
Concept explainers
When a wood shelf of mass 6.6 kg is fastened inside a slot in a vertical support as shown in Fig. 12–76, the support exerts a torque on the shell. (a) Draw a free-body diagram for the shelf, assuming three vertical forces (two exerted by the support slot—explain why). Then calculate (b) the magnitudes of the three forces and (c) the torque exerted by the support (about the left end of the shelf).
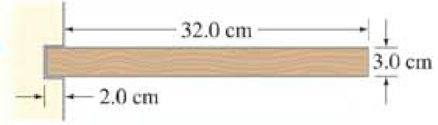
FIGURE 12–76
Problem 61.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- A wooden door 2.1 m high and 0.90 m wide is hung by two hinges 1.8 m apart. The lower hinge is 15 cm above the bottom of the door. The center of mass of the door is at its geometric center, and the weight of the door is 260 N, which is supported equally by both hinges. Find the horizontal force exerted by each hinge on the door.arrow_forwardA uniform horizontal strut weighs 400.0 N. One end of the strut is attached to a hinged support the wall and the other end of the strut is attached to a sign that weighs 200.0 N The strut is also supported by a cable attached between the end of the strut and the wall. Assuming that the entire weight of the sign is attached at the very end of the s find the tension in the cable and the force at the hinge of the strut.arrow_forwardIn Figure 9.21, the cg of the pole held by the pole vaulter is 2.00 m from the left hand, and the hands are 0.700 m apart. Calculate the force exerted by (a) his right hand and (b) his left hand. (c) If each hand supports half the weight of the pole in Figure 9.19, show that the second condition for equilibrium (net =0 ) is satisfied for a pivot other than the one located at the center of gravity of the pole. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for static equilibrium described above. Figure 9.21 A pole vaulter is holding a pole horizontally with both hands. The center of gravity is to the left side of the vaulter.arrow_forward
- Check Your Understanding A 50-kg person stands 1.5 m away from one end of a uniform 6.0-m-long scaffold of mass 70.0 kg. Find the tensions in the two vertical ropes supporting the scaffold.arrow_forwardA uniform beam is hinged at one end and held in a hori- zontal position by a cable, as shown in Fig. 9–42. The tension in the cable (a) must be at least half the weight of the beam, no matter what the angle of the cable. (b) could be less than half the beam's weight for some angles. (c) will be half the beam's weight for all angles. (d) will equal the beam's weight for all angles. FIGURE 9–42 MisConceptual Question 3: beam and cable.arrow_forward10) One end of a uniform beam is hinged to a wall and the other end is supported by a tension wire that makes angles 0 = 25° with both the wall and the beam as shown in the figure below. The beam is 1 m long and weighs 222 N with its center of mass located at the half of its total length. Find (a) the tensile force in the wire, (b) the horizontal component of the force of the hinge on the beam, and (c) the vertical component of the force of the hinge on the beam. Hingearrow_forward
- (II) A 20.0-m-long uniform beam weighing 650 N rests on walls A and B, as shown in Fig. 9–62. (a) Find the maxi- mum weight of a person who can walk to the extreme end D without tipping the beam. Find the forces that the walls A and B exert on the beam when the person is stand- ing: (b) at D; (c) 2.0 m to the right of A. - 20.0 m- A В D +3.0 m→ -12.0 m - FIGURE 9-62 Problem 22.arrow_forward(II) A uniform steel beam has a mass of 940 kg. On it is resting half of an identical beam, as shown in Fig. 9-60. What is the vertical support force at each end? •M •Marrow_forward(I) A tower crane (Fig. 9–48a) must always be carefully balanced so that there is no net torque tending to tip it. A particular crane at a building site is about to lift a 2800-kg air-conditioning unit. The crane's dimensions are shown in Fig. 9-48b. (a) Where must the crane's 9500-kg counterweight be placed when the load is lifted from the ground? (The counterweight is usually moved auto- matically via sensors and motors to precisely compensate for the load.) (b) Determine the maximum load that can be lifted with this counterweight when it is placed at its full extent. Ignore the mass of the beam. (a) Counterweight M = 9500 kg +3.4 m- 7.7 m m = 2800 kg FIGURE 9-48 (b) Problem 3.arrow_forward
- A woman holds a 2.0-m-long uniform 10.0-kg pole as shown in Fig. 9–78. (a) Determine the forces she must exert with each hand (magnitude and direction). To what position should she move her left hand so that neither hand has to exert a force greater than (b) 150 N? (c) 85 N? FIGURE 9–78 -32 cm→| Problem 59.arrow_forwardSir Lost-a-Lot dons his armor and sets out from the castle on his trusty steed (see figure below). Usually, the drawbridge is lowered to a horizontal position so that the end of the bridge rests on the stone ledge. Unfortunately, Lost-a-Lot's squire didn't lower the drawbridge far enough and stopped it at e = 20.0° above the horizontal. The knight and his horse stop when their combined center of mass is d = 1.25 m from the end of the bridge. The uniform bridge is { = 7.25 m long and has mass 2 500 kg. The lift cable is attached to the bridge 5.00 m from the hinge at the castle end and to a point on the castle wall h = 12.0 m above the bridge. Lost-a-Lot's mass combined with his armor and steed is 1 070 kg. While Lost-a-Lot ponders his next move, the enemy attacks! An incoming projectile breaks off the stone ledge so that the end of the drawbridge can be lowered past the wall where it usually rests. In addition, a fragment of the projectile bounces up and cuts the drawbridge cable! The…arrow_forward- 5. Two identical, uniform beams of length 3 m and weighing 260 N each are connected at one end by a frictionless hinge. A light horizontal crossbar, attached at the midpoints of the beams maintains an angle 50° between the beams. The beams are suspended from the ceiling by vertical wires so they form a V. See figure. (a) What force does the crossbar exert on each beam? (b) Is the crossbar under compression or tension, i.e. are the ends of the crossbar being pushed together or stretched farther apart? (c) What force (magnitude and direction) does the hinge exert on each beam? Crossbar Hingearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College


