
(a)
Interpretation:
The total
Concept Introduction:
The compound formula of Lead-Tin alloy is designated by 'Pb-Sn'.
- It appears in solid form.
- It appears in various shapes like wire, ingot, foil, bar, ribbon etc.
- It appears in silver color.
- Its melting point is 182-215 degree Celsius.
Lead-Tin are widely used as soldering alloys. They are compatible for all types of uses.
Answer to Problem 11.26P
The Total %
Explanation of Solution
Given:
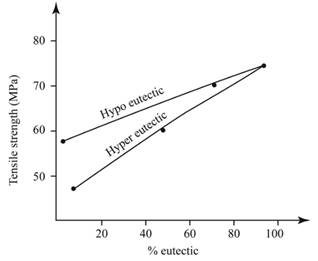
Calculations:
From the graph,
For %
% Eutectic = 0.
Thus, the evaluated value of %
(b)
Interpretation:
The total
Concept Introduction:
The compound formula of Lead-Tin alloy is designated by 'Pb-Sn'.
- It appears in solid form.
- It appears in various shapes like wire, foil, bar, ribbon etc.
- It appears in silver color.
- Its melting point is 182-215 degree Celsius.
Lead-Tin are widely used as soldering alloys. They are compatible for all types of uses.
Answer to Problem 11.26P
The Total %
Explanation of Solution
Given:
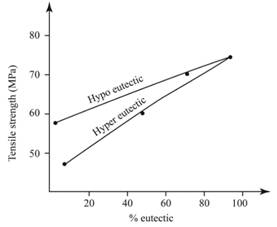
Calculations:
From the graph,
For %
% Eutectic =
The evaluated value of %
(c)
Interpretation:
The total
Concept Introduction:
The compound formula of Lead-Tin alloy is designated by 'Pb-Sn'.
- It appears in solid form.
- It appears in various shapes like wire, foil, bar, ribbon etc.
- It appears in silver color.
- Its melting point is 182-215 degree Celsius.
Lead-Tin are widely used as soldering alloys. They are compatible for all types of uses.
Answer to Problem 11.26P
The Total %
Explanation of Solution
Given:
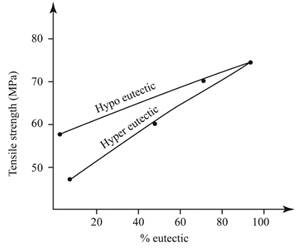
Calculations:
From the diagram,
For %
% Eutectic =
The evaluated value of %
(d)
Interpretation:
The total
Concept Introduction:
The compound formula of Lead-Tin alloy is designated by 'Pb-Sn'.
- It appears in solid form.
- It appears in various shapes like wire,foil, bar, ribbon etc.
- It appears in silver color.
- Its melting point is 182-215 degree Celsius.
Lead-Tin are widely used as soldering alloys. They are compatible for all types of uses.
Answer to Problem 11.26P
The Total %
Explanation of Solution
Given:
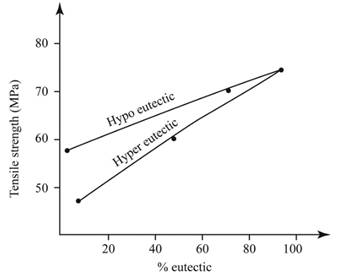
Calculations:
From the graph,
For %
% Eutectic =
The evaluated value of %
(e)
Interpretation:
The total
Concept Introduction:
The compound formula of Lead-Tin alloy is designated by 'Pb-Sn'.
- It appears in solid form.
- It appears in various shapes like wire, foil, bar, ribbon etc.
- It appears in silver color.
- Its melting point is 182-215 degree Celsius.
Lead-Tin are widely used as soldering alloys. They are compatible for all types of uses.
Answer to Problem 11.26P
The Total %
Explanation of Solution
Use spreadsheet to tabulate the % total
| Composition of % in entire phase diagram | Tensile Strength ( | Total % phase | % Eutectic |
| 10 | 30 | 8.2 | 0 |
| 20 | 40 | 18.6 | 2.3 |
| 50 | 50 | 49.5 | 72.3 |
| 60 | 60 | 59.8 | 95.6 |
| 80 | 70 | 80.4 | 49.6 |
| 95 | 80 | 95.9 | 7 |
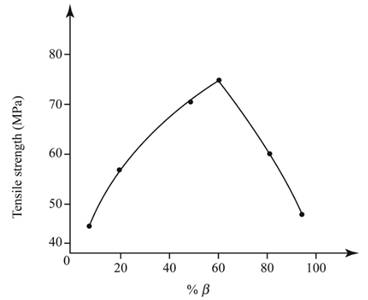
Given:
Calculations:
From the graph:
For %
% Eutectic =
Thus, by using the expression of eutectic, the required value obtained is 49.2%.
(f)
Interpretation:
The total
Concept Introduction:
The compound formula of Lead-Tin alloy is designated by 'Pb-Sn'.
- It appears in solid form.
- It appears in various shapes like wire, foil, bar, ribbon etc.
- It appears in silver color.
- Its melting point is 182-215 degree Celsius.
Lead-Tin are widely used as soldering alloys. They are compatible for all types of uses.
Answer to Problem 11.26P
The Total %
Explanation of Solution
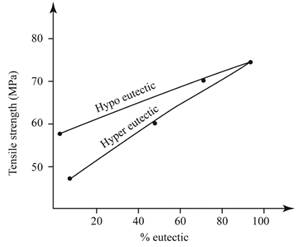
Given:
Calculations:
For %
% Eutectic =
(Mention Graph)
After Studying the graph of tensile strength vs %
The evaluated value of %
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, SI Edition
- A mass of ideal gas in a closed piston-cylinder system expands from 427 °C and 16 bar following the process law, pv1.36 = Constant (p times v to the power of 1.36 equals to a constant). For the gas, initial : final pressure ratio is 4:1 and the initial gas volume is 0.14 m³. The specific heat of the gas at constant pressure, Cp = 0.987 kJ/kg-K and the specific gas constant, R = 0.267 kJ/kg.K. Determine the change in total internal energy in the gas during the expansion. Enter your numerical answer in the answer box below in KILO JOULES (not in Joules) but do not enter the units. (There is no expected number of decimal points or significant figures).arrow_forwardheat and mass transferarrow_forwardA lighting load of 600 kW and a motor load of 707 kW at 0.707 p.f lagging are supplied by two alternators running in parallel. One machine supplies 900 kW at 0.9 p.f lagging. Find the load sharing and p.f of second machine?arrow_forward
- heat and mass transferarrow_forwardDevelop a signal design and timing for the intersection shown in the figure below. In each case accommodate both vehicular and pedestrian movements. In general, use the following values for the problem: pedestrian walking speed = 1 [m/s], vehicle deceleration = 3 [m/s²], driver reaction time = 1.5 [s], length of vehicle = 6 [m], and level grade = 0. If you need to assume other variables and parameters to solve this problem clearly state that in your report and explain the reason. A250 1100 One-way Speed limit = 50 [km/h] Pedestrian = 15 per each crosswalk Crosswalk widths = 3 [m] Lane width = 4 [m] Saturation flow = 1800 [veh/h/lane] 1100 ↑ 200 70 80 900arrow_forwardhow land use and urban structure contribute to financial stability or instability.arrow_forward
- Please draw out the circuitsarrow_forwardQ1 parts B and C but plz draw it out or something plz put it on a bread board with resistors and a voltage source please do not show it in the schematic way like in the picture there if you can show it on like thinkercadarrow_forwardQ2 but when you get to part 3, can you please draw it outarrow_forward
- please solve manually. I need the drawing and the values too. Thank you!arrow_forwardSketch the effective stress profile for the silt layer to a depth of 5 meters for a uniform layer of silt having a depth to the water table of 4 m (choose several discrete points with depth and plot by hand). Use Bishop's definition of effective stress for the silt layer, assuming x =S.. Assume a value of G. = 2.65 and that the gravimetric water content of the silt below the water table is 20%. Use the SWRC for the silt from the figure below. Assume that the air pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure (i.e., zero). Consider variations in total unit weight with the degree of saturation in your calculations. 100000 a. 10000 Sand: a = 0.3 kPa, n = 3.0 Silt: a=0.05 kPa, n=2.5 0.01 kPa, n = 1.8 1000 Clay: Matric suction (kPa) 00 100 10 10 1 0.1 ° 20 60 80 40 Saturation (%) 100 10arrow_forwardTwo alternators, Y-connected 6.6 kV supply a load of 3000 kW at 0.8 p.f lagging. The synchronous mpedance of first alternator is (0.5+j10) Q/ph and second alternator is (0.4+j12) /ph. First alternator delivers 150 amp at 0.875 lag p.f. The two alterators are shared load equally. Determine the current, p.f., induced e.m.f, load angel, and maximum developed power of each alternator?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





