
Concept explainers
What products would you expect from the reaction of 1-bromopropane with each of the following?
(a) NaNH2
(b) KOC(CH3)3
(c) NaI
(d) NaCN
(e) NaC≡CH
(f) Mg, then H2O
a)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
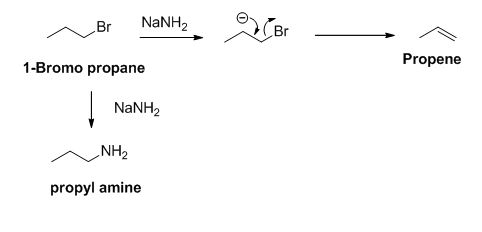
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
The product of the reaction is given below,
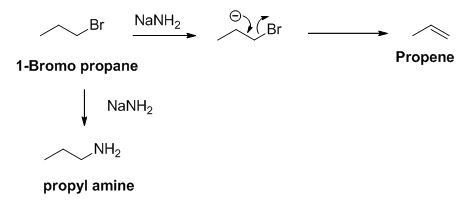
The sodium amide is acts as a base and it abstract the acidic proton from 1-bromo propane gives carbanion, this carbanion under goes elimination reaction gives propene as a major product.
1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction gives propyl amine as a minor product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
b)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
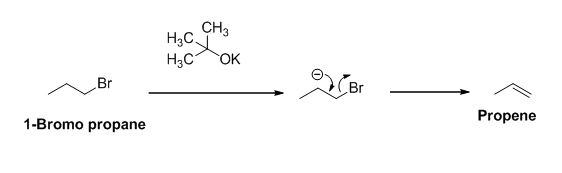
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
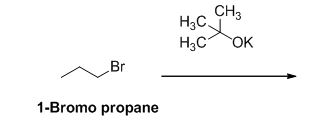
The product of the reaction is given below,
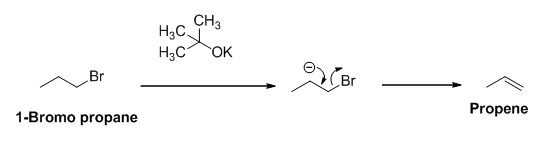
The potassium tertiary butoxide is acts as a base and it abstract the acidic proton from 1-bromo propane gives carbanion, this carbanion under goes elimination reaction gives propene as a major product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
c)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
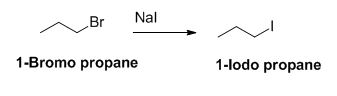
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
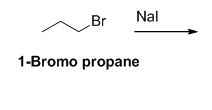
The product of the reaction is given below,
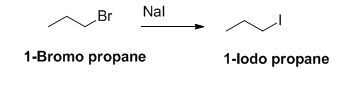
The sodium iodide is acts as nucleophile, 1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with sodium iodide gives 1-iodo propane.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
d)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
The product of the reaction is given below,
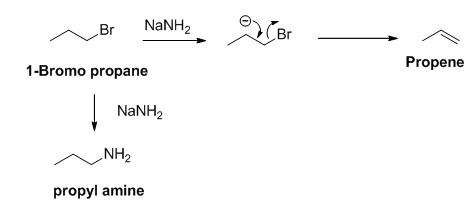
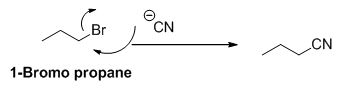
The sodium amide is acts as a base and it abstract the acidic proton from 1-bromo propane gives carbanion, this carbanion under goes elimination reaction gives propene as a major product.
1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction gives propyl amine as a minor product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
e)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
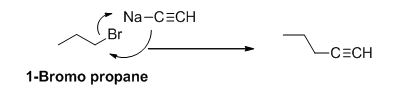
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
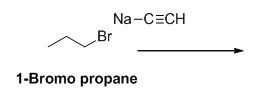
The product of the reaction is given below,
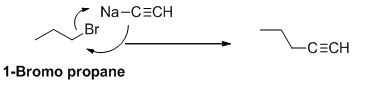
1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with given alkyne compound gives the corresponding alkyne product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
f)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
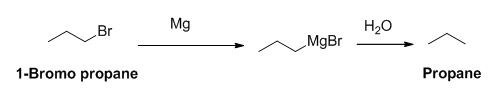
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
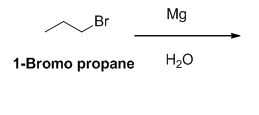
The product of the reaction is given below,
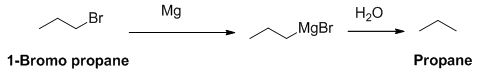
1-bromo propane reaction with magnesium gives Grignard reagent and it undergoes hydrolysis gives propane.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Explain why only the lone pairs on the central atom are taken into consideration when predicting molecular shapearrow_forward(ME EX1) Prblm #9/10 Can you explain in detail (step by step) I'm so confused with these problems. For turmber 13 can u turn them into lewis dot structures so I can better understand because, and then as well explain the resonance structure part. Thanks for the help.arrow_forwardProblems 19 and 20: (ME EX1) Can you please explain the following in detail? I'm having trouble understanding them. Both problems are difficult for me to explain in detail, so please include the drawings and answers.arrow_forward
- (ME EX1) Prblm #4-11 Can you please help me and explain these I'm very confused in detail please. Prblm number 9 I don't understand at all (its soo confusing to me and redraw it so I can better depict it).arrow_forwardME EX1) Prblm #19-20 I'm so confused with these problems. Can you please help me solve them and explain them? Problems number 19-20, and thanks! step by step and in detail for me please helparrow_forwardCalculate the flux of oxygen between the ocean and the atmosphere, given that: Temp = 18°C Salinity = 35 ppt Density = 1025 kg/m3 Oxygen concentration measured in bulk water = 263.84 mmol/m3 Wind speed = 7.4 m/s Oxygen is observed to be about 10% initially supersaturatedarrow_forward
- ( ME EX1) Prblm 27-28: Can you explain to me both prblms in detail and for prblm 28 what do you mean bi conjugated bi ponds and those structures I'm confused...arrow_forwardA. Determine the number of electrons in a system of cyclic conjugation (zero if no cyclic conjugation). B. Specify whether the species is "a"-aromatic, "aa"-anti-aromatic, or "na"-non-aromatic (neither aromatic nor anti-aromatic). (Presume rings to be planar unless structure obviously prevents planarity. If there is more than one conjugated ring, count electrons in the largest.) 1. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 18 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) a 2. A.Electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. 10 B.The compound is (a, aa, or na) naarrow_forwardWater is boiling at 1 atm pressure in a stainless steel pan on an electric range. It is observed that 2 kg of liquid water evaporates in 30 min. Find the rate of heat transfer to the water (kW).arrow_forward
- Could you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the resonance structures that were given please.arrow_forwardCould you please turn this into a complete Lewis dot structure formula for me so I can visualize it more clearly? and then do the explaining for the question.arrow_forwardplease solve. If the answer is "no error" and it asks me to type something, and i typed a-helix, its always wrong.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





