
(a)
Interpretation: The structure of the major product formed from alkene indicated should be predicted.
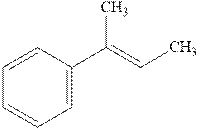
Concept introduction: Hydroboration-oxidation involves the sequence of two reactions. The hydroboration stage involves the treatment of alkene with diborane that generates alkyl borane. In second stage hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium is used to oxidize the alkyl borane produced in step 1 that leads to the synthesis of alcohols from
Hydroboration is essentially the addition of
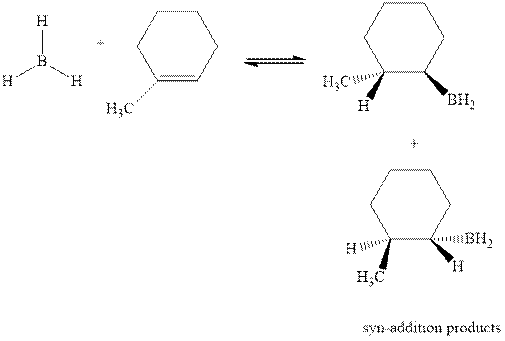
The mechanistic pathway can be illustrated as follows:
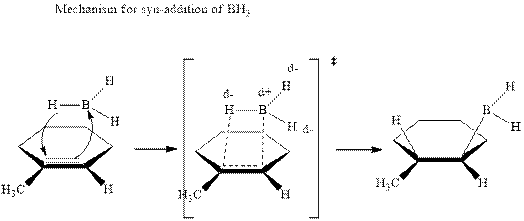
In the first step one equivalent of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The hydroboration-oxidation productis illustrated as below.
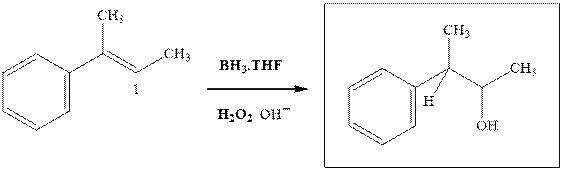
Anti-Markovnikov’s Rule serves as the basis of hydroboration. It states that the negative part of reagent must go to the carbon that has fewer alkyl substituents or more
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of the major product formed from alkene indicated should be predicted.
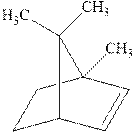
Concept introduction: Hydroboration-oxidation involves a sequence of two reactions. The hydroboration stage involves the treatment of alkene with diborane that generates alkyl borane. In second stage hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium is used to oxidize the alkyl borane produced in step 1 that leads to the synthesis of alcohols from alkenes.
Hydroboration is essentially the addition of
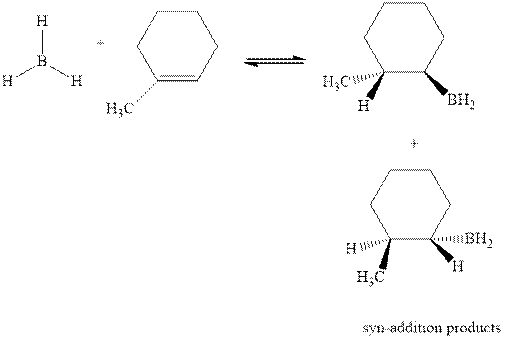
The mechanistic pathway can be illustrated as follows:
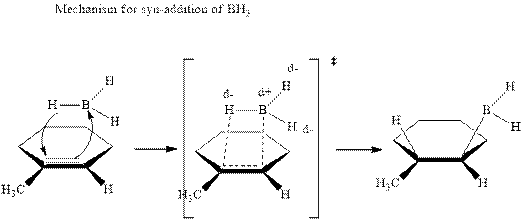
In the first step one equivalent of
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The hydroboration-oxidation product is illustrated as below.

Anti-Markovnikov’s Rule serves as a basis of hydroboration. It states that the negative part of reagent must go to the carbon that has fewer alkyl substituents or more
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of the major product formed from alkene indicated should be predicted.
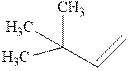
Concept introduction: Hydroboration-oxidation involves a sequence of two reactions. The hydroboration stage involves the treatment of alkene with diborane that generates alkyl borane. In second stage hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium is used to oxidize the alkyl borane produced in step 1 that leads to the synthesis of alcohols from alkenes.
Hydroboration is essentially the addition of
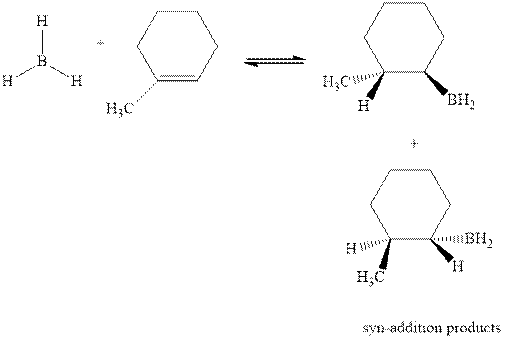
The mechanistic pathway can be illustrated as follows:
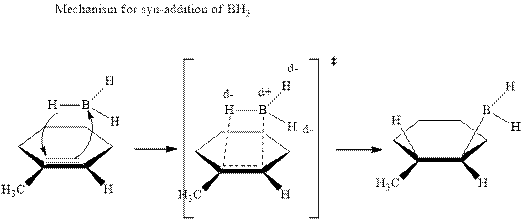
In the first step one equivalent of
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The hydroboration-oxidation product is illustrated as below.
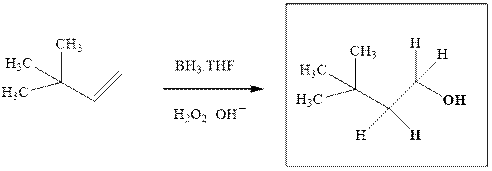
Anti-Markovnikov’s Rule serves as the basis of hydroboration. It states that the negative part of reagent must go to the carbon that has less alkyl substituents or more
Since the terminal olefinic carbon is less substituted
(d)
Interpretation: The structure of the major product formed from alkene indicated should be predicted.
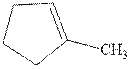
Concept introduction: Hydroboration-oxidation involves a sequence of two reactions. The hydroboration stage involves the treatment of alkene with diborane that generates alkyl borane. In second stage hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium is used to oxidize the alkyl borane produced in step 1 that leads to the synthesis of alcohols from alkenes.
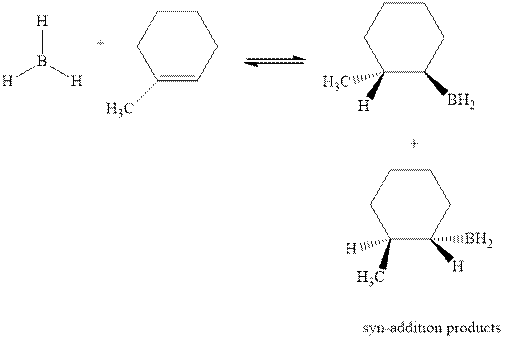
Hydroboration is essentially the addition of
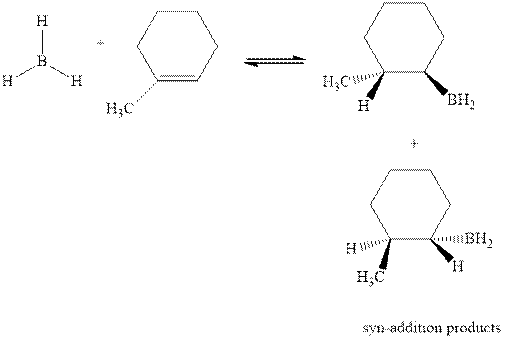
The mechanistic pathway can be illustrated as follows:
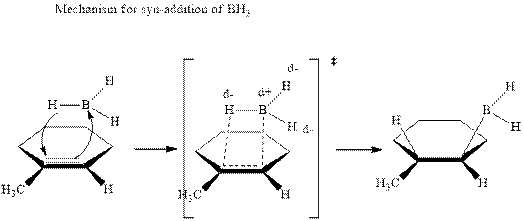
In the first step one equivalent of
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The hydroboration-oxidation product is illustrated as below.

Anti-Markovnikov’s Rule serves as the basis of hydroboration. It states that the negative part of reagent must go to the carbon that has less alkyl substituents or more
(e)
Interpretation: The structure of the major product formed from alkene indicated should be predicted.
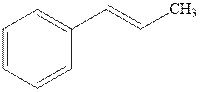
Concept introduction: Hydroboration-oxidation involves a sequence of two reactions. The hydroboration stage involves the treatment of alkene with diborane that generates alkyl borane. In second stage hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium is used to oxidize the alkyl borane produced in step 1 that leads to the synthesis of alcohols from alkenes.
Hydroboration is essentially the addition of
The mechanistic pathway can be illustrated as follows:
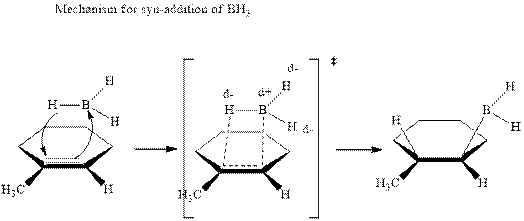
In the first step one equivalent of
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The hydroboration-oxidation product is illustrated as below.

Anti-Markovnikov’s rule serves as the basis of hydroboration. It states that the negative part of reagent must go to the carbon that has less alkyl substituents or more
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
- Complete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. + More... ☐ ☐ : ☐ + G 1. NaOMe Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forward6. Ammonia reacts with nitrogen monoxide and oxygen to form nitrogen and water vapor. If the rate of consumption of NO is 4.5 mollitermin) (a) Find the rate of reaction (b) Find the rate of formations of N; and HO (c) Find the rate of consumption of NH, and O 4NH: 4NO 0:4: +60arrow_forward34. Give the expected major product of each of the following reactions. Conc. HI a. CH3CH2CH2OH b. (CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH Conc. HBr H Conc. HI C. OH Conc.HCI d. (CH3CH2)3COHarrow_forward
- 42. Which of the following halogenated compounds can be used successfully to prepare a Grignard reagent for alcohol synthesis by subsequent reaction with an aldehyde or ketone? Which ones cannot and why? H3C CH3 a. Br H OH b. Cl C. I H H d. Cl e. H OCH3 Br Harrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. ? Will the first MgBr product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? olo ? OH جمله O Yes Ⓒ No MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Yes No X ☐ : ☐ टे PHarrow_forwardAssign all the protonsarrow_forward
- 9 7 8 C 9 8 200 190 B 5 A -197.72 9 8 7 15 4 3 0: ང་ 200 190 180 147.52 134.98 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 90 OH 10 4 3 1 2 -143.04 140. 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 CI 3 5 1 2 141.89 140.07 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 ៖- 90 129. 126.25 80 70 60 -60 50 40 10 125.19 -129.21 80 70 3.0 20 20 -8 60 50 10 ppm -20 40 128.31 80 80 70 60 50 40 40 -70.27 3.0 20 10 ppm 00˚0-- 77.17 30 20 20 -45.36 10 ppm -0.00 26.48 22.32 ―30.10 ―-0.00arrow_forwardAssign all the carbonsarrow_forwardC 5 4 3 CI 2 the Righ B A 5 4 3 The Lich. OH 10 4 5 3 1 LOOP- -147.52 T 77.17 -45.36 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm B -126.25 77.03 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 TO LL <-50.00 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 ppm 45.06 30.18 -26.45 22.36 --0.00 45.07 7.5 1.93 2.05 -30.24 -22.36 C A 7 8 5 ° 4 3 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 8 5 4 3 ཡི་ OH 10 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 5 4 3 2 that th 7 I 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 115 2.21 4.00 1.0 ppm 6.96 2.76 5.01 1.0 ppm 6.30 1.00arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
