
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and
Cycloalkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that contain a ring of carbon atoms with or without alkyl substituents on it. The general molecular formula for cycloalkanes is
In a line-angle structural formula of cycloalkanes, the intersection of two lines represent a methylene group (
(a)
Answer to Problem 12.108EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of cycloalkane is 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane. From the name it is understood that the parent cycloalkane is five carbon cyclic ring which is cyclopentane. The substituents present on the cyclopentane ring are two methyl groups, each at first and second carbon. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane can be drawn as shown below,
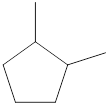
The above structure is a line-angle structural formula representation. This structure has a total of five intersections and two end lines. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is found to be seven.
The molecular formula for the given cycloalkane can be found using the general molecular formula. General molecular formula for cycloalkane is
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found to be
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found as
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Cycloalkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that contain a ring of carbon atoms with or without alkyl substituents on it. The general molecular formula for cycloalkanes is
In a line-angle structural formula of cycloalkanes, the intersection of two lines represent a methylene group (
(b)
Answer to Problem 12.108EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of cycloalkane is 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane. From the name it is understood that the parent cycloalkane is five carbon cyclic ring which is cyclopentane. The substituent present on the cyclopentane ring are two methyl groups, each at first and third carbon. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane can be drawn as shown below,
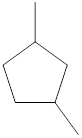
The above structure is a line-angle structural formula representation. This structure has a total of five intersections and two end lines. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is found to be seven.
The molecular formula for the given cycloalkane can be found using the general molecular formula. General molecular formula for cycloalkane is
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found to be
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found as
(c)
Interpretation:
Molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Molecular formula of the
(c)
Answer to Problem 12.108EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alkane is 2,2-dimethylpentane. From the name it is understood that the parent alkane is five carbon chain which is pentane. The substituent present on the hexane are two methyl groups, on the second carbon atom. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 2,2-dimethylpentane can be drawn as shown below,
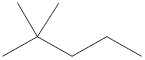
In line-angle structural representation of molecule, carbon atom is present where two lines meet and at the end of the lines. In the above structure there are three points where the lines meet and four end points. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is 7.
To determine the molecular formula of alkane, the value of “n” has to be substituted as 7 in the general formula of alkane.
Therefore, the molecular formula of the given hydrocarbon is determined as
The molecular formula of the hydrocarbon was determined as
(d)
Interpretation:
Molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Molecular formula of the alkanes can be found by using the general formula
(d)
Answer to Problem 12.108EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alkane is 2,3-dimethylpentane. From the name it is understood that the parent alkane is five carbon chain which is pentane. The substituent present on the hexane are two methyl groups, each at second and third carbon. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 2,3-dimethylpentane can be drawn as shown below,
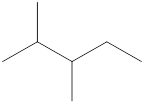
In line-angle structural representation of molecule, carbon atom is present where two lines meet and at the end of the lines. In the above structure there are three points where the lines meet and four end points. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is 7.
To determine the molecular formula of alkane, the value of “n” has to be substituted as 7 in the general formula of alkane.
Therefore, the molecular formula of the given hydrocarbon is determined as
The molecular formula of the given hydrocarbon was determined as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- For Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardI need help with the follloaingarrow_forward
- For a CARS experiment on a Raman band 918 cm-1, if omega1= 1280 nm, calculate the omega2 in wavelength (nm) and the CARS output in wavelength (nm).arrow_forwardI need help with the following questionarrow_forwardFor CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardConvert 1.38 eV into wavelength (nm) and wavenumber (cm-1) (c = 2.998 x 108 m/s; h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s).arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




