
Concept explainers
The absolute pressure in water at a depth of 9 m is read to be 185 kPa. Determine (a) the local atmospheric pressure and (b) the absolute pressure at a depth of 5 m in a liquid whose specific gravity is 0 85 at the same location.
(a)
The local atmospheric pressure in a liquid.
Answer to Problem 53P
The local atmospheric pressure in a liquid is
Explanation of Solution
Show the free body diagram of the absolute pressure in water.
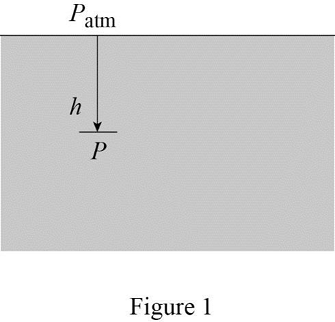
Determine the density of the liquid.
Here, the specific gravity is
Write the expression of atmospheric pressure.
Here, the absolute pressure is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, local atmospheric pressure in a liquid is
(b)
The absolute pressure in a liquid.
Answer to Problem 53P
The absolute pressure in a liquid is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression of absolute pressure.
Here, the absolute pressure is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the absolute pressure in a liquid is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS (LL)-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Modern Database Management
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. με ? VB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ☐ о Α NB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. The crate is originally at rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is μk = 0.2. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of 8.1 m/s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 500 N 1 of 1 Α S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forwardThe differential equation of a DC motor can be described by the following equation Find the transfer function between the applied voltage ( Va)and the motor speed (thetadot m). What is the steady state speed of the motor after a voltage (Va = 10V) has been applied. Find the transfer function between the applied voltage (Va) and the shaft angle (thetadot m) .arrow_forward
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review The sports car has a mass of 2.5 Mg and accelerates at 6 m/s², starting from rest. (Figure 1) If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind is FD = (10v) N, where v is the velocity in m/s, determine the power supplied to the engine when t = 5 s. The engine has a running efficiency of € = 0.66. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 о Α ? P = Value Units Submit Request Answer Return to Assignment Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Study Area mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Document Sharing User Settings The car in (Figure 1) having a mass of 2 Mg is originally traveling at 2 m/s. Assume 0 = 22°. Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review Determine the distance it must be towed by a force F = 4 kN in order to attain a speed of 6 m/s. Neglect friction and the mass of the wheels. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Α ? S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forward
- Derive the Laplace transform of the following functions. Use the definition of Laplace transform. f(t)=sin4t and f(t)=cos2t Auto Controlsarrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Marbles having a mass of 5 g fall from rest at A through the glass tube and accumulate in the can at C. (Figure 1) Figure Aarrow_forwardVC Vc B S TDC -BDC S TQ Tp = Pg A (asne) [1+ % CUSA] At what position (in degrees after top dead center) would you want the peak pressure of combustion to occur to create the maximum torque on the crankshaft? For a 100mm piston digimeter acting on a connecting. rod with a length of 80mm use the equation above to calculate the torque (NIM) on the crankshaft at this crank position for an engine that develops a peak pressure of 135 bararrow_forward
- Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The man having a weight of 180 lb is able to run up a 18-ft-high flight of stairs shiwn in (Figure 1) in 4 s. Figure 1 of 1 R mylabmastering.pearson.com Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Determine the power generated. Express your answer in horsepower to three significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ. Η vec P = Submit Request Answer Part B ? hp How long would a 100-W light bulb have to burn to expend the same amount of energy? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HÅ ? t = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Review Next >arrow_forwardThe tension in the belt is 46 lb. Determine the moment of the force F1 about the pin at A. Determine the moment of the force F2 about the pin at A.arrow_forward1. Describe each of the tolerances in the following drawing: 0.01 A 09±0.025 .10±0.01 0.015 AB 6.76 08.51 03±0.05 0.015 MAB 14±0.03 60 14±0.02 12±0.08 0.01 A Barrow_forward
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
