
(a)
Interpretation:
In the given phase diagram, whether the alloy Al-4% Si is hypo-eutectic or hyper-eutectic needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An alloy is a mixture of metals or the mixture of non-metals with another metal. A metallic bonding character defines alloys. For practical applications, the alloy constituents are generally evaluated by mass proportion and for fundamental science studies in the atomic fraction. Alloys are generally categorized as a replacement or interstitial alloys, based on the alloy's nuclear structure.
Answer to Problem 11.30P
The alloy is hypo-eutectic because its composition lies between eutectic reaction and eutectic composition.
Explanation of Solution
The phase diagram given is as follows:
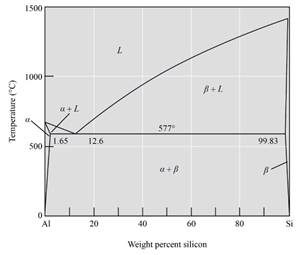
From the phase diagram oftheAl-Si alloy system,
The alloy is hypo-eutectic because the composition is between eutectic reaction and the eutectic composition, and it lies between 1.65% and 12.6%Si.
Thus, from the phase diagram of the Al-Si alloy system, this alloy is hypo-eutectic because the composition lies between eutectic reaction and eutectic composition.
(b)
Interpretation:
The composition of the first solid to form during solidification needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An alloy is a mixture of metals or the mixture of non-metals with another metal. A metallic bonding character defines alloys. For practical applications, the alloy constituents are generally evaluated by mass proportion and for fundamental science studies in the atomic fraction. Alloys are generally categorized as a replacement or interstitial alloys, based on the alloy's nuclear structure.
Answer to Problem 11.30P
The composition of the first form during solidification is 1%.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
It is given that % of Al=96%,wt. of Si=4gm, molar mass of Si=63.54 g/mol, molar mass of Al=26.891g/mol.
Calculations:
The formula for finding the composition of the first solid to form during solidification is,
Putting the values,
Thus,
%Si
Therefore, from the formula, the composition of first solid to form during solidification is 1%.
(c)
Interpretation:
The amounts and compositions of each phase at
Concept Introduction:
An alloy is a mixture of metals or the mixture of non-metals with another metal. A metallic bonding character defines alloys. For practical applications, the alloy constituents are generally evaluated by mass proportion and for fundamental science studies in the atomic fraction. Alloys are generally categorized as a replacement or interstitial alloys, based on the alloy's nuclear structure.
Answer to Problem 11.30P
The amounts and compositions of each phase at
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The given phase diagram is as follows:
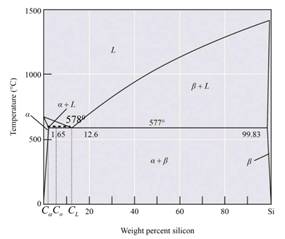
The above-given diagram is the phase diagram of the Al-Si alloy system for the eutectic temperature of
Calculations:
The eutectic reaction of the Al-Si alloy is in the form of
Thus, the liquid phase composition is
Thus, from the given phase diagram of Al-Si the amount and composition is
(d)
Interpretation:
The amounts and compositions at each phase and each micro-constituent at
Concept Introduction:
An alloy is a mixture of metals or the mixture of non-metals with another metal. A metallic bonding character defines alloys. For practical applications, the alloy constituents are generally evaluated by mass proportion and for fundamental science studies in the atomic fraction. Alloys are generally categorized as a replacement or interstitial alloys, based on the alloy's nuclear structure.
Answer to Problem 11.30P
The amounts and compositions of each phase at
Explanation of Solution
GivenInfromation:
The below diagram is the phase diagram of the Al-Si alloy system of eutectic temperature at
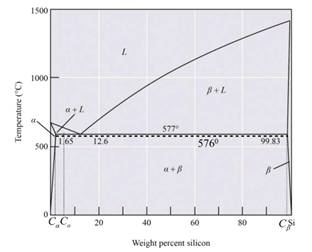
Calculation:
For the Al-Si alloy, the eutectic phase reaction is in the form of
Therefore, the solid phase is calculated as,
The Al-Si alloy contains two stages. Therefore, the Al-Si alloy micro-constituent is primary and eutectic. Solid forming before an alloy is cooled to eutectic temperature is known as the primary micro-constituent and the strong forming is known as eutectic after the cooling temperature. The structure of micro-constituents is the primary
Thus from the phase diagram of Al-Si, the amounts and compositions of each phase at
(e)
Interpretation:
The amounts and compositions at each phase
Concept Introduction:
An alloy is a mixture of metals or the mixture of non-metals with another metal. A metallic bonding character defines alloys. For practical applications, the alloy constituents are generally evaluated by mass proportion and for fundamental science studies in the atomic fraction. Alloys are generally categorized as a replacement or interstitial alloys, based on the alloy's nuclear structure.
Answer to Problem 11.30P
The amounts and compositions of each phase at
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
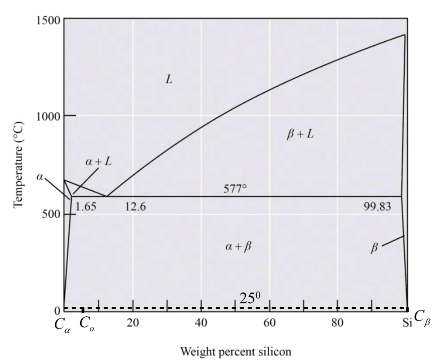
The above diagram is the phase diagram of the Al-Si alloy system of eutectic temperature at
Calculation:
For the Al-Si alloy, the eutectic phase reaction is in the form of
Therefore, the solid phase is calculated as,
Thus from the phase diagram of Al-Si the amounts and compositions of each phase at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, SI Edition
- 1. The rotating steel shaft is simply supported by bearings at points of B and C, and is driven by a spur gear at D, which has a 6-in pitch diameter. The force F from the drive gear acts at a pressure angle of 20°. The shaft transmits a torque to point A of TA =3000 lbĘ in. The shaft is machined from steel with Sy=60kpsi and Sut=80 kpsi. (1) Draw a shear force diagram and a bending moment diagram by F. According to your analysis, where is the point of interest to evaluate the safety factor among A, B, C, and D? Describe the reason. (Hint: To find F, the torque Tд is generated by the tangential force of F (i.e. Ftangential-Fcos20°) When n=2.5, K=1.8, and K₁ =1.3, determine the diameter of the shaft based on (2) static analysis using DE theory (note that fatigue stress concentration factors need to be used for this question because the loading condition is fatigue) and (3) a fatigue analysis using modified Goodman. Note) A standard diameter is not required for the questions. 10 in Darrow_forward3 N2=28 P(diametral pitch)=8 for all gears Coupled to 25 hp motor N3=34 Full depth spur gears with pressure angle=20° N₂=2000 rpm (1) Compute the circular pitch, the center-to-center distance, and base circle radii. (2) Draw the free body diagram of gear 3 and show all the forces and the torque. (3) In mounting gears, the center-to-center distance was reduced by 0.1 inch. Calculate the new values of center-to-center distance, pressure angle, base circle radii, and pitch circle diameters. (4)What is the new tangential and radial forces for gear 3? (5) Under the new center to center distance, is the contact ratio (mc) increasing or decreasing?arrow_forward2. A flat belt drive consists of two 4-ft diameter cast-iron pulleys spaced 16 ft apart. A power of 60 hp is transmitted by a pulley whose speed is 380 rev/min. Use a service factor (Ks) pf 1.1 and a design factor 1.0. The width of the polyamide A-3 belt is 6 in. Use CD=1. Answer the following questions. (1) What is the total length of the belt according to the given geometry? (2) Find the centrifugal force (Fc) applied to the belt. (3) What is the transmitted torque through the pulley system given 60hp? (4) Using the allowable tension, find the force (F₁) on the tight side. What is the tension at the loose side (F2) and the initial tension (F.)? (5) Using the forces, estimate the developed friction coefficient (f) (6) Based on the forces and the given rotational speed, rate the pulley set. In other words, what is the horse power that can be transmitted by the pulley system? (7) To reduce the applied tension on the tight side, the friction coefficient is increased to 0.75. Find out the…arrow_forward
- The tooth numbers for the gear train illustrated are N₂ = 24, N3 = 18, №4 = 30, №6 = 36, and N₁ = 54. Gear 7 is fixed. If shaft b is turned through 5 revolutions, how many turns will shaft a make? a 5 [6] barrow_forwardplease explain step by step and use the ACI codearrow_forwardFind: 1. The support reactions 2. Internal forces (shear, and moments) 3. Deflectionarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





