
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
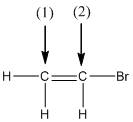
The shape around the labelled atoms needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Shape of a molecule is determined by including only the bond pair not lone pairs on the central atom while geometry includes both the bond pairs and lone pairs on the central atom. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory used in chemistry as a model for the prediction of shape of various molecules by knowing the electron pairs on the central atom. There will be repulsion between the electron pairs present on central atom, so to minimize the repulsion they adopt an arrangement with minimum repulsion, thus determining molecule's shape. And by knowing the shape we can easily determine the bond angles.
The following table should be used while determining the shapes:
| Number of groups | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle | |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
(b)
Interpretation:
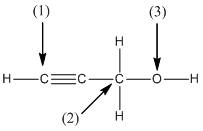
The shape around the labelled atoms needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Shape of a molecule is determined by including only the bond pair not lone pairs on the central atom while geometry includes both the bond pairs and lone pairs on the central atom. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory used in chemistry as a model for the prediction of shape of various molecules by knowing the electron pairs on the central atom. There will be repulsion between the electron pairs present on central atom, so to minimize the repulsion they adopt an arrangement with minimum repulsion, thus determining molecule's shape. And by knowing the shape we can easily determine the bond angles.
The following table should be used while determining the shapes:
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
(c)
Interpretation:
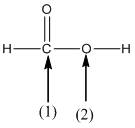
The shape around the labelled atoms needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Shape of a molecule is determined by including only the bond pair not lone pairs on the central atom while geometry includes both the bond pairs and lone pairs on the central atom. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory used in chemistry as a model for the prediction of shape of various molecules by knowing the electron pairs on the central atom. There will be repulsion between the electron pairs present on central atom, so to minimize the repulsion they adopt an arrangement with minimum repulsion, thus determining molecule's shape. And by knowing the shape we can easily determine the bond angles.
The following table should be used while determining the shapes:
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
(d)
Interpretation:
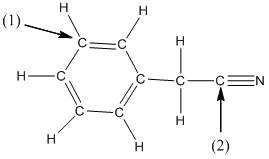
The shape around the labelled atoms needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Shape of a molecule is determined by including only the bond pair not lone pairs on the central atom while geometry includes both the bond pairs and lone pairs on the central atom. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory or VSEPR theory used in chemistry as a model for the prediction of shape of various molecules by knowing the electron pairs on the central atom. There will be repulsion between the electron pairs present on central atom, so to minimize the repulsion they adopt an arrangement with minimum repulsion, thus determining molecule's shape. And by knowing the shape we can easily determine the bond angles.
The following table should be used while determining the shapes:
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





