
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
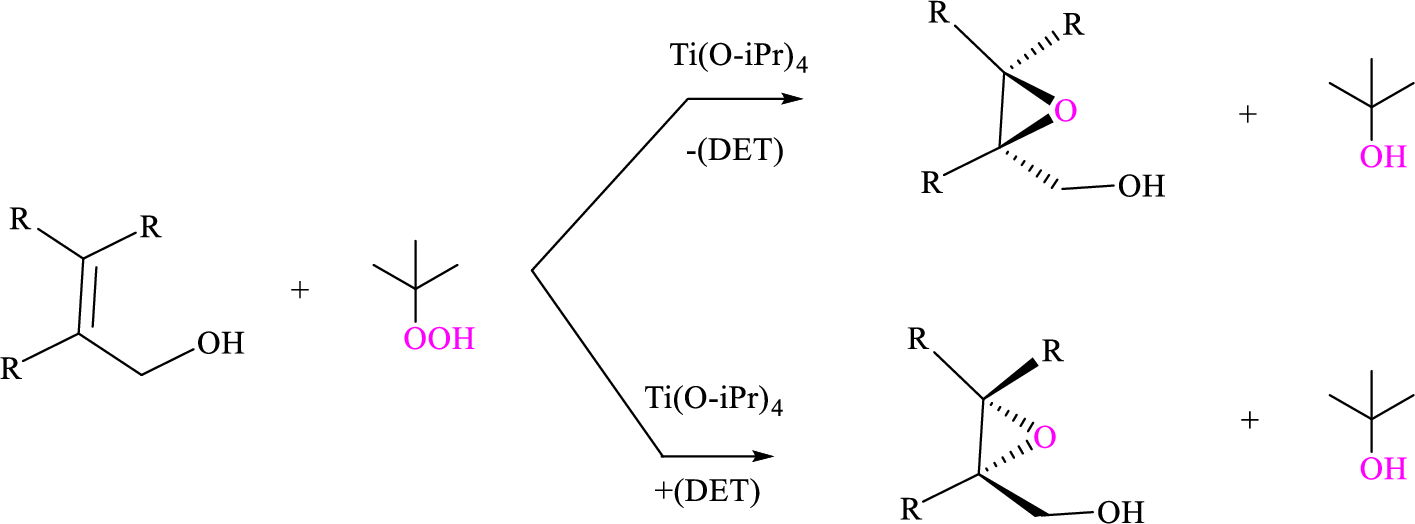
Using Sharpless epoxidation, the allylic alcohol that can be used to prepare the given enantiomer has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Sharpless asymmetric epoxidation: Titanium-catalyzed asymmetric epoxidation of primary allylic alcohols is proposed by the Barry Sharpless known as Sharpless epoxidation. The reagent consists of tert-butyl hydroperoxide, titanium tetraisoproxide
Sharpless epoxidation is stereospecific based on the diethyl tartrate
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forward
- At 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forwardHow many grams of solid NaCN have to be added to 1.5L of water to dissolve 0.18 mol of Fe(OH)3 in the form Fe(CN)63 - ? ( For simplicity, ignore the reaction of CN - ion with water) Ksp for Fe(OH)3 is 2.8E -39, and Kform for Fe(CN)63 - is 1.0E31arrow_forward
- Draw the most stable chair conformation of 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane, clearly showing the axial and equatorial substituents. [4] Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC name for each of the following compounds; [5] i) 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane ii) trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexane iii) Cyclobutylcycloheptane iv) cis-1,4-di-isopropylcyclohexane (chair conformation) v) 3-Ethyl-5-isobutylnonanearrow_forwardDraw and name molecules that meet the following descriptions; [4] a) An organic molecule containing 2 sp2 hybridised carbon and 1 sp-hybridised carbon atom. b) A cycloalkene, C7H12, with a tetrasubstituted double bond. Also answer question 2 from the imagearrow_forwardH 14. Draw the line angle form of the following molecule make sure you use the proper notation to indicate spatial positioning of atoms. F F H 15. Convert the following condensed form to line angle form: (CH3)3CCH2COCH2CON(CH2CH3)2arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

