
Concept explainers
Answer the following questions about aldosterone, a compound that helps to control the absorption of Na+and Cl- ions in the kidneys and, as a result, affects water retention.
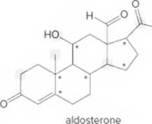
- Identify the
functional groups. - Draw in all lone pairs on O atoms.
- How many C’s does aldosterone contain?
- How many H’s are present at each C labeled with an asterisk (*)?
- Give the shape around each atom labeled in gray.
- Label all polar bonds.
(a)
Interpretation:
The functional group in aldosterone should be midentified.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the atoms or group of atoms that gives chemical properties to an organic compound and also chemical reactivity centre. Examples of functional groups are aldehyde, ketone, alcohol, double bond.
Answer to Problem 83P
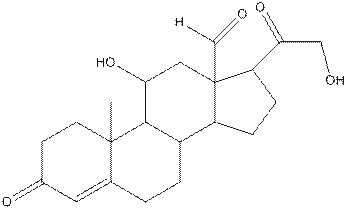
In aldosterone, functional groups present are alcohol, aldehyde, ketone and alkene.
Explanation of Solution
Functional groups are the atoms or group of atoms that gives chemical properties to an organic compound and also chemical reactivity centre. Structures of different functional groups are as follows:
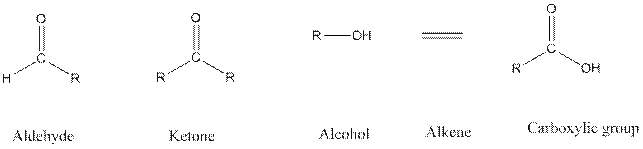
R represents any alkyl chain.
In functional group ketone carbonyl carbon is bonded to two alkyl groups, in aldehyde carbonyl carbon is attached to one alkyl group and one hydrogen atom, in alcohol functional group an −OH is bonded to an alkyl group.
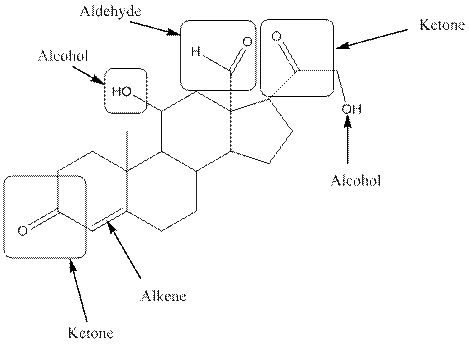
The compound aldosterone consists of two alcohol frunctional group, two ketone functional groups and one aldehyde functional group and one alkene. So, four types of functional group, that is, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone and alkene.
(b)
Interpretation:
All the lone pairs on oxygen atom of aldosterone should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxygen atom has six valence electrons. The electrons which are used in bond formation are called bonding electrons. The electrons that remain on an atom after bond formation are called lone pair electrons.
Answer to Problem 83P
The structure of aldosterone having all lone pairs on oxygen atom is,
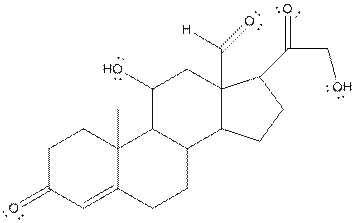
Explanation of Solution
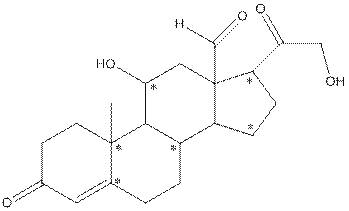
The structure of aldosterone is as follows:
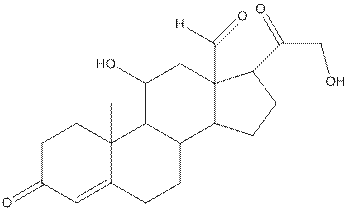
In the compound, three double bonded oxygen atoms present. Oxygen has six valence electrons. Two electrons in all double bonded oxygen atoms are used for formation of double bond. Remaining four electrons present as two lone pair. Also the compound contains three single bonded oxygen atoms. One electron is used for making O-H bond and one electron is used for making O-C bond. Remaining four electrons present as two lone pairs on each single bonded oxygen atom. Hence, the structure having all lone pairs on oxygen atom is,
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of carbon atoms in the structure of aldosterone should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
Answer to Problem 83P
Twenty one carbon atoms present in the aldosterone.
Explanation of Solution
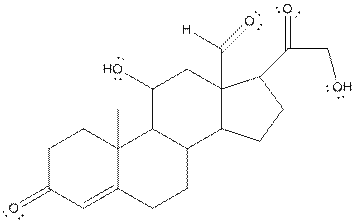
The structure of aldosterone is given as follows:
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
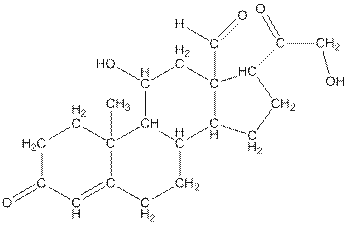
Hence, twenty one carbon atoms present in the compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of hydrogen atoms present in the * carbon atoms in aldosterone should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
Answer to Problem 83P
The * carbon atoms have total five hydrogen atoms.
Explanation of Solution
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
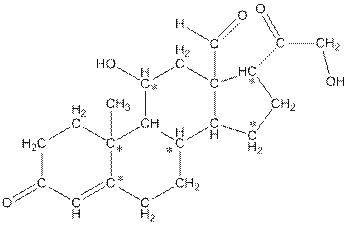
Hence, the * carbon atoms have total five hydrogen atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:
The shape around each indicated carbon atom in aldosterone should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The following table should be used while determining the shape around an atom.
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
Answer to Problem 83P
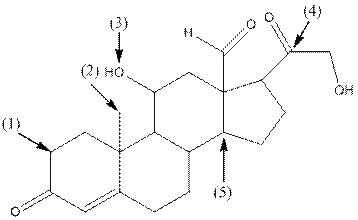
- Shape around carbon (1) is tetrahedral, shape around carbon (2) is tetrahedral, shape around oxygen (3) is bent, shape around carbon (4) is trigonal planar and shape around carbon (5) is tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
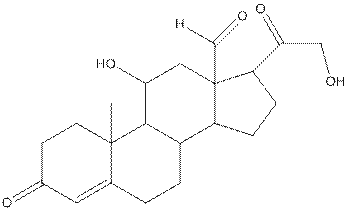
The complete structure of aldosterone is as follows:
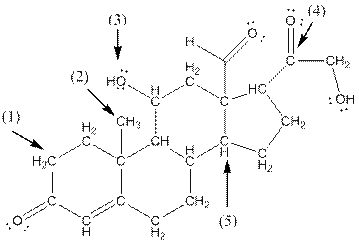
- Carbon (1) has four groups ( two hydrogen and two carbon) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (1) is tetrahedral.
- Carbon (2) has four groups (three hydrogen and one carbon) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (2) is tetrahedral.
- Oxygen (3) has two groups (one carbon and one hydrogen) and two lone pairs surrounding it. So, shape around oxygen (3) is bent.
- Carbon (4) has three groups (two carbon and one oxygen) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (4) is trigonal planar.
- Carbon (5) has four groups (three carbon and one hydrogen) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (5) is tetrahedral.
(f)
Interpretation:
All the polar bonds in aldosterone should be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 83P
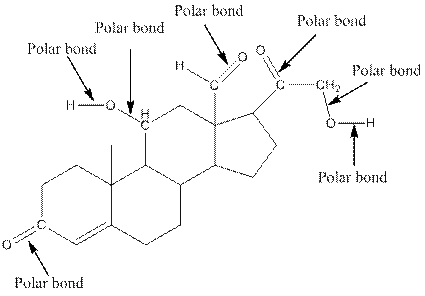
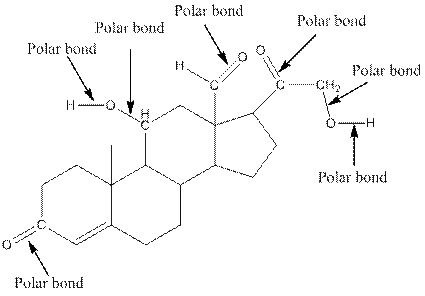
The structure of aldosterone with all polar bonds is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
In organic compound, most of the polar bonds formed between carbon and heteroatoms like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. To identify the polar bonds in the compound aldosterone, find the bonds between carbon and oxygen or oxygen and hydrogen because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. In aldostrone, five polar bonds are formed between carbon and oxygen (oxygen is more electronegative than carbon) and two polar bonds present between oxygen and hydrogen (oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen). Thus, the polar bonds are:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Please answer the questions in the photos and please revise any wrong answers. Thank youarrow_forward(Please be sure that 7 carbons are available in the structure )Based on the 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT 135 NMR and DEPT 90 NMR, provide a reasoning step and arrive at the final structure of an unknown organic compound containing 7 carbons. Dept 135 shows peak to be positive at 128.62 and 13.63 Dept 135 shows peak to be negative at 130.28, 64.32, 30.62 and 19.10.arrow_forward-lease help me answer the questions in the photo.arrow_forward
- For the reaction below, the concentrations at equilibrium are [SO₂] = 0.50 M, [0] = 0.45 M, and [SO3] = 1.7 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K? 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) Report your answer using two significant figures. Provide your answer below:arrow_forwardI need help with this question. Step by step solution, please!arrow_forwardZn(OH)2(s) Zn(OH)+ Ksp = 3 X 10-16 B₁ = 1 x 104 Zn(OH)2(aq) B₂ = 2 x 1010 Zn(OH)3 ẞ3-8 x 1013 Zn(OH) B4-3 x 1015arrow_forward
- Help me understand this by showing step by step solution.arrow_forwardscratch paper, and the integrated rate table provided in class. our scratch work for this test. Content attribution 3/40 FEEDBACK QUESTION 3 - 4 POINTS Complete the equation that relates the rate of consumption of H+ and the rate of formation of Br2 for the given reaction. 5Br (aq) + BrO3 (aq) + 6H (aq) →3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l) • Your answers should be whole numbers or fractions without any decimal places. Provide your answer below: Search 尚 5 fn 40 * 00 99+ 2 9 144 a [arrow_forward(a) Write down the structure of EDTA molecule and show the complex structure with Pb2+ . (b) When do you need to perform back titration? (c) Ni2+ can be analyzed by a back titration using standard Zn2+ at pH 5.5 with xylenol orange indicator. A solution containing 25.00 mL of Ni2+ in dilute HCl is treated with 25.00 mL of 0.05283 M Na2EDTA. The solution is neutralized with NaOH, and the pH is adjusted to 5.5 with acetate buffer. The solution turns yellow when a few drops of indicator are added. Titration with 0.02299 M Zn2+ requires 17.61 mL to reach the red end point. What is the molarity of Ni2+ in the unknown?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

