1 Introduction And Basic Concepts 2 Energy, Energy Transfer, And General Energy Analysis 3 Properties Of Pure Substances 4 Energy Analysis Of Closed Systems 5 The Second Law Of Thermodynamics 6 The Second Law Of Thermodynamics 7 Entropy 8 Exergy 9 Gas Power Cycles 10 Vapor And Combined Power Cycles 11 Refrigeration Cycles 12 Thermodynamic Property Relations 13 Gas Mixtures 14 Gascfvapor Mixtures And Air-conditioning 15 Chemical Reactions 16 Chemical And Phase Equilibrium 17 Compressible Flow expand_more
1.1 Thermodynamics And Energy 1.2 Importance Of Dimensions And Units 1.3 Systems And Control Volumes 1.4 Propert Ies Of A System 1.5 Density And Specific Gravity 1.6 State And Equilibrium 1.7 Processes And Cycles 1.8 Temperature And The Zeroth Law Of Thermodynamics 1.9 Pressure 1.10 Pressure Measurement Devices 1.11 Problem-solving Technique expand_more
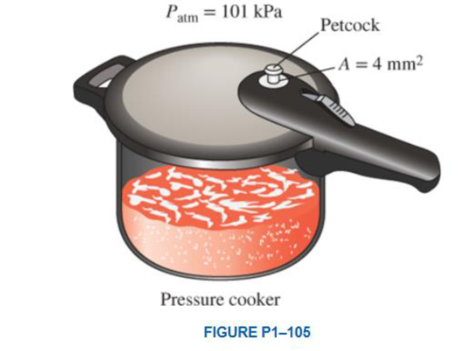
Problem 1P: The value of the gravitational acceleration g decreases with elevation from 9.807 m/s2 at sea level... Problem 2P: One of the most amusing things a person can experience is when a car in neutral appears to go uphill... Problem 3P: An office worker claims that a cup of cold coffee on his table warmed up to 80C by picking up energy... Problem 4P: What is the difference between the classical and the statistical approaches to thermodynamics? Problem 5P: Explain why the light-year has the dimension of length. Problem 6P: What is the difference between pound-mass and pound-force? Problem 7P: What is the net force acting on a car cruising at a constant velocity of 70 km/h (a) on a level road... Problem 8P: What is the weight, in N, of an object with a mass of 200 kg at a location where g = 9.6 m/s2? Problem 9P: If the mass of an object is 10 lbm, what is its weight, in lbf, at a location where g = 32.0 ft/s2? Problem 10P: The acceleration of high-speed aircraft is sometimes expressed in gs (in multiples of the standard... Problem 11P: The value of the gravitational acceleration g decreases with elevation from 9.807 m/s2 at sea level... Problem 12P: A 3-kg plastic tank that has a volume of 0.2 m3 is filled with liquid water. Assuming the density of... Problem 13P: A 2-kg rock is thrown upward with a force of 200 N at a location where the local gravitational... Problem 14P: Solve Prob. 113 using appropriate software. Print out the entire solution, including the numerical... Problem 15P: A 4-kW resistance heater in a water heater runs for 3 hours to raise the water temperature to the... Problem 16P: A 150-lbm astronaut took his bathroom scale (a spring scale) and a beam scale (compares masses) to... Problem 17P: The gas tank of a car is filled with a nozzle that discharges gasoline at a constant flow rate.... Problem 18P: How would you define a system to determine the rate at which an automobile adds carbon dioxide to... Problem 19P: A large fraction of the thermal energy generated in the engine of a car is rejected to the air by... Problem 20P: A can of soft drink at room temperature is put into the refrigerator so that it will cool. Would you... Problem 21P: How would you define a system to determine the temperature rise created in a lake when a portion of... Problem 22P: How would you describe the state of the air in the atmosphere? What kind of process does this air... Problem 23P: What is the difference between intensive and extensive properties? Problem 24P: The specific weight of a system is defined as the weight per unit volume (note that this definition... Problem 25P: Is the number of moles of a substance contained in a system an extensive or intensive property? Problem 26P: Is the state of the air in an isolated room completely specified by the temperature and the... Problem 27P: What is a quasi-equilibrium process? What is its importance in engineering? Problem 28P: Define the isothermal, isobaric, and isochoric processes. Problem 29P: What is specific gravity? How is it related to density? Problem 31P: What are the ordinary and absolute temperature scales in the SI and the English system? Problem 32P: Consider an alcohol and a mercury thermometer that read exactly 0C at the ice point and 100C at the... Problem 33P: Consider two dosed systems A and B. System A contains 3000 kJ of thermal energy at 20C, whereas... Problem 34P: Consider a system whose temperature is 18C. Express this temperature in R, K, and F. Problem 35P: Steam enters a heat exchanger at 300 K. What is the temperature of this steam in F? Problem 36P: The temperature of a system rises by 130C during a heating process. Express this rise in temperature... Problem 37P: The temperature of a system drops by 45F during a cooling process. Express this drop in temperature... Problem 38P: The temperature of the lubricating oil in an automobile engine is measured as 150F. What is the... Problem 39P: Heated air is at 150C. What is the temperature of this air in F? Problem 40P: What is the difference between gage pressure and absolute pressure? Problem 41P: Explain why some people experience nose bleeding and some others experience shortness of breath at... Problem 42P: A health magazine reported that physicians measured 100 adults blood pressure using two different... Problem 43P: Someone claims that the absolute pressure in a liquid of constant density doubles when the depth is... Problem 44P: Consider two identical fans, one at sea level and the other on top of a high mountain, running at... Problem 45P: The absolute pressure in a compressed air tank is 200 kPa. What is this pressure in psia? Problem 46P: A manometer measures a pressure difference as 40 inches of water What is this pressure difference in... Problem 47P: A vacuum gage connected to a chambee reads 35 kPa at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 92... Problem 48P: The maximum safe air pressure of a tire is typically written on the tire itself. The label on a tire... Problem 49P: A pressure gage connected to a tank reads 50 psi at a location where the barometric reading is 29 1... Problem 50P: A pressure gage connected to a tank reads 500 kPa at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 94... Problem 51P: A 200-pound man has a total foot imprint area of 72 in2. Determine the pressure this man exerts on... Problem 52P: The gage pressure in a liquid at a depth of 3 m is read to be 42 kPa. Determine the gage pressure m... Problem 53P: The absolute pressure in water at a depth of 9 m is read to be 185 kPa. Determine (a) the local... Problem 54P: Consider a 1.75-m-tall man standing vertically in water and completely submerged in a pool.... Problem 55P: The barometer of a mountain hiker reads 750 mbars at the beginning of a hiking trip and 650 mbars at... Problem 56P: The basic barometer can be used to measure the height of a building. If the barometric readings at... Problem 58P: A gas is contained in a vertical, frictionless pistoncylinder device. The piston has a mass of 3.2... Problem 59P: Reconsider Prob. 158. Using appropriate software, investigate the effect of the spring force in the... Problem 60P: The piston of a vertical piston-cylinder device containing a gas has a mass of 60 kg and a... Problem 61P: Both a gage and a manometer are attached to a gas tank to measure its pressure. If the reading on... Problem 62P: Reconsider Prob. 161. Using appropriate software, investigate the effect of the manometer fluid... Problem 63P: A manometer containing oil ( = 850 kg/m3) is attached to a tank filled with air. If the oil-level... Problem 64P: A manometer is used to measure the air pressure in a tank. The fluid used has a specific gravity of... Problem 65P: A mercury manometer ( = 13.600 kg/m3) is connected to an air duct to measure the pressure inside.... Problem 66P: Repeat Prob. 165 for a differential mercury height of 45 mm. Problem 67P: The pressure in a natural gas pipeline is measured by the manometer shown in Fig. P167E with one of... Problem 68P: Repeat Prob. 167E by replacing air with oil with a specific gravity of 0.69. Problem 69P: Blood pressure is usually measure by wrapping a closed air-filled jacket equipped with a pressure... Problem 70P: The maximum blood pressure in the upper arm of a healthy parson is about 120 mmHg. If a vertical... Problem 71P: Consider a U-tube whose arms are open to the atmosphere. Now water is poured into the U-tube from... Problem 72P: Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown in Fig. P172. If the specific... Problem 73P: Calculate the absolute pressure. P1, of the manometer shown In Fig. 173 in kPa. The local... Problem 74P: Consider the manometer in Fig. 173. If the specific weight of fluid A is 100 kN/m5, what is the... Problem 75P: Consider the manometer in Fig. 173. If the specific weight of fluid B is 20 kN/m3, what is the... Problem 76P: The hydraulic lift in a car repair shop has an output diameter of 30 cm and is to lift cars up to... Problem 77P: Consider the system shown in Fig. 177. If a change of 0.7 kPa in the pressure of air causes the... Problem 78P: The gage pressure of the air in the tank shown in Fig. 178 is measured to be 80 kPa. Determine the... Problem 79P: Repeat Prob. 178 for a gage pressure of 40 kPa. Problem 80P: What is the value of the engineering software packages in (a) engineering education and (b)... Problem 81P: Determine a positive real root of this equation using appropriate software: 2x210x0.53x=3 Problem 82P: Solve this system of two equations with two unknowns using appropriate software: x3y2=5.93xy+y=3.5 Problem 83P: Solve this system of three equations with three unknowns using appropriate software:... Problem 84P: Solve this system of three equations with three unknowns using appropriate software:... Problem 85RP: The reactive force developed by a jet engine to push an airplane forward is called thrust, and the... Problem 86RP: The reactive force developed by a jet engine to push an airplane forward is called thrust, and the... Problem 87RP: A man goes to a traditional market to buy a steak for dinner. He finds a 12-oz steak (1 lbm = 16 oz)... Problem 88RP: What is the weight of a 1-kg substance in N, kN, kgm/s2, kgf, lbmft/s2, and lbf? Problem 89RP: The pressure in a steam boiler is given to be 92 kgf/cm2. Express this pressure in psi, kPa, atm,... Problem 90RP: A hydraulic lift is to be used to lift a 1900-kg weight by putting a weight of 25 kg on a piston... Problem 91RP: The average atmosphere pressure on earth is approximated as a function of attitude by the relation... Problem 92RP: Hyperthermia of 5C (i.e., 5C rise above the normal body temperature) is considered fatal. Express... Problem 93RP: The boiling temperature of water decreases by about 3C for each 1000-m rise in altitude. What is the... Problem 94RP: A house is losing heat at a rate of 1800 kJ/h per C temperature difference between the indoor and... Problem 95RP: The average body temperature of a person rises by about 2C during strenuous exercise. What is the... Problem 96RP: The average temperature of the atmosphere in the world is approximated as a function of altitude by... Problem 97RP: A vertical, frictionless pistoncylinder device contains a gas at 180 kPa absolute pressure. The... Problem 98RP: A vertical pistoncylinder device contains a gas at a pressure of 100 kPa. The piston has a mass of... Problem 99RP: The force generated by a spring is given by F = kx, where k is the spring constant and x is the... Problem 100RP: An air-conditioning system requires a 35-m-long section of 15-cm-diameier ductwork to be laid... Problem 101RP: Balloons are often filled with helium gas because it weighs only about one-seventh of what air... Problem 102RP: Reconsider Prob. 1101. Using appropriate software, investigate the effect of the number of people... Problem 103RP: Determine the maximum amount of load, in kg, the balloon described in Prob. 1101 can carry Answer:... Problem 104RP: The lower half of a 6-m-high cylindrical container is filled with water ( = 1000 kg/m3) and the... Problem 105RP: A pressure cooker cooks a lot faster than an ordinary pan by maintaining a higher pressure and... Problem 106RP: The pilot of an airplane reads the altitude 6400 m and the absolute pressure 45 kPa when flying over... Problem 107RP: A glass tube is attached to a water pipe, as shown in Fig. 1107. If the water pressure at the bottom... Problem 108RP: Consider a U-tube whose arms are open to the atmosphere. Now equal volumes of water and light oil (... Problem 109RP: A water pipe is connected to a double-U manometer as shown m Fig. 1109E at a location where the... Problem 110RP: A gasoline line is connected to a pressure gage through a double-U manometer, as shown in Fig. 1110.... Problem 111RP: Repeat Prob. 1110 for a pressure gage reading of 180 kPa. Problem 112RP: When measuring small pressure differences with a manometer, often one arm of the manometer is... Problem 113RP: Pressure transducers are commonly used to measure pressure by generating analog signals usually in... Problem 114RP: Consider the flow of air through a wind turbine whose blades sweep an area of diameter D (in m). The... Problem 115RP: The drag force exerted on a car by air depends on a dimensionless drag coefficient, the density of... Problem 116RP: It is well known that cold air feels much colder in windy weather than what the thermometer reading... Problem 117RP: Reconsider Prob. 1116E. Using appropriate software, plot the equivalent wind chill temperatures in F... Problem 118FEP: During a heating process, the temperature of an object rises by 10C. This temperature rise is... Problem 119FEP: An apple loses 3.6 kJ of heat as it cools per C drop in its temperature. The amount of heat loss... Problem 120FEP: At sea level, the weight of 1 kg mass in SI units is 9.81 N. The weight of 1 lbm mass in English... Problem 121FEP: Consider a fish swimming 5 m below the free surface of water. The increase in the pressure exerted... Problem 122FEP: The atmospheric pressures at the top and the bottom of a building are read by a barometer to be 96.0... Problem 123FEP: Consider a 2.5-m-deep swimming pool. The pressure difference between the top and bottom of the pool... format_list_bulleted


 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning