
A 2-zn-high, 4-zn-wide rectangular advertisement panel is attached to a 4-rn-wide. 0.15-rn-high rectangular concrete block (density = 2300 kg/m3) by two 5-cm-diameter. 4-m-high (exposed part) poles, as shown in Fig. 11-96. If the sign is to withstand 150 kin/h winds from any direction, determine (a) the maximum drag force on the panel. (b) the drag force acting on the poles, and (c) the minimum length L of the concrete block for the panel to resist the winds. Take the density of air to be 1.30 kg/m3.
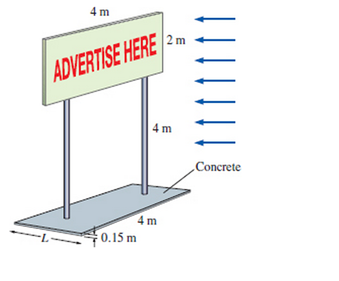
(a)
The maximum drag force on the panel.
Answer to Problem 96P
The maximum drag force on the panel is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The height of the rectangular advertisement panel is
Write the expression for the drag force for the panel.
Here, the drag force coefficient is
Write the expression for the frontal area of the panel.
Here, the height of the rectangular advertisement panel is
Calculation:
The drag coefficient for the turbulent flow for the thin rectangular plate is
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The maximum drag force on the panel is
(b)
The drag force acting on the pole.
Answer to Problem 96P
The drag force acting on the pole is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the frontal area of the pole.
Here, the diameter of the pole is
Write the expression for the drag force for the pole.
Calculation:
The drag coefficient for the turbulent flow for circular rod is
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The drag force acting on the pole is
(c)
The minimum length
Answer to Problem 96P
The minimum length
Explanation of Solution
Draw the diagram for the side view of the advertisement panel.
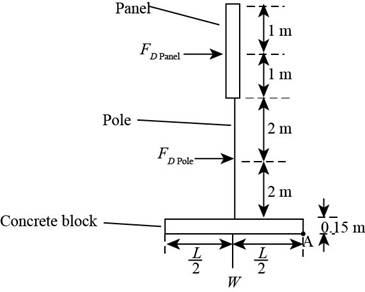
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the moment about point A.
Here, the minimum length of the concrete block for the panel to resist the winds is
Write the expression for the weight of the concrete block.
Here, the mass of the block is
Write the expression for the volume of the block.
Here, the height of the rectangular concrete block is
Write the expression for the mass of the block.
Here, the density of the concrete block is
Substitute
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The minimum length
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
FLUID MECHANICS FUND. (LL)-W/ACCESS
- 5. Estimate the friction pressure gradient in a 10.15 cm bore unheated horizontal pipe for the following conditions: Fluid-propylene Pressure 8.175 bar Temperature-7°C Mass flow of liquid-2.42 kg/s. Density of liquid-530 kg/m³ Mass flow of vapour-0.605 kg/s. Density of vapour-1.48 kg/m³arrow_forwardDescribe the following HVAC systems. a) All-air systems b) All-water systems c) Air-water systems Graphically represent each system with a sketch.arrow_forwardTwo large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of 6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If, initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt. A 6 L/min 0.2 kg/L x(t) 100 L 4 L/min x(0) = 0 kg 3 L/min 1 L/min B y(t) 100 L y(0) = 20 kg 2 L/min Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t≥ 0: Analytically (hand calculations) Using MATLAB Numerical Functions (ode45) Creating Simulink Model Plot all solutions on the same graph for the first 15 min. The graph must be fully formatted by code.arrow_forward
- ased on the corresponding mass flow rates (and NOT the original volumetric flow rates) determine: a) The mass flow rate of the mixed air (i.e., the combination of the two flows) leaving the chamber in kg/s. b) The temperature of the mixed air leaving the chamber. Please use PyscPro software for solving this question. Notes: For part (a), you will first need to find the density or specific volume for each state (density = 1/specific volume). The units the 'v' and 'a' are intended as subscripts: · kgv = kg_v = kgv = kilogram(s) [vapour] kga = kg_a =kga = kilogram(s) [air]arrow_forwardThe answers to this question s wasn't properly given, I need expert handwritten solutionsarrow_forwardI need expert handwritten solutions to this onlyarrow_forward
- Two large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of 6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If, initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt. A 6 L/min 0.2 kg/L x(t) 100 L 4 L/min x(0) = 0 kg 3 L/min B y(t) 100 L y(0) = 20 kg 2 L/min 1 L/min Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t > 0: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forwardTwo springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m₂ = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and k₂ = 2 N/m. www.m k₁ = 3 (y₁ = 0). m₁ = 1 k2=2 (y₂ = 0) |m₂ = 1 Y2 y 2 System in static equilibrium (Net change in spring length =32-31) System in motion Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system Determine the equations of motion y₁(t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forward100 As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is subjected to the harmonic external force f(t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forward
- this is answer to a vibrations question. in the last part it states an assumption of x2, im not sure where this assumption comes from. an answer would be greatly appreciatedarrow_forwardPlease answer with the sketches.arrow_forwardThe beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic material. Determine the shape factor for the cross section of the beam (Figure Q3). [Take σy = 250 MPa, yNA = 110.94 mm, I = 78.08 x 106 mm²] y 25 mm 75 mm I 25 mm 200 mm 25 mm 125 Figure Q3arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





