
(a)
Interpretation:
The acyl chloride and carboxylate ion that could be used to form the given mixed anhydride have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Mixed anhydrides are unsymmetrical anhydrides which have different alkyl groups.
Example:
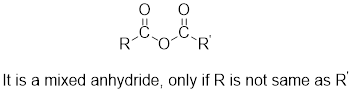
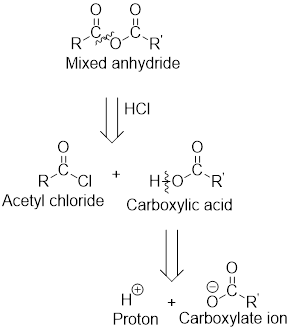
The acetyl chloride and carboxylate ion that could be used to form any given mixed anhydride can be analysed using the simple retro analysis as shown here:
(b)
Interpretation:
The other reagents that could be used to form the given mixed anhydride have to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Mixed anhydrides are unsymmetrical anhydrides which have different alkyl groups.
Example:
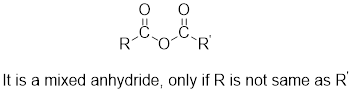
Any anhydride can be obtained using the following two pairs of reagents:
- 1. Acetyl chloride and a carboxylate ion.
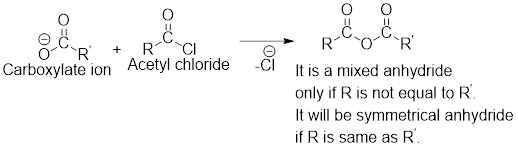
- 2. Two different carboxylic acids if mixed or unsymmetrical anhydride has to be formed or two same carboxylic acids if symmetrical anhydride has to be formed.
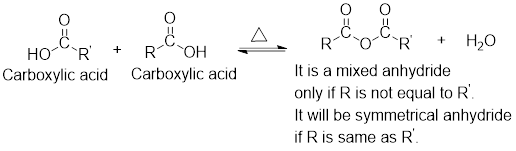
For any simple anhydride, the two carboxylic acids from which it has been formed can be found by the simple retro analysis as shown here:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Pearson eText for Essential Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Drawing Arrows 1 I I 1 heat 1 51 MO + Drag To Und Settings Done 0 0 Jan 31 3:5arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardGramicidin A can adopt more than one structure; NMR spectroscopy has revealed an “end-to-end” dimer form, and x-ray crystallography has revealed an “anti-parallel double- helical” form. Briefly outline and describe an experimentalapproach/strategy to investigate WHICH configuration (“end-to-end dimer” vs “anti-paralleldouble helical”) gramicidin adopts in an actual lipid bilayer.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCHEM2323 Problem 2-24 Tt O e: ל Predict the product(s) of the following acid/base reactions. Draw curved arrows to show the formation and breaking of bonds. If the bonds needed are not drawn out, you should redraw them. + BF3 (a) (b) HI + (c) OH -BF Problem 2-25 Use curved arrows and a proton (H+) to draw the protonated form of the following Lewis bases. Before starting, add all missing lone pairs. (a) (b) :0: (c) N 1 CHEM2323 PS CH02 Name:arrow_forwardCHEM2323 Problem 2-26 Tt O PS CH02 Name: Use the curved-arrow formalism to show how the electrons flow in the resonance form on the left to give the one on the right. (Draw all lone pairs first) (a) NH2 NH2 + (b) Problem 2-27 Double bonds can also act like Lewis bases, sharing their electrons with Lewis acids. Use curved arrows to show how each of the following double bonds will react with H-Cl and draw the resulting carbocation. (a) H2C=CH2 (b) (c) Problem 2-28 Identify the most electronegative element in each of the following molecules: (a) CH2FCI F Problem 2-29 (b) FCH2CH2CH2Br (c) HOCH2CH2NH2 (d) CH3OCH2Li F 0 0 Use the electronegativity table in Figure 2.3 to predict which bond in the following pairs is more polar and indicate the direction of bond polarity for each compound. (a) H3C-Cl or Cl-CI (b) H3C-H or H-CI (c) HO-CH3 or (CH3)3Si-CH3 (d) H3C-Li or Li-OHarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


