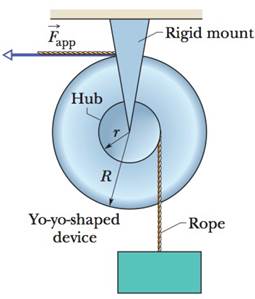
Problem 1Q: Figure 10-20 is a graph of the angular velocity versus time for a disk rotating like a... Problem 2Q: Figure 10-21 shows plots of angular position versus time t for three cases in which a disk is... Problem 3Q: A force is applied to the rim of a disk that can rotate like a merry-go-round, so as to change its... Problem 4Q: Figure 10-22b is a graph of the angular position of the rotating disk of Fig. 10-22a. Is the angular... Problem 5Q: In Fig. 10-23, two forces F1 and F2 act on a disk that turns about its center like a merry-go-round.... Problem 6Q: In the overhead view of Fig. 10-24, five forces of the same magnitude act on a strange... Problem 7Q: Figure 10-25a is an overhead view of a horizontal bar that can pivot: two horizontal forces act on... Problem 8Q: Figure l0-25b shows an overhead view of a horizontal bar that is rotated about the pivot point by... Problem 9Q: Figure 10-26 shows a uniform metal plate that had been square before 25 of it was snipped off. Three... Problem 10Q: Figure 10-27 shows three flat disks of the same radius that can rotate about their centers like... Problem 11Q: Figure 10-28a shows a meter stick, hall wood and half steel, that is pivoted at the wood end at O. A... Problem 12Q: Figure 10-29 shows three disks, each with a uniform distribution of mass. The radii R and masses M... Problem 1P: A good baseball pitcher can throw a baseball toward home plate at 85 mi/h with a spin of 1800... Problem 2P: What is the angular speed of a the second hand, b the minute hand, and c the hour hand of a smoothly... Problem 3P: When a slice of buttered toast is accidentally pushed over the edge of a counter, it rotates as it... Problem 4P: The angular position of a point on a rotating wheel is given by = 2.0 4.0t2 2.0t3, where is in... Problem 5P: ILW A diver makes 2.5 revolutions on the way from a 10-m-high platform to the water. Assuming zero... Problem 6P: The angular position of a point on the rim of a rotating wheel is given by = 4.0t - 3.0t2 t3,... Problem 7P: The wheel in Fig. 10-30 has eight equally spaced spokes and a radius of 30 cm. It Is mounted on a... Problem 8P: The angular acceleration of a wheel is = 6.0t4 4.0t2, with in radians per second-squared and t in... Problem 9P: A drum rotates around its central axis at an angular velocity of 12.60 rad/s. If the drum then slows... Problem 10P: Starting from rest, a disk rotates about its central axis with constant angular acceleration. In 5.0... Problem 11P: A disk, initially rotating at 120 rad/s, is slowed down with a constant angular acceleration of... Problem 12P: The angular speed of an automobile engine is increased at a constant rate from 1200rev/min to... Problem 13P: ILW A flywheel turns through 40 rev as it slows from an angular speed of 1.5 rad/s to a stop. a... Problem 14P: GO A disk rotates about its central axis starling from rest and accelerates with constant angular... Problem 15P: SSM Starting from rest, a wheel has constant = 3.0 rad/s2. During a certain 4.0 s interval, it... Problem 16P: A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.50rad/s2. How long does it take... Problem 17P: At t = 0, a flywheel has an angular velocity of 4.7 rad/s, a constant angular acceleration of 0.25... Problem 18P: A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star that emits a radio beam the way a lighthouse emits a... Problem 19P: What are the magnitudes of a the angular velocity, b the radial acceleration, and c the tangential... Problem 20P: An object rotates about a fixed axis, and the angular position of a reference line on the object is... Problem 21P: Between 1911 and 1990, the top of the leaning bell tower at Pisa, Italy, moved toward the south at... Problem 22P: An astronaut is tested in a centrifuge with radius 10 m and rotating according to = 0.30t2. At t =... Problem 23P: SSM WWW A flywheel with a diameter of 1.20 m is rotating at an angular speed of 200 rev/min. a What... Problem 24P: A vinyl record is played by rotating the record so that an approximately circular groove in the... Problem 25P: SSM a What is the angular speed about the polar axis of a point on Earths surface at latitude 40 N?... Problem 26P: The flywheel of a steam engine runs with a constant angular velocity of 150 rev/min. When steam is... Problem 27P: A seed is on a turntable rotating at 3313 rev/min, 6.0 cm from the rotation axis. What are a the... Problem 28P: In Fig. 10-31, wheel A of radius rA = 10 cm is coupled by belt B to wheel C of radius rC = 25 cm.... Problem 29P: Figure 10-32 shows an early method of measuring the speed of light that makes use of a rotating... Problem 30P: A gyroscope flywheel of radius 2.83 cm is accelerated from rest at 14.2 rad/s2 until its angular... Problem 31P: GO A disk, with a radius of 0.25 m. is to be rotated like a merry-go-round through 800 rad, starting... Problem 32P: A car starts from rest and moves around a circular track of radius 30.0 m. Its speed increases at... Problem 33P: SSM Calculate the rotational inertia of a wheel that has a kinetic energy of 24 400 J when rotating... Problem 34P: Figure 10-33 gives angular speed versus time for a thin rod that rotates around one end. The scale... Problem 35P: SSM Two uniform solid cylinders, each rotating about its central longitudinal axis at 235 rad/s,... Problem 36P: Figure 10-34a shows a disk that can rotate about an axis at a radial distance h from the center of... Problem 37P: SSM Calculate the rotational inertia of a meter stick, with mass 0.56 kg, about an axis... Problem 38P: Figure 10-35 shows three 0.0100 kg particles that have been glued to a rod of length L = 6.00 cm and... Problem 39P: Trucks can be run on energy stored in a rotating flywheel, with an electric motor getting the... Problem 40P: Figure 10-36 shows an arrangement of 15 identical disits tlial have been glued together in a... Problem 41P: GO In Fig. 10-37, two particles, each with mass m = 0.85 kg, are fastened to each other, and to a... Problem 42P: The masses and coordinates of four particles are as follows: 50 g, x = 2.0 cm, y = 2.0 cm; 25 g, x =... Problem 43P: SSM WWW The uniform solid block in Fig. 10-38 has mass 0.172 kg and edge lengths a = 3.5 cm, b = 8.4... Problem 44P: Four identical particles of mass 0.50 kg each are placed at the vertices of a 2.0 m 2.0 m square... Problem 45P: SSM ILW The body in Fig. 10-39 is pivoted at O, and two forces act on it as shown. If r1 = 1.30 m,... Problem 46P: The body in Fig. 10-40 is pivoted at O. Three forces act on it: FA = 10 N at point A, 8.0 m from O;... Problem 47P: SSM A small ball of mass 0.75 kg is attached to one end of a 1.25-m-long massless rod, and the other... Problem 48P: The length of a bicycle pedal arm is 0.152 m, and a downward force of 111 N is applied to the pedal... Problem 49P: SSM ILW During the launch from a board, a divers angular speed about her center of mass changes from... Problem 50P: If a 32.0 N m torque on a wheel causes angular acceleration 25.0 rad/s2, what is the wheels... Problem 51P Problem 52P: GO In Fig. 10-42, a cylinder having a mass of 2.0 kg can rotate about its central axis through point... Problem 53P: GO Figure 10-43 shows a uniform disk that can rotate around its center like a merry-go-round. The... Problem 54P: In a judo foot-sweep move, you sweep your opponents left foot out from under him while pulling on... Problem 55P: In Fig. 10-45a, an irregularly shaped plastic plate with uniform thickness and density mass per unit... Problem 56P: Figure 10-46 shows particles 1 and 2, each of mass m, fixed to the ends of a rigid massless rod of... Problem 57P: GO A pulley, with a rotational inertia of 1.0 103 kgm2 about its axle and a radius of 10 cm, is... Problem 58P: a IF R= 12 cm, M = 400 g, and m = 50 g in Fig. 10-19, find the speed of the block after it has... Problem 59P: An automobile crankshaft transfers energy from the engine to the axle at the rate of 100 hp = 74.6... Problem 60P: A thin rod of length 0.75 m and mass 0.42 kg is suspended freely from one end. It is pulled to one... Problem 61P: A 32.0 kg wheel, essentially a thin hoop with radius 1.20 m, is rotating at 280 rev/min. It must be... Problem 62P: In Fig. 10-35, three 0.0100 kg particles have been glued to a rod of length L = 6.00 cm and... Problem 63P: SSM ILW A meter stick is held vertically with one end on the floor and is then allowed to fall. Find... Problem 64P: A uniform cylinder of radius 10 cm and mass 20 kg is mounted so as to rotate freely about a... Problem 65P: GO A tall, cylindrical chimney fall;; over when its base is ruptured. Treat the chimney as a thin... Problem 66P: GO A uniform spherical shell of mass M = 4.5 kg and radius R = 8.5 cm can relate about a vertical... Problem 67P: GO Figure 10-48 shows a rigid assembly of a thin hoop of mass m and radius R = 0.150 m and a thin... Problem 68P Problem 69P Problem 70P: A wheel, starling from rest, rotates with a constant angular acceleration of 2.00 rad/s2. During a... Problem 71P: SSM In Fig. 10-50, two 6.20 kg blocks are connected by a massless siring over a pulley of radius... Problem 72P Problem 73P: A uniform helicopter rotor blade is 7.80 m long, has a mass of 110 kg, and is attached to the rotor... Problem 74P Problem 75P Problem 76P: Starting from rest at t = 0, a wheel undergoes a constant angular acceleration. When t = 2.0 s, the... Problem 77P: SSM A record turntable rotating at 3313 rev/min slows down and stops in 30 s alter the motor is... Problem 78P Problem 79P Problem 80P: A disk rotates al constant angular acceleration, from angular position 1 = 10.0 rad to angular... Problem 81P: GO The thin uniform rod in Fig. 10-53 has length 2.0 m and can pivot about a horizontal,... Problem 82P Problem 83P Problem 84P: At 7:14 A.M. on June 30, 1908, a huge explosion occurred above remote central Siberia, at latitude... Problem 85P: A golf ball is launched at an angle of 20 to the horizontal, with a speed of 60 m/s and a rotation... Problem 86P Problem 87P: GO IN Fig. 10-55, a wheel of radius 0.20 m is mounted on a frictionless horizontal axle. A massless... Problem 88P: A thin spherical shell has a radius of 1.90 m. An applied torque of 960 Nm gives the shell an... Problem 89P Problem 90P: The flywheel of an engine is rotating at 25.0 rad/s. When the engine is turned off, the flywheel... Problem 91P: SSM In Fig. 10-19a, a wheel of radius 0.20 m is mounted on a frictionless horizontal axis. The... Problem 92P: Our Sun is 23 104 ly light-years from the center of our Milky Way galaxy and is moving in a circle... Problem 93P: SSM A wheel of radius 0.20 m is mounted on a frictionless horizontal axis. The rotational inertia of... Problem 94P: If an airplane propeller rotates at 2000 rev/min while the airplane flies at a speed of 480 km/h... Problem 95P: The rigid body shown in Fig. 10-57 consists of three particles connected by massless rods. It is to... Problem 96P: Beverage engineering. The pull tab was a major advance in the engineering design of beverage... Problem 97P: Figure 10-58 shows a propeller blade that rotates at 2000 rev/min about a perpendicular axis al... Problem 98P: A yo-yo-shaped device mounted on a horizontal frictionless axis is used to lift a 30 kg box as shown... Problem 99P Problem 100P: Two thin rods each of mass 0.20 kg are joined together to form a rigid body as shown in Fig. 10-60.... Problem 101P: In Fig. 10-61, four pulleys are connected by two belts. Pulley A radius 15 cm is the drive pulley,... Problem 102P Problem 103P: In Fig. 10-63, a thin uniform rod mass 3.0 kg, length 4.0 m rotates freely about a horizontal axis A... Problem 104P Problem 105P Problem 106P: A point on the rim of a 0.75-m-diameler grinding wheel changes speed at a constant rate from 12 m/s... Problem 107P: A pulley wheel that is 8.0 cm in diameter has a 5.6-m-long cord wrapped around its periphery.... Problem 108P: A vinyl record on a turntable rotates at 3313 rev/min. a What is its angular speed in radians per... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University




