
(a)
Interpretation: The IR spectra of absorption associated with the C=C bond and cis relationship vinylic H atoms for the spectral data for 2-methyl-2-pentene given in the figure needs to be determined.
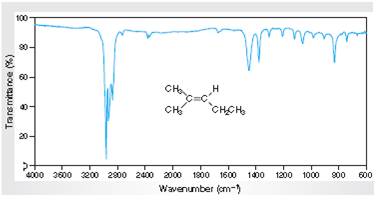
Concept Introduction:
Spectroscopy is the method of identification of structure of the organic molecules with the help of their absorption of certain
(b)
Interpretation Interpret H1 spectra for various resonance to the hydrogen nuclei responsible for them in 2-methyl-2-pentene.
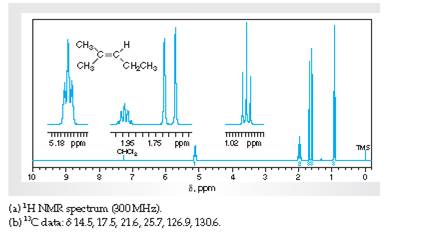
Concept Introduction:
Spectroscopy is the method of identification of structure of the organic molecules with the help of their absorption of certain electromagnetic radiations.
The H1spectroscopy or NMR is based on the nuclear magnetic resonance of radio waves on the H atoms bonded to C atoms present in the organic molecule.
(c)
Interpretation:The C13 spectra for various resonance to the C nuclei responsible for them in 2-methyl-2-pentene needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Spectroscopy is the method of identification of structure of the organic molecules with the help of their absorption of certain electromagnetic radiations.
The H1spectroscopy or NMR is based on the nuclear magnetic resonance of radio waves on the H atoms bonded to C atoms present in the organic molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

