
(a)
Value of current IDQ1 and ICQ2 .
(a)
Answer to Problem 12.40P
Value of current is,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given values are:
The given circuit is shown below.
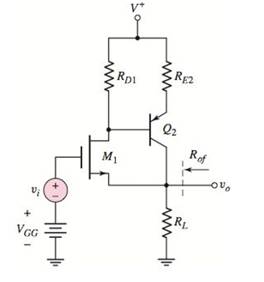
Calculation:
Modified circuit diagram is shown below.
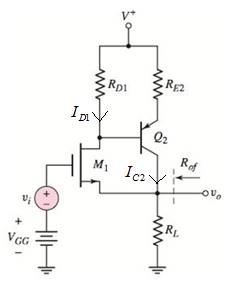
Neglecting base current.
Equation of current ID1 is,
Equation of voltage VD is,
Equation of current IC2 is,
Value of voltage VGS is,
Value of current IDQ1 is,
Value of current ICQ2 is,
(b)
Value of small signal voltage gain.
(b)
Answer to Problem 12.40P
Value of small signal voltage gain is 0.88.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Given values are:
Calculation:
Small signal circuit is shown below.
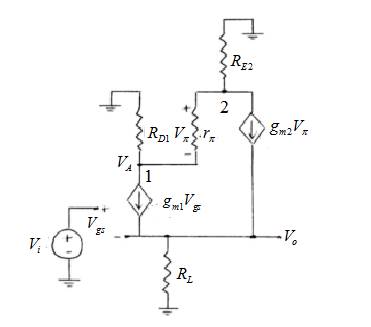
Value of trans-conductance of transistor 1 is,
Value of trans-conductance of transistor 2,
Value of small signal resistance is,
Applying KCL at node (2),
Equation of output voltage is,
Applying KCL at node (1),
Value of small signal voltage gain is,
(c)
Value of small signal output resistance.
(c)
Answer to Problem 12.40P
Value of small signal output resistance is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Given values are,
Calculation:
Small signal circuit for output resistance calculation ( Vi =0) is,
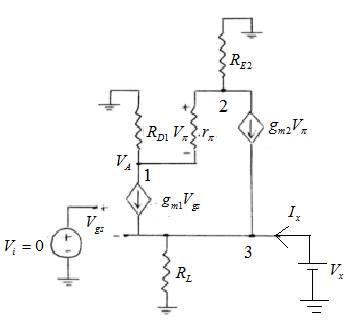
Applying KCL at node 3 for output resistance,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- 2.80+4'selevision stations are to be transmited deough a single fiber optic cable using uncompressed PCM and TDM. Each station comprises one 22 kHz audio channel samplod at (1+0.24) times the Nyquist rate and encoded at a bit dop of 12 bSa, plan one 2.0 MHz video channel sampled at the mininum rite The video signal must be transmitted with an accuracy of better than (20 3) Find De (minimum) bit depth of the video signal. b) Find the bit rate associated with a single television station, including both audio and video e) Find the minimus bandwidth (the total multiplexed PCM signal.arrow_forward5. Consider a Shor who (4) Skh the impulse repom of the Chor for -5%, a-2+5. Omie weer de Sher is drain canal and explain sty odical, chronic sale of a hat will result in a coal for, and expls why itarrow_forwardFind the inverse Z-transform of X(z) using partial fraction method X(z) = z²+Z Z2-3Z+2 for i) ROC 12 iii) ROC |z| <1arrow_forward
- .The previous solution does not explain the steps Consider the signal: f(t) = 글씨를 1 0, otherwise Use the Fourier transform formula to find F(w).arrow_forward3. Find the transfer function and show all steps.arrow_forward8. Determine the center frequency and Bandwidth of the following bandpass filter, show all steps.arrow_forward
- 5. Find the Transfer Function of the following circuit. Prove that it’s a low pass filter, show all steps.arrow_forward2. Find the transfer function, show all steps.arrow_forwardI have this fsk function code: function [x]=fsk_encode(b,s,f0,f1,N,Fs,K) % b= bit sequence vector % s(1)= output level for 0 % s(2)= output level for 1 % N= length of bit sequence % Fs= Sampling frequency y=zeros(1,N*K); %Setup output vector %for each bit calculatee the rando samples for n=1:N for k=1:K t = (k - 1) / Fs; if(b(n)==0) y((n-1)*K+k)=cos(2*pi*f0*t); % pulse=0 else y((n-1)*K+k)=cos(2*pi*f1*t); % pulse=1 end end x=y; %set output end And this is another code that calls the function in order to get the power density spectrum: clc;clear; % EE 382 Communication Systems- Lab 8 % Plots the power spectrum of the ASK modulation % First specify some parameters N=256; % number of bits per realization M=100; % number of realizations in the ensemble T=0.001; % bit duration in seconds delf =2e+3; fc=10e+3; f0=fc-delf; f1=fc+delf; Fs=8*f1; % sampling frequency (this is needed to calibrate the frequency axis) K=(T/(1/Fs)); % Define arrays for bit sequences and sampled waveforms…arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





