
During major windstorms, high vehicles such as RVs and semis may be thrown off the road and boxcars off their tracks, especially when they are empty and in open areas. Consider a 6000-kg semi that is
10 m long, 2.5 m high, and 2 in wide. The distance between the bottom of the truck and the road is 0.8 in. Now the truck is exposed to winds from its side surface. Determine the wind velocity that will tip the truck over to its side. Take the air density to be 1.1 kg/m3 and assume the weight to be uniformly distributed.
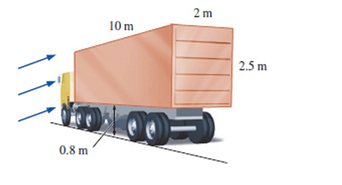
The wind velocity that will tip the truck over to its side.
Answer to Problem 43P
The wind velocity that will tip the truck over to its side is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the truck is
Write the expression of weight of the truck.
Here, the mass of the truck is
Write the expression of frontal area.
Here, the length of the truck is
The below figure represent the forces acting on the truck.
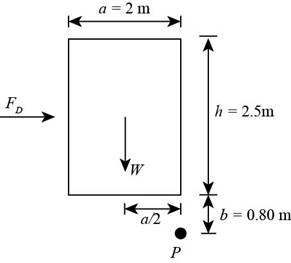
Figure-(1)
Write the expression of equilibrium of momentum about point
Here, the width of the truck is
Refer table 11.2 "Representative drag coefficient
Write the expression of drag force acting on the truck.
Here, the density of the air is
Write the expression of characteristics length of the truck.
Here, the perimeter of the truck is
Write the expression of perimeter of the truck.
Write the expression of Reynolds number.
Here, the kinematic viscosity is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer table A-9 "Properties of air" to find the value of kinematic viscosity of air as
Substitute
So, the Equation used for
Conclusion:
The wind velocity that will tip the truck over to its side is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
FLUID MECHANICS FUND. (LL)-W/ACCESS
- Heat energy is transferred to 1.36 kg of air which causes its temperature to increase from 40" CO 468°C. Calculate, for the two separate cases of heat transfer at (a) constant volume, (b) constant pressure: the quantity of heat energy transferred, (ii) the external work done, (iii) the increase in internal energy. Take cv and cp as 0.718 and 1.005 kJ/kgK respectivelyarrow_forwardA flat circular plate is 500 mm diameter. Calculate the theoretical quantity or heat radiated per hour when its temperature is 215°C and the temperature of its surrounds is 45°C. Take the value of the radiation constant to be 5.67 × 10^11 kJ/m2s K4.arrow_forwardDescribe Atmospheric Air and how it reacts with carbon in combustionarrow_forward
- 0.5 kg of ice at —5°C is put into a vessel containing 1.8kg of water at 17°C and mixed together, the result being a mixture of ice and water at 0°C. Calculate the final masses of ice and water, taking the water equivalent of the vessel to be 0.148 kg, specific heat of ice 2.04 kilkg K and latent heat of fusion 335 kJ/kg.arrow_forwardA condenser vacuum gauge reads 715 mmHg when the barometer stands at 757 mmHg. State the absolute pressure in the condenser in kN/m2 and bars.arrow_forwardSketch and Describe a timing diagram for a 2 stroke diesel enginearrow_forward
- Manipulate the formula for converting temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsiusarrow_forwardDefine Temperature, Pressure, and Absolute Temperature.arrow_forwardAn air reservoir contains 20 kg of air at 3200 kN/m2 gauge and 16°C. Calculate the new pressure and heat energy transfer if the air is heated to 35°C. Neglect any expansion of the reservoir, take R for air = 0.287 kJ/kgK, specific heat at constant volume c, = 0.718 kJFg K, and atmospheric pressure = 100 kN/m2arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





