page is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. (a) Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q, i.e., 7%, for unit vectors ₁₁, 2, 3.arrow_forwardCan you solve for v? Also, what is A x uarrow_forwardThe external loads on the element shown below at the free end are F = 1.75 kN, P = 9.0 kN, and T = 72 Nm. The tube's outer diameter is 50 mm and the inner diameter is 45 mm. Given: A(the cross-sectional area) is 3.73 cm², Moment inertial I is 10.55 cm4, and J polar moment inertial is 21.1 cm4. Determine the following. (1) The critical element(s) of the bar. (2) Show the state of stress on a stress element for each critical element. -120 mm- Farrow_forward
- A crate weighs 530 lb and is hung by three ropes attached to a steel ring at A such that the top surface is parallel to the xy plane. Point A is located at a height of h = 42 in above the top of the crate directly over the geometric center of the top surface. Use the dimensions given in the table below to determine the tension in each of the three ropes. 2013 Michael Swanbom ↑ Z C BY NC SA b x B у D Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 30 in b 43 in с 4.5 in The tension in rope AB is lb The tension in rope AC is lb The tension in rope AD is lbarrow_forwardThe airplane weighs 144100 lbs and flies at constant speed and trajectory given by 0 on the figure. The plane experiences a drag force of 73620 lbs. a.) If = 11.3°, determine the thrust and lift forces required to maintain this speed and trajectory. b.) Next consider the case where is unknown, but it is known that the lift force is equal to 7.8 times the quantity (Fthrust Fdrag). Compute the resulting trajectory angle - and the lift force in this case. Use the same values for the weight and drag forces as you used for part a. Уллу Fdrag 10. Ө Fthrust cc 10 2013 Michael Swanbom BY NC SA Flift Fweight The lift force acts in the y' direction. The weight acts in the negative y direction. The thrust and drag forces act in the positive and negative x' directions respectively. Part (a) The thrust force is equal to lbs. The lift force is equal to Part (b) The trajectory angle is equal to deg. The lift force is equal to lbs. lbs.arrow_forwardThe hoist consists of a single rope and an arrangement of frictionless pulleys as shown. If the angle 0 = 59°, determine the force that must be applied to the rope, Frope, to lift a load of 4.4 kN. The three-pulley and hook assembly at the center of the system has a mass of 22.5 kg with a center of mass that lies on the line of action of the force applied to the hook. e ΘΕ B CC 10 BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Fhook Note the figure may not be to scale. Frope = KN HO Fropearrow_forward
- Determine the tension developed in cables AB and AC and the force developed along strut AD for equilibrium of the 400-lb crate. x. 5.5 ft C 2 ft Z 2 ft D 6 ft B 4 ft A 2.5 ftarrow_forwardA block of mass m hangs from the end of bar AB that is 7.2 meters long and connected to the wall in the xz plane. The bar is supported at A by a ball joint such that it carries only a compressive force along its axis. The bar is supported at end B by cables BD and BC that connect to the xz plane at points C and D respectively with coordinates given in the figure. Cable BD is elastic and can be modeled as a linear spring with a spring constant k = 400 N/m and unstretched length of 6.34 meters. Determine the mass m, the compressive force in beam AB and the tension force in cable BC. Z D (c, 0, d) C (a, 0, b), A e B y f m BY NC SA x 2016 Eric Davishahl Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 8.1 m b 3.3 m C 2.7 m d 3.9 m e 2 m f 5.4 m The mass of the block is The compressive force in bar AB is The tension in cable S is N. kg.arrow_forwardTwo squirrels are sitting on the rope as shown. The squirrel at A has a weight of 1.2 lb. The squirrel at B found less food this season and has a weight of 0.8 lb. The angles 0 and > are equal to 50° and 60° respectively. Determine the tension force in each of the rope segments (T₁ in segment, T₂ in segment Я, and T3 in segment DD) as well as the angle a in degrees. Ө A α B Note the figure may not be to scale. T₁ = lb lb T2 T3 = = lb απ deg A BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbomarrow_forward
- Each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 500 N. Determine the largest mass of pipe that can be supported. B 60° A E Harrow_forward2. Link BD consists of a single bar 1 in. wide and 0.5 in. thick. Knowing that each pin has a in. diameter, determine (a) the maximum value of the normal stress in link BD and the bearing stress in link BD if 0 = 0, (b) the maximum value of the normal stress in link BD if 0 = 90. -6 in.- 12 in. 30° D 4 kipsarrow_forwardIn the image is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q for e hat unit vectors.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





