
(a)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration which is likely to form negative ion needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An element that by accepting electron will achieve a half-filled or full-filled electronic configuration will likely to form a negative ion.
(a)
Answer to Problem 74A
Explanation of Solution
If the
(b)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration which is likely to have low ionization energy needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Removal of an electron that will give the most stable half-filled and full-filled electronic configuration will have the lowest ionization energy.
(b)
Answer to Problem 74A
Explanation of Solution
When an electron is removed from
Now,
(c)
Interpretation:
The most reactive metal is to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Metals which easily donate electrons to achieve stable half-filled or full-filled configuration are most reactive. Alkali metals are reactive due to their electronic configuration.
(c)
Answer to Problem 74A
Explanation of Solution
If the
Now,
(d)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration which is likely to have more unpaired of electrons needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
When an electron does not get paired up in orbital but occupies the orbital singly then it is called an unpaired electron.
(d)
Answer to Problem 74A
Explanation of Solution
Orbital diagram of
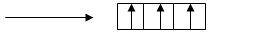
It is obvious from the diagram that there are three unpaired electrons which is highest among the options given.
(e)
Interpretation:
The metal that will combine with oxygen in
Concept Introduction:
A metal which can donate two electrons from its valence to complete the octet of oxygen will combine with oxygen in
(e)
Answer to Problem 74A
Explanation of Solution
Magnesium (Mg) will donate two electrons from its
(f)
Interpretation:
The formula the compound formed between
Concept Introduction:
A stable compound is formed when both the atoms participating in the combination achieves complete octet.
(f)
Answer to Problem 74A
The formula of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
So, 3
(g)
Interpretation:
The formula the compound formed between
Concept Introduction:
A stable compound is formed when both the atoms participating achieves complete octet.
(g)
Answer to Problem 74A
The formula of the compound is
Explanation of Solution
Three
(h)
Interpretation:
The order of ionization energy needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Ionization energy is a measure of the difficulty in removing an electron from an atom or ion or the tendency of an atom or ion to lose an electron. It is the energy required. So, this process is endothermic.
(h)
Answer to Problem 74A
Order of increase in ionization energy is
Explanation of Solution
- The ionization energy of the elements usually increases throughout the period.
- The ionization energy of the elements usually decreases throughout the group.
- Ionization energies of noble gases are very high because of octet completion. That is why neon has the highest ionization energy of all the elements given.
Considering all facts, the order of increasing ionization energy is
Chapter 11 Solutions
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
- Extra for Experts: Your Future in Chemistry. As you now know, there are countless jobs that involve chemistry! Research a chemistry profession that interests you. In your answer, discuss which aspects of the job most appeal to you.arrow_forwardMISSED THIS? Read Section 19.9 (Pages 878-881); Watch IWE 19.10 Consider the following reaction: CH3OH(g) CO(g) + 2H2(g) (Note that AG,CH3OH(g) = -162.3 kJ/mol and AG,co(g)=-137.2 kJ/mol.) Part A Calculate AG for this reaction at 25 °C under the following conditions: PCH₂OH Pco PH2 0.815 atm = 0.140 atm 0.170 atm Express your answer in kilojoules to three significant figures. Ο ΑΣΦ AG = -150 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer □? kJ × Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining Calculate the free energy change under nonstandard conditions (AGrxn) by using the following relationship: AGrxn = AGrxn + RTInQ, AGxn+RTInQ, where AGxn is the standard free energy change, R is the ideal gas constant, T is the temperature in kelvins, a is the reaction quotient. Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forwardIdentify and provide a brief explanation of Gas Chromatography (GC) within the context of chemical analysis of food. Incorporate the specific application name, provide a concise overview of sample preparation methods, outline instrumental parameters and conditions ultilized, and summarise the outcomes and findings achieved through this analytical approach.arrow_forward
- Identify and provide a concise explanation of the concept of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the context of chemical analysis. Provide specific examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide a concise explanation of a specific analytical instrument capable of detecting and quantifying trace compounds in food samples. Emphasise the instrumental capabilities relevant to trace compound analysis in the nominated food. Include the specific application name (eg: identification and quantification of mercury in salmon), outline a brief description of sample preparation procedures, and provide a summary of the obtained results from the analytical process.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of what 'Seperation Science' is. Also describe its importance with the respect to the chemical analysis of food. Provide specific examples.arrow_forward
- 5. Propose a Synthesis for the molecule below. You may use any starting materials containing 6 carbons or less (reagents that aren't incorporated into the final molecule such as PhзP do not count towards this total, and the starting material can have whatever non-carbon functional groups you want), and any of the reactions you have learned so far in organic chemistry I, II, and III. Your final answer should show each step separately, with intermediates and conditions clearly drawn. H3C CH3arrow_forwardState the name and condensed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardState the name and condensed formula of the isothiazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and thiosemicarbazide.arrow_forward
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





