
a)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,
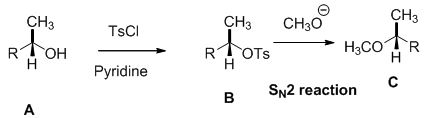
SN2 reaction is second order
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
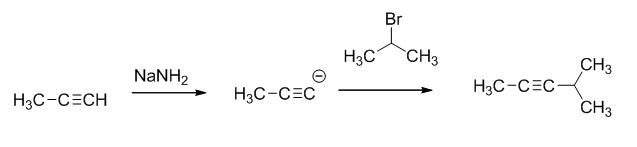
The product of the reaction is given below,
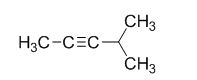
The reaction is given below,
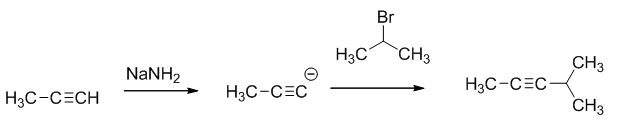
The sodium amide is acts as a base and it abstract the highly acidic proton from propylene gives carbanion, this carbanion react with 2-bromo propane gives the corresponding product.
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
b)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,

SN2 reaction is second order reaction, the rate of the reaction is depending on the both substrate and nucleophiles.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
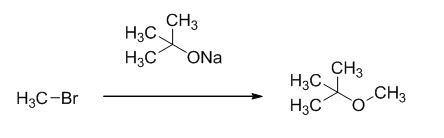
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The product of the reaction is given below,
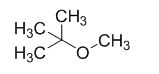
The reaction is given below,
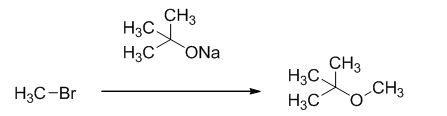
The sodium tertiary butoxide is acts as a base and it react with methyl bromide gives the corresponding ether product.
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
c)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,

SN2 reaction is second order reaction, the rate of the reaction is depending on the both substrate and nucleophiles.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
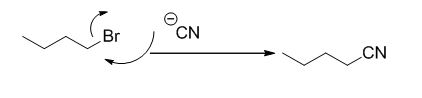
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The product of the reaction is given below,
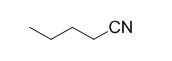
The reaction is given below,
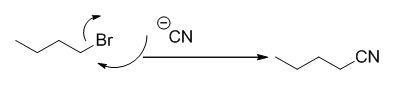
n-butyl bromide undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with cyanide (sodium cyanide) gives the corresponding cyanide product.
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
d)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,

SN2 reaction is second order reaction, the rate of the reaction is depending on the both substrate and nucleophiles.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
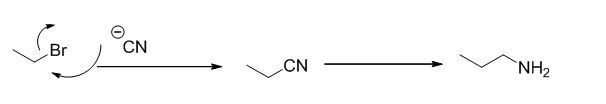
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reaction is given below,
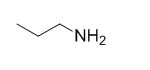
The reaction is given below,
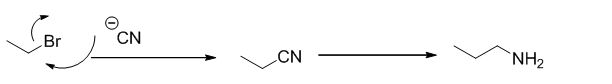
Ethyl bromide undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with cyanide (sodium cyanide) gives the corresponding cyanide product, this cyanide undergoes catalytic reduction using Pt (metal reduction) gives
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward
- 3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). H-Br CH2Cl2arrow_forwardWrite the aldol condensation mechanism and product for benzaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base. Then trans-cinnamaldehyde + acetone in base. Then, trans-cinnamaldehyde + cyclohexanone in a base.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

