
Concept explainers
If life exists elsewhere in our solar system, it may not have developed independently from life on Earth. Instead, it’s possible that microbes from Earth may have colonized other planets or moons by hitching a ride on a rock blasted from Earth’s surface by a meteor impact. If the impact gives the rock enough energy to escape into space (while at the same time not raising its temperature so high as to “cook” the microbes), the rock may eventually reach another body in the solar system. In fact, rocks from Mars are known to have reached Earth in just this way, although none are currently known to have contained microbes. Computer modeling can be used to estimate the probability that a rock ejected from the surface of the Earth with a speed greater than the escape speed will reach another planet. These computer models indicate that under the influence of gravitational fields from the other objects in the solar system, an ejected rock can take millions of years to travel from one planet to another. During this time any life “aboard” is continually exposed to the high
The accompanying plot shows the residual speed of an ejected object—that is, the speed the object would have when infinitely far from the Earth—as a function of its speed at the surface of the Earth (its original ejection speed). By simulating the motion of rocks ejected from the Earth with a variety of speeds, researchers conclude that 0.03% of the rocks ejected such that they have a residual speed of 2.5 km/s will have reached Mars 2.0 million years later. Although this doesn’t seem like a high probability, there have been so many meteor impacts over the long history of the Earth that many ejected rocks must have reached Mars—though whether they carried microbes, and if they did, whether the microbes would have survived, are open questions.
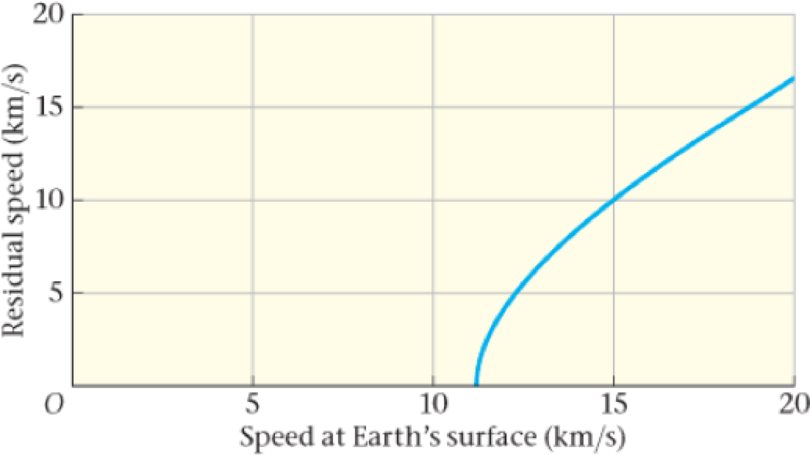
94. •• Consider a similar plot for rocks ejected from Mars. Where would this plot intercept the x axis?
- A. The plot for Mars would intercept the x axis at 5.0 km/s.
- B. The plot for Mars would intercept the x axis at 16.2 km/s.
- C. The plot for Mars would intercept the x axis at 11.2 km/s.
- D. The plot for Mars would not intercept the x axis.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
- Mars and Europa are two Solar System bodies that are considered possible habitats for Earth-like life. Why?arrow_forwardMolecules of which gas were needed in Earths atmosphere for life to evolve from living in the sea to living on the land? Why?arrow_forwardWhat evidence do scientists have that life on Earth began in the sea?arrow_forward
- In a globular cluster, astronomers (someday) discover a star with the same mass as our Sun, but consisting entirely of hydrogen and helium. Is this star a good place to point our SETI antennas and search for radio signals from an advanced civilization? Group of answer choices No, because such a star (and any planets around it) would not have the heavier elements (carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, etc.) that we believe are necessary to start life as we know it. Yes, because globular clusters are among the closest star clusters to us, so that they would be easy to search for radio signals. Yes, because we have already found radio signals from another civilization living near a star in a globular cluster. No, because such a star would most likely not have a stable (main-sequence) stage that is long enough for a technological civilization to develop. Yes, because such a star is probably old and a technological civilization will have had a long time to evolve and develop there.arrow_forwardasap pleasearrow_forwardIf you detected radio signals with an average wavelength of 68 cm and suspected that they came from a civilization on a distant Earth-like exoplanet, roughly how much of a change in wavelength (in cm) should you expect to detect as a result of the orbital motion of the distant exoplanet? (Hint: Use the Doppler shift formula.) (Note: Earth's orbital velocity is 30 km/s.)arrow_forward
- Why was the development of photosynthesis a major milestone in the evolution of life?arrow_forwardLife on Earth exists because of oxygen in Earths atmosphere. True false? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardThe evidence is overwhelming that the Grand Canyon was dug over a span of millions of years by the erosive power of the Colorado River and that river's tributary streams. Does this evidence support a catastrophic theory or an evolutionary theory?arrow_forward

 Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
 Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and GalaxiesPhysicsISBN:9781305120785Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning





