
One of the popular demonstrations in science museums involves the suspension of a ping-pong ball by an upward air jet. Children are amused by the ball always coming back to the center when it is pushed by a finger to the side of the jet. Explain this phenomenon using the Bernoulli equation. Also determine the velocity of air if the ball has a mass of 3.1 g and a diameter of 4.2 cm. Assume the air is at 1 atm and 25°C. 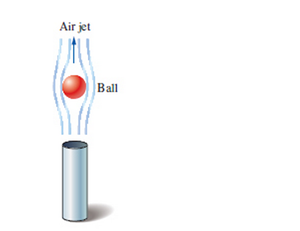
FIGURE P11-68
The velocity of air and an explanation of the phenomenon using Bernoulli equation.
Answer to Problem 68P
The velocity of the air is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the ball is
Write the expression for the drag force acting on the ball.
Here, the drag ball on the ball is
Write the expression for the buoyancy force acting on the ball.
Here, the buoyancy force is
Write the expression for the weight of the body.
Here, the weight of the body is
Write the expression for the Reynolds number.
Here, the Reynolds number is
Write the expression for the weight of the ball.
Here, the mass of the ball is
Write the expression for the Bernoulli's equation.
Here, the pressure at the point 1 is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer the Table-11.2, "Representative drag coefficients for various three dimensional bodies based on the frontal area for Reynolds number unless stated otherwise" to obtain the value of the coefficient of drag is
Substitute
Refer the Table-B-1, "Physical properties of air at standard atmospheric Pressure" to obtain the value of the kinematic viscosity is
Substitute
By using the Bernoulli's equation, the datum at the point 1 is lesser then the datum at the point 2. If the ball is pushed by the finger to the side of the jet, the ball will come back to the centre of the jet. This is so because, in the middle portion of the jet, the velocity is higher than the velocity at point 1, which is,
Conclusion:
The velocity of the air is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Q10) Body A weighs 600 lb contact with smooth surfaces at D and E. Determine the tension in the cord and the forces acting on C on member BD, also calculate the reaction at B and F. Cable 6' 3' wwwarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forwardQ3: Find the resultant of the force system.arrow_forward
- Question 1 A three-blade propeller of a diameter of 2 m has an activity factor AF of 200 and its ratio of static thrust coefficient to static torque coefficient is 10. The propeller's integrated lift coefficient is 0.3.arrow_forward(L=6847 mm, q = 5331 N/mm, M = 1408549 N.mm, and El = 8.6 x 1014 N. mm²) X A ΕΙ B L Y Marrow_forwardCalculate the maximum shear stress Tmax at the selected element within the wall (Fig. Q3) if T = 26.7 KN.m, P = 23.6 MPa, t = 2.2 mm, R = 2 m. The following choices are provided in units of MPa and rounded to three decimal places. Select one: ○ 1.2681.818 O 2. 25745.455 O 3. 17163.636 O 4. 10727.273 ○ 5.5363.636arrow_forward
- If L-719.01 mm, = 7839.63 N/m³, the normal stress σ caused by self-weight at the location of the maximum normal stress in the bar can be calculated as (Please select the correct value of σ given in Pa and rounded to three decimal places.) Select one: ○ 1. 1409.193 2. 845.516 O 3. 11273.545 ○ 4.8455.159 ○ 5.4509.418 6. 2818.386 7.5636.772arrow_forwardTo calculate the rotation at Point B, a suitable virtual structure needs to be created. Which equation in the following choices most accurately represents the functional relationship between the bending moment, Mv2 ( Units: N.mm), of the virtual structure and the spatial coordinate x (Units: mm) if the applied unit virtual moment is clockwise? Select one: O 1. Mv2 1.000 O 2. Mv2=x+1.000 O 3. Mv2=x+0.000 4. Mv2 = -x-1.000 O 5. Mv2 -1.000 6. Mv2=-x+0.000arrow_forwardThe vertical deflection at Point B can be calculated as ( The following choices are provided in units of mm and rounded to three decimal places ; the downward deflection is negative and upward deflection is positive. ) Select one: 1. 1703.065 2. -1703.065 3. -2043.679 4.1362.452 5. -1362.452 6. 2043.679arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





