
The circuit shown in Figure P12.38 is an ac equivalent circuit of a feedback amplifier. The transistor parameters are
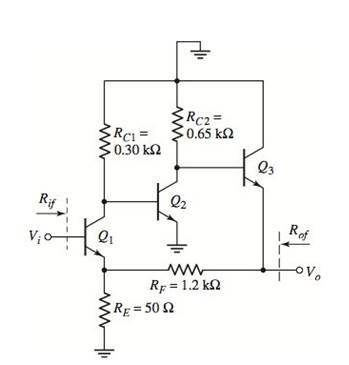
Figure P12.38
(a)
The value of the closed loop voltage gain.
To compare: The approximate value with the ideal value of the closed loop gain.
Answer to Problem 12.38P
The value of closed loop gain is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is shown in Figure 1.
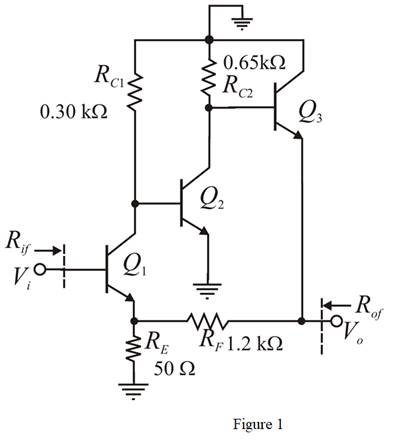
Calculation:
The small signal model of the given circuit is shown in Figure 2.
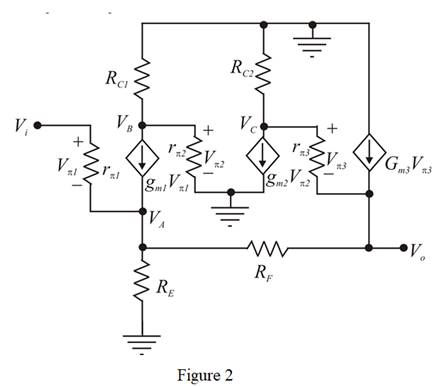
The expression for the small signal input resistance is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the trans-conductance of the first transistor is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the small signal input resistance is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the trans-conductance of the first transistor is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the small signal input resistance is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the trans-conductance of the first transistor is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the
Apply KCL at
Substitute
Substitute
Apply KCL at
Substitute
Substitute
Apply KCL at
Substitute
Substitute
Apply KCL at
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The approximate ideal value of the closed loop voltage gain is given by,
The closed loop voltage gain is by formula
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of closed loop gain is
(b)
The value of the resistance
Answer to Problem 12.38P
The value
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is shown in Figure 1.
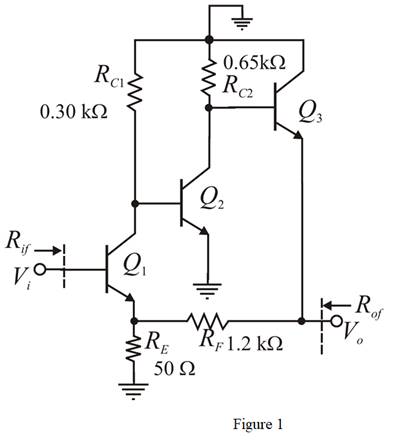
Calculation:
Consider the equation for the voltage
Substitute
The expression for the current
Substitute
Substitute
Apply KCL at the output.
Substitute
The equation for the
Evaluate the equation of the voltage
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- Given the following, assume 0.7 V votlage drop across LEDs when they are positively biased.(a) When VB=0V, which LED is on?(b) When VB=5V, which LED is on?(c) If you want to limit the current through the LEDs to 10mA for both cases of 3(a) and 3 (b), find out the resistor values of RG and RR.arrow_forwardGiven the following, the intial condtion of output Q is high (H). (a) When /ALM is pushed on, creating a short to ground, what are the inputvoltages of S and R, and the output voltage Q?(b) After (a) happens, /ALM is released. What is the output voltage Q?(c) After (a) and (b) happen, /RESET is pushed on, creating a short to ground,what are the input voltages of S and R, and the output voltage Q?(d) After (a), (b) and (c) happen, /RESET is released. What is the output voltageQ?arrow_forwardHelp on this question about mass-spring system below?arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





